In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, problem-solving techniques have become indispensable for success. From optimizing processes to enhancing customer experiences, these innovative solutions empower businesses to navigate complexities, seize opportunities, and stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly dynamic and interconnected global economy.
Today, we will cover one of these problem-solving methods, the DMAIC Model. It is a structured model used in Six Sigma and other process improvement initiatives. We will explain this model in detail with its examples, advantages, and disadvantages. You will also see answers to some frequently asked questions about the subject. Now, let’s delve into the subject.
What does the DMAIC Model mean?
The DMAIC model offers a structured problem-solving methodology used in Six Sigma and other process improvement endeavors.
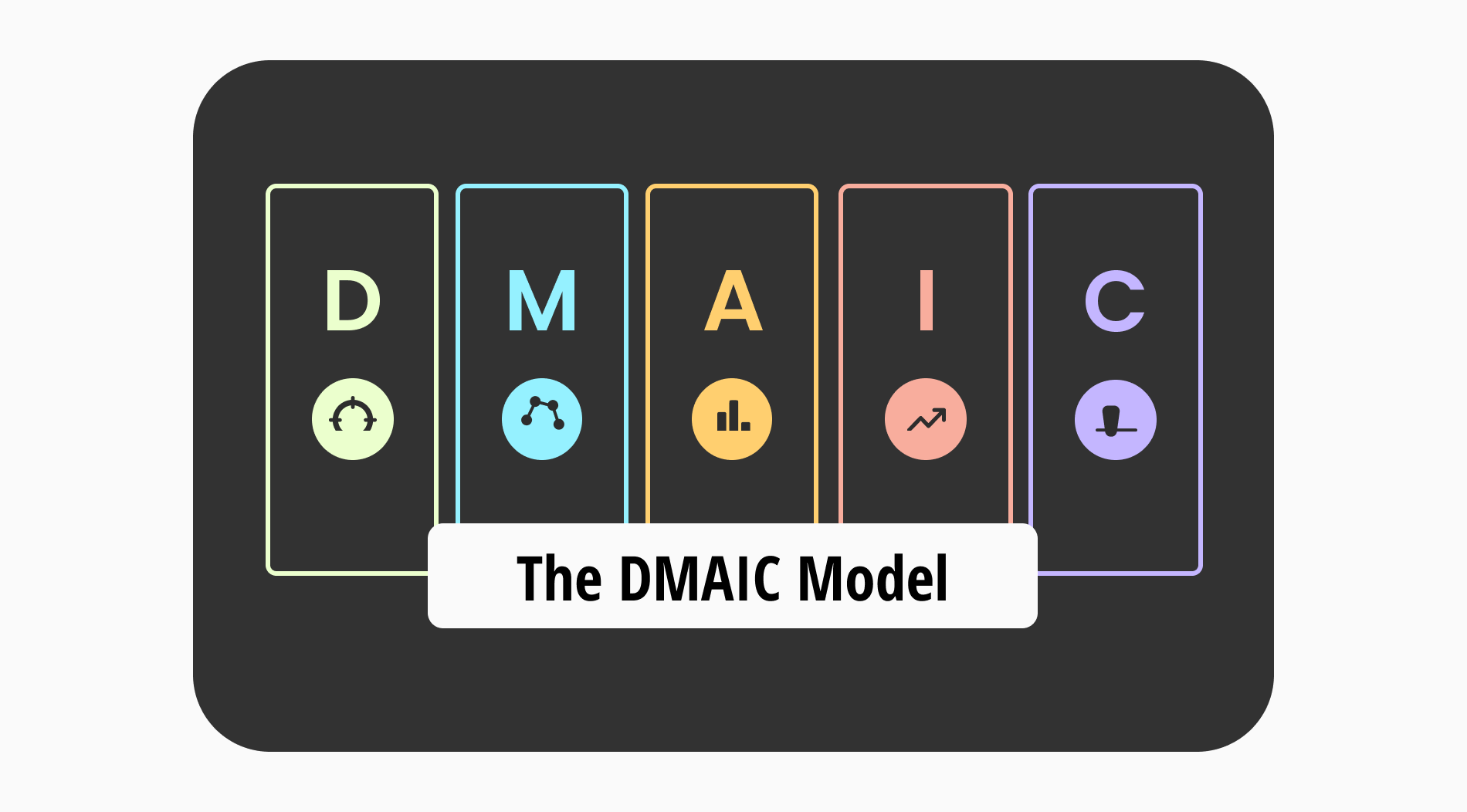
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, representing the five phases of the process. It helps organizations to identify, analyze, and address issues in their processes to achieve better quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
What is the DMAIC methodology?
THE DMAIC process serves as a methodical problem-solving approach utilized within Six Sigma and other process enhancement procedures.
It includes five distinct stages: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It guides teams through the process of pinpointing improvement opportunities, analyzing issues’ root causes, implementing effective solutions, and ensuring sustained process enhancement. Now, let’s look at the acronym itself:
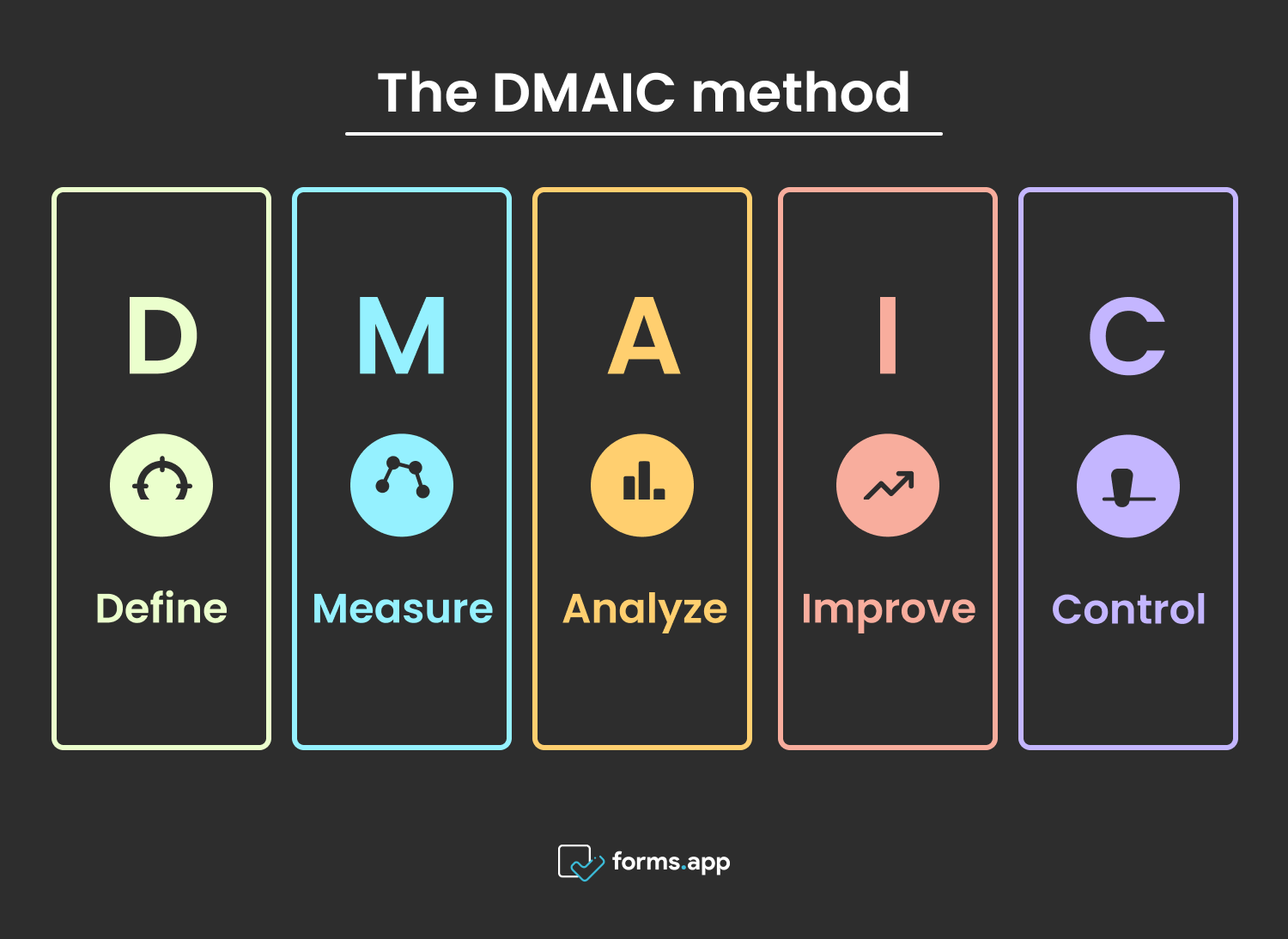
The DMAIC template
1. Define
In the Define phase, the project goals and scope are established. This involves identifying the problem or opportunity for improvement and defining specific objectives that align with organizational goals and customer requirements. A key component here is the creation of a project charter, outlining the project scope, objectives, deliverables, stakeholders, and timeline. Teams can ensure alignment and focus throughout the process.
2. Measure
The Measure phase focuses on gathering data to understand the process. This involves identifying process metrics and establishing a baseline performance measurement. Data collection methods may include process observations, surveys, interviews, and the use of measurement tools and technology. The goal of this phase is to quantify the problem or opportunity for improvement and provide a basis for analysis.
3. Analyze
In the Analyze phase, the collected data is analyzed to identify the root causes of process issues or variations. Various statistical and analytical techniques are used to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. The goal is to gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing process performance and to discover areas for improvement.
4. Improve
The Improve phase focuses on developing and implementing solutions to address the root causes identified in the previous phase. Creative problem-solving techniques are used to generate and evaluate potential improvement ideas. Once solutions are selected, they are tested and implemented on a small scale to assess their effectiveness before full-scale implementation.
5. Control
The Control phase is concerned with sustaining the improvements achieved and preventing the recurrence of problems. Control measures, such as standard operating procedures, process controls, and monitoring systems, are implemented to ensure that the process remains stable and meets the desired performance targets over time. Continuous monitoring and periodic review are essential to ensure long-term success.
Example of the DMAIC Model
The DMAIC framework can seem complex in theory, but it is quite simple. There are a lot of DMAIC examples in the business world. You can implement it in your own business by creating a DMAIC template. Now, let’s look at a hypothetical scenario in which the company XYZ uses the DMAIC methodology and obtains positive results.
XYZ Company
XYZ Company, a manufacturing firm, applies the DMAIC model to enhance the efficiency of its production process for Product A. Initially facing high defect rates and customer complaints, the company defines the problem, measures defect rates, and analyzes root causes, including machine calibration issues and raw material quality.
Implementing improvements such as machinery recalibration and enhanced quality control measures, XYZ company achieves significant reductions in defect rates, leading to improved product quality, reduced rework, and increased profitability. By following DMAIC’s structured approach XYZ Company systematically identified and addressed the process inefficiencies. It improved its operational performance.
Pros and Cons of Using the DMAIC Model
DMAIC is used to improve processes and ensure continuous improvement. While it offers numerous benefits and advantages in terms of structured problem-solving and continuous improvement, businesses should also be mindful of potential challenges and disadvantages to address them and maximize the model’s effectiveness. That said, let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages:
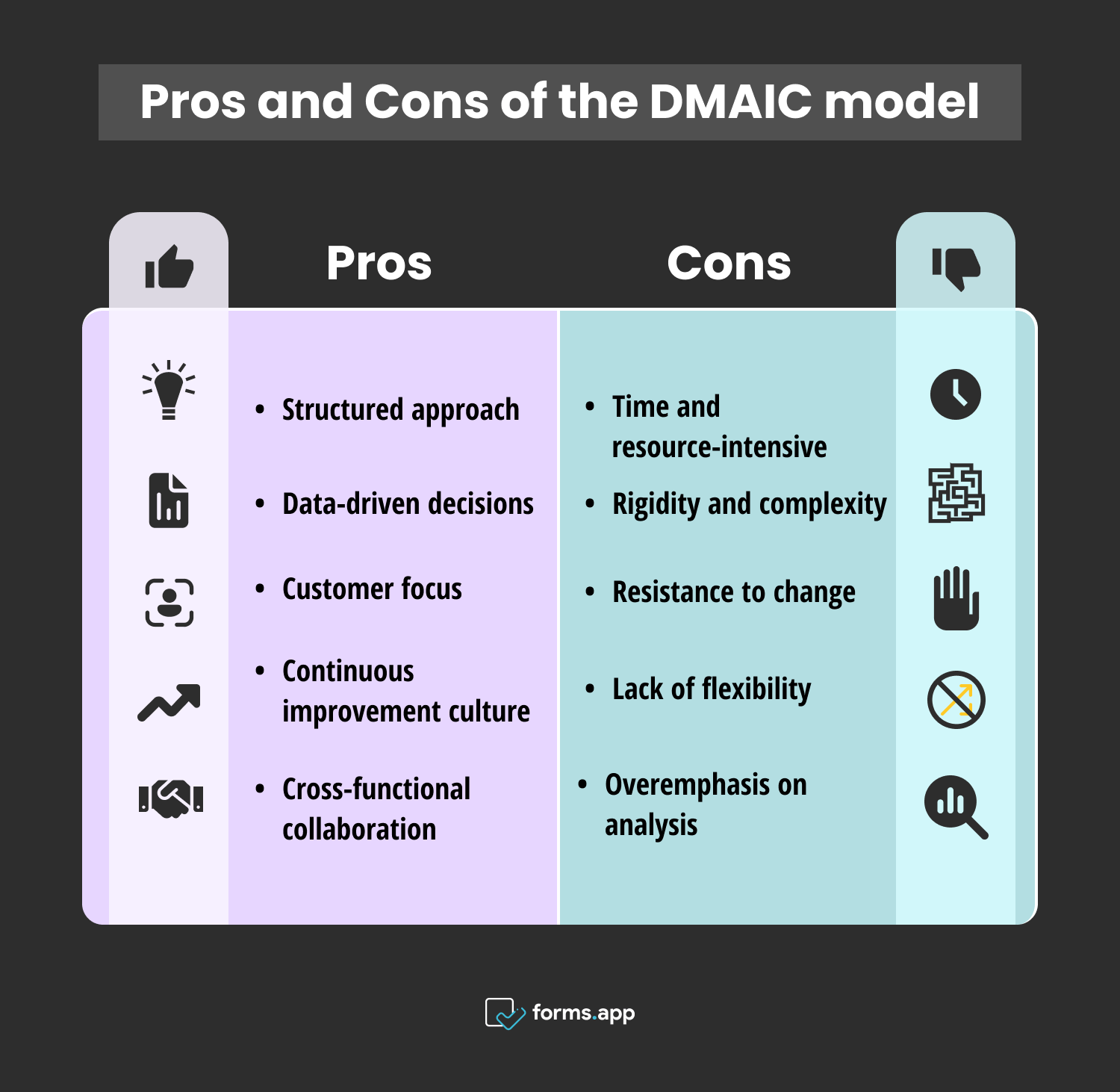
Advantages and Disadvantages of the DMAIC model
1. Pros
The DMAIC model is more than just a framework. It is a catalyst for organizational transformation. By providing a structured roadmap, it empowers businesses and offers many advantages. Let’s look at some of the advantages and witness how it boosts competitiveness:
- Structured approach: The DMAIC model provides a systematic framework with defined stages (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), guiding teams through a structured problem-solving process from problem identification to solution implementation.
- Data-driven decisions: It emphasizes the collection and analysis of relevant data to understand process performance, identify root causes of problems, and make informed decisions for team members based on evidence rather than assumptions.
- Customer focus: Prioritizing the voice of the customer ensures that process improvements align with customer requirements and expectations, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Continuous improvement culture: The DMAIC framework fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations by encouraging teams to regularly review and refine processes, driving incremental enhancements and sustainable performance gains over time.
- Cross-functional collaboration: It promotes collaboration among diverse stakeholders, including process owners, subject matter experts, and frontline employees, encouraging teamwork and shared accountability for problem-solving and improvement initiatives.
2. Cons
Although the DMAIC model boasts numerous advantages in optimizing processes and quality improvement, it may pose challenges for some organizations. Despite its structured approach, some factors, such as resource constraints and resistance to change, can hinder its effectiveness. Let’s explore these potential disadvantages:
- Time and resource-intensive: Implementing DMAIC can require significant time, resources, and investment, particularly for large-scale projects or organizations with complex processes, potentially posing challenges for teams with limited capacity or budget constraints.
- Rigidity and complexity: The structured nature of DMAIC may be perceived as overly rigid and complex, particularly for smaller-scale projects or teams with limited experience in process improvement methodologies, leading to resistance or difficulty in application.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist the changes introduced by DMAIC, particularly if they perceive it as disruptive to established workflows or if there is a lack of buy-in or understanding of the benefits of process improvement initiatives.
- Lack of flexibility: The DMAIC model’s predefined stages and sequential approach may lack flexibility, making it less adaptable to dynamic or rapidly changing environments where agile or iterative problem-solving approaches may be more suitable.
- Overemphasis on analysis: Excessive focus on data analysts and measurement in DMAIC may lead to analysis paralysis, where teams become overly focused on data collection and analysis at the expense of action and implementation, delaying progress and limiting the effectiveness of improvement efforts.
Frequently asked questions about the DMAIC model
As we can see, the DMAIC model has both advantages and disadvantages, which means you should always be careful and consider your specific requirements and constraints. Now, let’s answer some of the most frequently asked questions about the DMAIC framework:
The process of Decision Matrix Analysis entails defining the decision problem, identifying relevant criteria, assigning weights to criteria, listing available options, evaluating options against criteria, scoring options, and selecting the option with the highest score. This structured approach enables decision-makers to objectively assess choices, prioritize preferences, and ultimately make sound decisions based on thorough analysis.
The DMAIC model comprises five sequential phases. Firstly, “Define” sets project objectives and customer requirements. “Measure” quantifies data to establish baselines. “Analyze” identifies the root causes of the problem. “Improve” develops and implements solutions. Finally “Control” established measures to sustain improvements and monitor performance, ensuring continued effectiveness in addressing operational challenges.
The primary goal of DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is to systematically identify, analyze, and improve processes within an organization to enhance efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. By following this structured problem-solving approach, DMAIC aims to drive continuous improvement, optimize performance, and achieve sustainable results, ultimately fostering a culture of excellence and competitiveness.
The “Measure” phase of the DMAIC model involves quantifying and collecting data related to the identified problem or process. Its primary goal is to establish a baseline understanding of the current state, providing a factual basis for analysis. Through careful measurement and analysis, this phase enables organizations to gain insights into process performance, identify areas for improvement, and track progress.
The Six Sigma or DMAIC Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aiming to improve business processes and reduce defects or variations. It consists of five steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. In the Define phase, the project goals, customer requirements, and deliverables are established.
The Measure phase involves quantifying and collecting data to understand the current process performance and establish a baseline for improvement. In the Analyze phase, data is analyzed to identify root causes. The Improve phase focuses on developing and implementing solutions to address identified issues and optimize the process. Solutions are tested and refined to ensure their effectiveness.
Final words
In conclusion, the DMAIC Model is a valuable tool to improve quality. Businesses can use this 5-step framework to encourage dynamic problem-solving. We have seen a detailed definition, an example as well as advantages and disadvantages of this model. You can start implementing it in your own business and see the difference!
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications