You did some research, but there are some problems. The results were not as you expected. However, you thought you were doing everything properly. So what exactly is the reason for this? Could you have made a sampling error?
If you ask what sampling error is, do not rush because it will be explained extensively in the rest of the article, but know this much: sampling error is something that every person is familiar with in the world of analysis, and you, unfortunately, have to deal with it.
Let’s start from the beginning: What is sampling error?
A sampling error is a research problem that arises when a population studied does not actually reflect the entire population.
The main reason for this standard error is that the population sample is not compatible with the true population in terms of diversity and number. Although researchers include a margin of error in their research, sampling error is always an issue they must deal with.
Sampling error types in market research
Businesses often resort to analysis to get to a better position. However, when these analyses are not done carefully, they may cause some inaccuracies, such as sampling errors. The most frequently observed types of sampling errors are listed below:
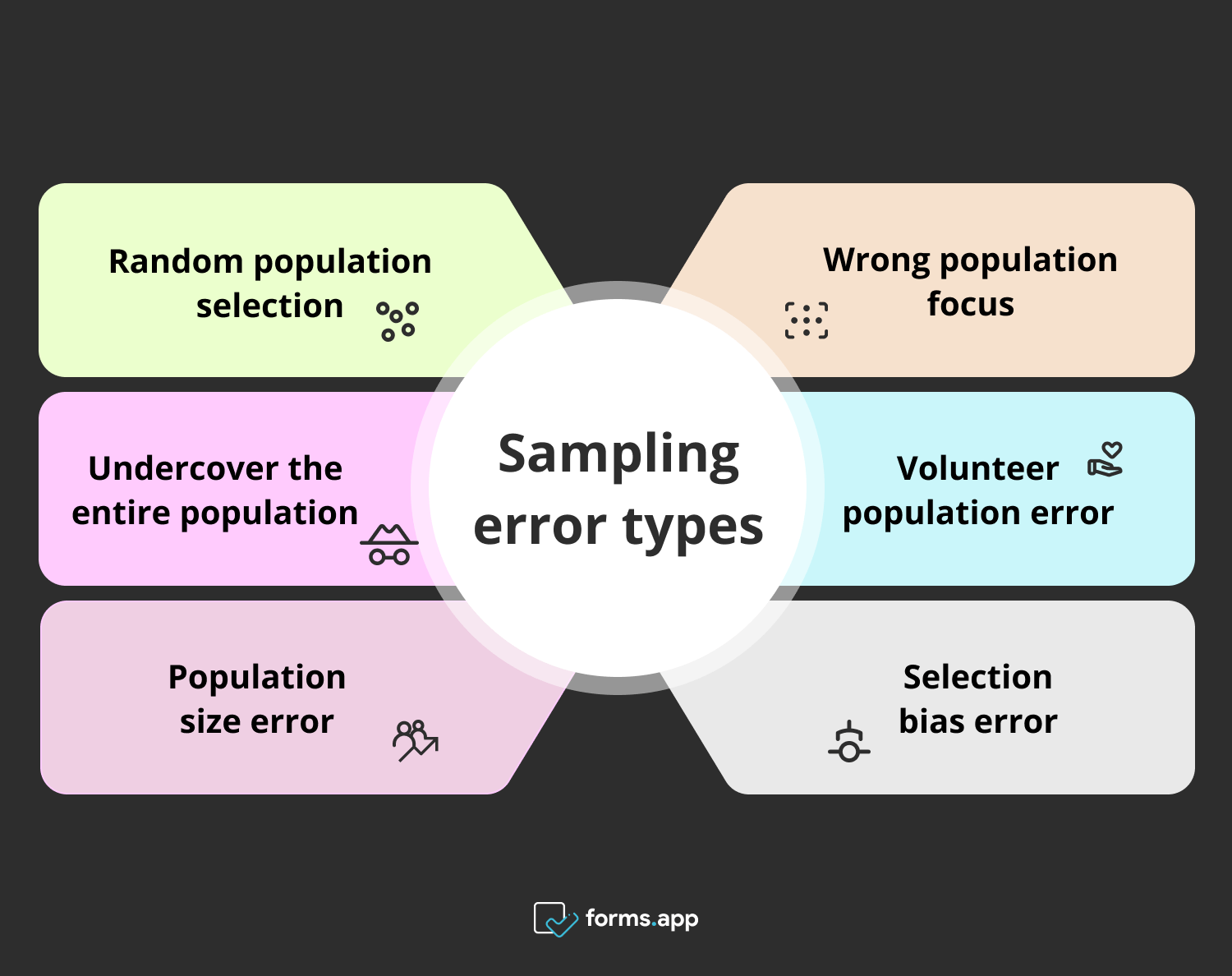
Sampling error types in market research
- Random population selection: A random population selection may leave room for error, as it means leaving the research entirely to chance. But if you do this systematically, then it is called systematic sampling, which is a decent technique.
- Wrong population focus: This error occurs when the researchers select a population that they think is suitable for the research but is irrelevant to the research's purpose.
- Undercover the entire population: For example, conducting a survey on the Internet means ignoring the population that does not use the Internet or can not use it.
- Volunteer population error: Like random population selection, volunteer groups are also known to negatively affect the research's outcome.
- Population size error: The sample size may need to be kept large or small depending on the focus of the research. If the researchers do not maintain this balance, they will encounter wrong results.
- Selection bias error: This error also occurs when the researcher selects the population in favor of the research to prove the research hypothesis. So, this method does not reflect reality.
Example of the sampling error
An example of a sampling error will be given here. However, first of all, you should know how to calculate sampling error. You can generally use analysis programs and artificial intelligence as a sample error calculator, but it may still be useful to know the sampling error formula.
Sampling error = Z x STD/Sqrt (N)
Z- is the z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level (1.96 for a 95% confidence level).
STD- is the population standard deviation.
N- is the sample size.
For example, market research aims to reach the number of people using hats in summer. For this, a firm conducts a survey to estimate the proportion of people who wear hats during the summer season in a small town. They selected a random sample of 400 individuals and found that 120 of them reported wearing hats regularly during the summer. Researchers used the above formula to find the margin of error.
The margin of error for the estimated proportion of people who wear hats during the summer season is approximately 0.0448. This means that with a 95% confidence level, the true proportion of hat-wearers in the population is likely to fall within 4.48 percentage points of the observed proportion (30%) obtained from the sample.
Sampling error vs. Non-sampling error
Sampling errors are not the only statistical errors found in research; there are also non-sampling errors. Both of these negatively affect the outcome of the research. So, what exactly are the differences between these two?
- Sampling errors are caused by problems related only to the wrong population parameters of research.
- These often occur due to research bias, measurement error, and incorrect or random sampling.
- Non-sampling errors are caused by other parts of the research. There are more types of this because there are different errors depending on whether the research is in parts such as data collection, data analysis, and data interpretation.
- Non-sampling error examples are generally problems such as lack or inaccuracy of data, inconsistency of analysis or problematic coding, incorrect design of the survey, or poor quality of questions.
How to minimize the sampling error
In order for research to yield precise and reliable results, the margin of error must be quite low. This margin of error is generally considered acceptable between 5% and 3%. So, when you repeat a survey, the result must be more or less the same. Otherwise, there will be a sampling error, etc. There may be an error. So, how should you take precautions against this error?
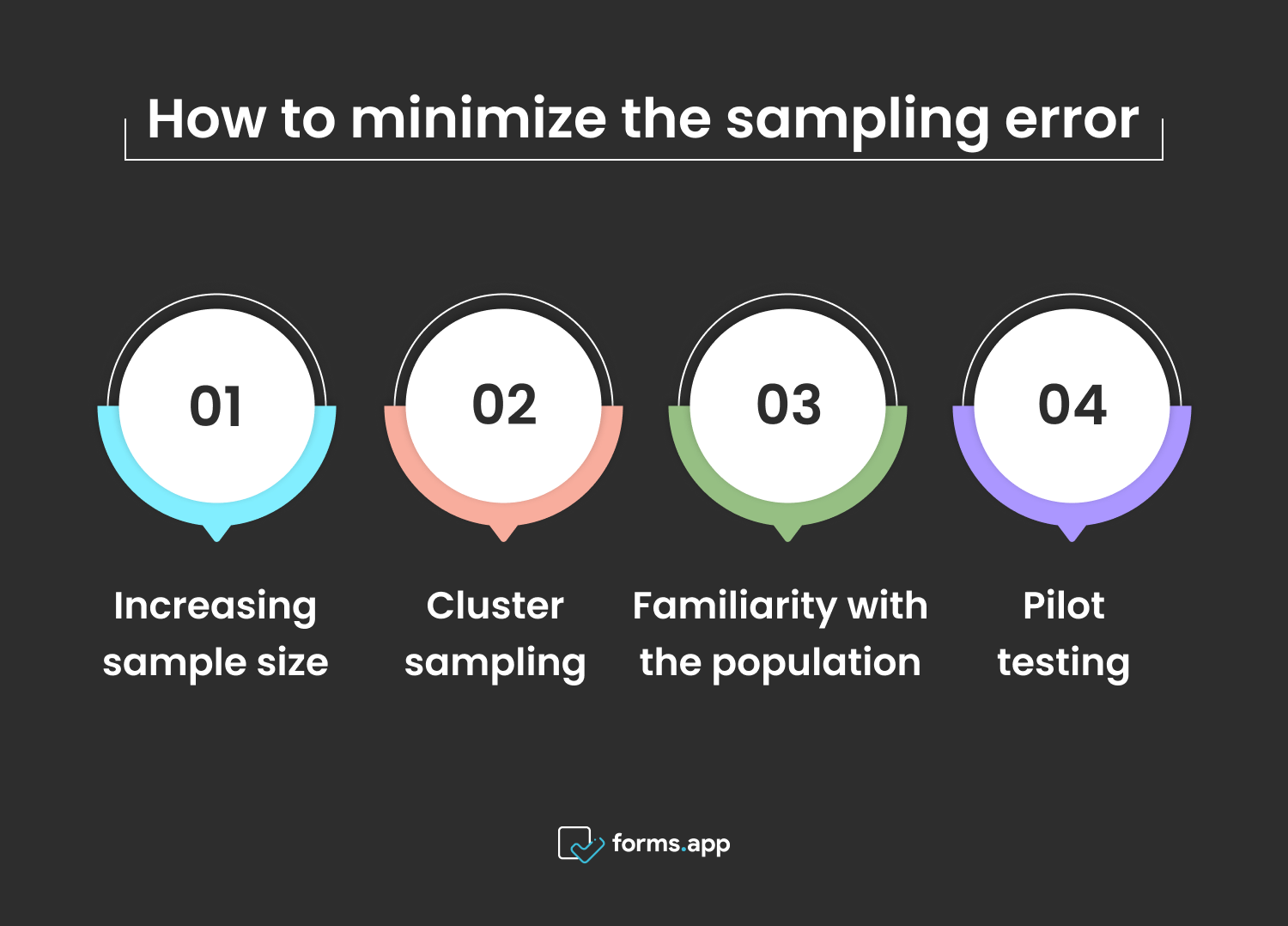
How to reduce the sampling error
- Increasing sample size: The larger a population a study covers, the closer to reality it will be. Because a small sample size has many disadvantages and therefore causes errors. The main disadvantages of these are failure to determine differences between groups, researcher bias, and generalization error.
- Cluster sampling: Dividing the target population of the research into groups makes it possible to classify them more easily and ask the right questions. This is very useful as it is not only a practical solution but also known as a cost-effective solution.
- Familiarity with the population: It is essential for researchers to have prior knowledge about the population that is the subject of research. This ensures that the research is free from random or irregularly prepared survey questions. It also improves the performance of the analysis in general by enabling better evaluation of the results.
- Pilot testing: Finally, you can pilot test a research in a small group or region. Of course, this may show a result that is far from the result of the research, but you can use this method to clearly determine the purpose and method of your research and solve potential issues beforehand.
Frequently asked questions about the sampling error
In this section, you can easily find what you are curious about and want to learn more about sampling error.
In biology, sampling error occurs when samples of living organisms, tissues, or cells do not match the characteristics of the general population. This inconsistency is caused by incorrect or incomplete sample selection. Reducing sampling error is a must for biological statistical analyses to be more successful.
An error, as the name suggests, is an undesirable situation. It adversely affects the health of any research. First of all, it causes predictions and calculations to be inaccurate and incomplete. Therefore, it reduces the accuracy of the results. It causes a loss of time and money as the research will need to be resampled and edited again.
Avoiding sampling errors is actually quite simple. You don't need to have vast knowledge for this job; you just need to do the following.
- Always keep the size of the sample large
- Avoid homogeneous groups and apply controlled random sampling
- Determine your research focus and sampling frame well
- Conduct pilot studies
- Get help from expert statisticians
- Ensure that the research is valid at all times
Sampling error is, by and large, a reflection of cursory research and an inexperienced researcher. To explain these reasons further, for example, leaving the course of the research to chance, not clustering the target groups or keeping the sample size small, continuing the research without any methodology and recording, not using analysis techniques improperly, and collecting incorrect data are some of them.
Final words
As a result, sampling errors are misleading data collection and analysis errors for the target population. You need to avoid this so that your research can provide accurate results.
This article explains the definition and types of sampling errors with examples. It also shows the formula calculation you can use for sampling error. Its difference from non-sampling error and how you can minimize sampling error are explained. Thus, you now have more information about sampling error.
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications