Are you considering starting a business? If so, you are in the right place because you are about to read what you should know before you start. Starting your own business is a risk. However, knowing the common reasons for the failure of startups will prevent you from making the same mistakes. Statistics on startup failures will help you understand the problems better.
This article has gathered 25+ startup failure statistics you need to know, including top reasons and rates. You will also get an insight into the top reasons why they fail and the common problems that lead to failure. Without wasting any more time, let's move on to our article that will contribute to the success of your startup.
Why do startups fail? (Top reasons)
Starting a new business takes a lot of work. You can see in many sources that ninety percent of startups fail. There are a lot of reasons why a startup can fail. It may even be a combination of several reasons. The most common reasons why startups fail are:

Top reasons for the failure of start-ups
- Being in the wrong market: One of the most common reasons for company failure is a lack of market need or demand for what the startup offers. In this situation, the product cannot be successful in the market because the team does not target the appropriate audience.
- A lack of research: Market research is critical in product creation. You must be sure about your product and understand what your customers desire. Many people fail to recognize that no one wants that product or service. So, you have to do your homework and investigate your market.
- Ineffective marketing: Marketing is as essential as any other aspect of your business. Without effective marketing strategies, your product will not see the value it deserves. So, you should be great at selling the product as much as building it. If not, you should get help from an expert.
- Bad partnership: Partners who are experts in different fields can also be beneficial for the success of the startup. However, when your ideas clash with your partner, internal conflicts start within the company if you cannot find a solution. The business can fall apart because partnerships don't work. Having a clear business plan and job descriptions will avoid the vast majority of conflicts.
- Poor financial planning: Proper financial planning before you start your startup will make your startup solid and long-lasting. Create a realistic budget for your startup and track your expenses.
- Lack of financing or investors: We have already mentioned that for your startup to be successful, it needs to be in the right market and meet the right audience. Just as important as these factors are the quality of your product and meeting the users' expectations.
- Running out of cash: One of the most critical reasons startups fail is that they run out of money. You should see if your cash flow can carry you to a positive point. Mismanaging costs and failing to secure sufficient financing will make your startup fail.
- Poor management: Having a good management team can prevent many of the problems we have seen above. Your startup can only be successful if you manage properly and have the right team.
Startup failure rates by stage
This paragraph will describe the startup failure rate statistics at different stages. From the early days of idea creation to the later stages, you can encounter many other problems. Each stage has its unique obstacles that contribute to startup failure rates. According to Failory:

Startup failure rates by stage
- 20% failure rate until the end of the 1st year
- 30% failure rate until the end of the 2nd year
- 50% failure rate until the end of the 5th year
- 70% failure rate until the end of the 10th year
When we look at the statistics, we can see that the rate of failed startups at the end of the first year is lower than in other years. The failure rate of startups has increased over the years. Factors such as market conditions can become difficult to deal with over time. This can lead to failure for startups over time.
Startup failure rates by industry
Just as it varies by stage, the failure rate of startups also varies by industry and business model. We will now examine the failure rates of startups by industry with a few examples.
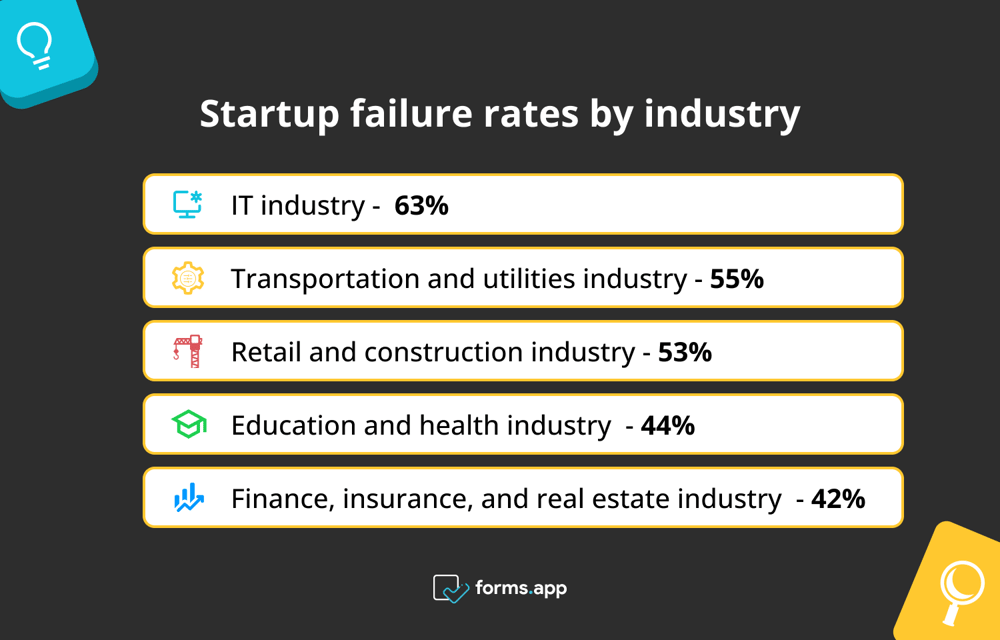
Startup failure rates by industry
- At 63%, the IT industry has the highest percentage of startup failure: Startup statistics show that more than 50% of failed startups belong to tech startups. The intense competition in the market causes many startups to fail to attract enough customers. In addition, startups fail because they fail to keep up with the times (Moneyzine).
- With a failure rate of 55%, the transportation and utilities industry ranks second: This sector has the second-highest failure rate among startups. Factors such as high capital requirements contribute to the failure rate in this sector (Moneyzine).
- With a failure rate of 53%, the retail and construction industries tied for third place (Moneyzine).
- On the other hand, finance, insurance, and real estate have the lowest failure rate of any industry (42%). Education and health come in second with a 44% failure rate (Moneyzine).
25+ Insightful statistics about startup failures
Let's take a look at more than 25 statistics on startup failures. These statistics will guide you through why startups fail and help you learn from the experiences of those who have been there. Take a look at these statistics before you start your business plan:
1. In the United States, 20.8% of private sector startups fail within the first year. By the end of the fifth year, 48.4% had died. 65.1% of startups fell by the end of ten years (Lendingtree).
2. Columbia is the region in the United States with the highest rate of venture failures in the first year. The nation's capital has the highest failure rate at 28%, followed by Missouri and Rhode Island at 27.2% (Lendingtree).
3. According to the most recent data on the March 2022 state of enterprises launched in March 2021, nearly 21% of private sector businesses in the United States fail within the first year (LendingTree).
4. The IT sector has the highest proportion of businesses that fail in the first year, at around 26%. The IT sector includes processes such as producing information and cultural products and processing data (Lendingtree).
5. Professional, scientific, and technical services (23.4%) and administrative and waste services (23.1%) industries had the second and third-highest one-year failure rates (Lendingtree).
6. Only one in every twelve entrepreneurs succeeds in developing a profitable startup. According to a 2019 study, only 8.3% of entrepreneurs create a successful business. This equates to only one in twelve entrepreneurs (Luisa Zhou).
7. Startups fail at a rate of greater than 90%. Over nine out of ten startups fail, with about 20% failing within the first year of operation (Luisa Zhou).
8. Long-term failure rates for all startups are 70%. By the end of year five, the failure rate increased to 50%, and by year 10, it grew to 70% (Luisa Zhou).
9. 20% of startups fail because they need to catch up to the competition. In addition to poor management and market fit, one in five startups die because they cannot overtake their competitors (Luisa Zhou).
10. Leading causes of startup failures include poor business concepts at 19%, regulatory or legal challenges at 18%, and pricing issues at 15% (Luisa Zhou).
11. In 2018, 82% of startups were reported to have closed because of cash flow concerns (Demandsage).
12. The failure rate of owners starting a business for the first time is 82% (Demandsage).
13. 6% of startups failed because of technology-related issues, such as incorrect security systems or outdated solutions (Demandsage).
14. Between March 2020 and February 2021, the pandemic drove 25% more firms to close than the average (tech.co).
15. Only two out of every five startups make a profit. Three out of five enterprises either break even or cause a loss (Marketsplash).
16. 75% of venture-backed businesses never return profits to funders (Failory).
17. In 30-40% of cases, investors lose their entire original investment (Failory).
18. Finding a market fit for a new startup takes two or three times as long as many entrepreneurs estimate. In addition, before product-market fit, founders overestimate the value of their intellectual property by up to 255% (Luisa Zhou).
19. 35% of startups fail because there is no market need for their product (Luisa Zhou).
20. Startups have three critical phases: Pre-seed, Series A, and maturity. Approximately 60% of organizations that get pre-seed funding fail to advance to Series A (Luisa Zhou).
21. 99.9% of unicorn startups fail. Companies are called "unicorn startups" when they reach a valuation of over 1 billion dollars without going public. Only 0.00006% of startups achieve unicorn status (Luisa Zhou).
22. According to The National Venture Capital Association, 25% to 30% of firms that receive VC funding fail (Luisa Zhou).
23. More than 75% of Fintech (Financial Technology) startups fail. Popular industries for fintech startups include mobile banking, bitcoin, and investment apps (Luisa Zhou).
24. Disruptive startups have a 90% failure rate. Disruptive startups establish new markets or reinvent current ones (Luisa Zhou).
25. 23% of startups fail because they don't have the right team in place. This is the third most common reason for startup failure (tech.co).
Key points to take away
In this article, you have seen some critical information about the failure rates of startups through statistics. The startup statistics will show you why startups fail and the failure rates by stages and sectors. You can make inferences from these statistics and ensure your business succeeds. Here are a few key points to consider before launching your startup:
- Make sure you are addressing the right audience.
- Make sure you are using the right resources and working with the right team members.
- Conduct effective market research.
By analyzing these statistics, you can create an effective plan for your business. Now, you have all the data you need for a successful startup!
Contributors
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications