An empathy map means a commonly used method that visualizes the behaviors of each user. They were initially made to avoid misunderstandings and miscommunications among the users. They aid in understanding the user’s needs and expectations and therefore are used as a bridge between the business company and customer experience.
When designers convey user research, they gain insights into user experience. Therefore, empathy maps play a big part in the design-thinking process. An empathy map is divided into four quadrants - says, thinks, feels, and does. These essential elements help create better products or services and solve problems for the target audience.
What is an Empathy Map?
An empathy map is a tool for design team members to understand users’ emotional state, deeper insights in decision-making process, and users’ attitudes for product development.
It points out gaps in individuals’ research, and helps with finding out what is necessary about users’ needs.
What are the 4 aspects of an empathy map?
An empathy map consists of four essential elements as aforementioned, which are says, thinks, feels, and does. The user being the centre of these four elements, designers can have a clear understanding of what a user needs and what they look for in a product or service in order to provide them with an excelling experience. Let’s take a closer look at these four aspects:
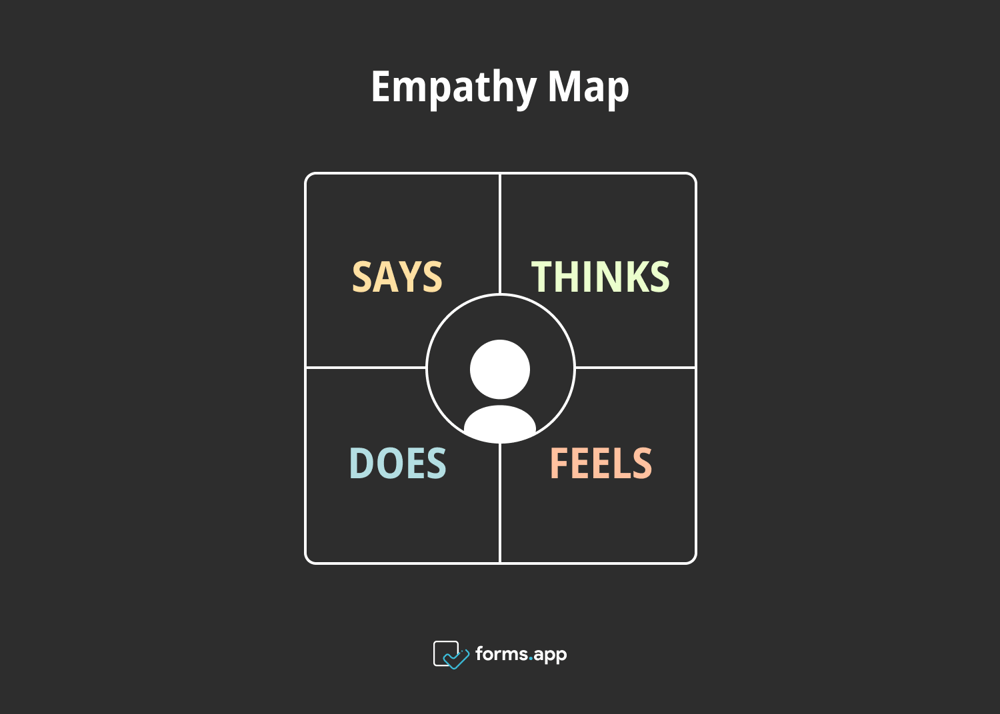
Aspects of the empathy map
Says
This element represents what the user says. This data is mainly collected from the research data which communicates the wants and needs of a user. Quick surveys, such as a pop-up survey, can help better understand users’ opinions and expectations of a product or service they are researching.
Thinks
The element of thinking is highly correlated to saying. This is to discover users’ buying experience, what they value, and their judgment on a service they consider to try or purchase. Through qualitative research, you can access more in-depth information related to what truly your target audience thinks of a product. This will help companies figure out what is important to their customers.
Feels
Feeling aspect is connected to the emotional state of the user. This emotional state can be complex; however, it is valuable for businesses to be aware of what makes their customers happy and fulfilled, or anxious and confused about choosing or using a product/service, or doing a task. To provide the best customer service and bring out more positive emotions, it is important to understand what users’ emotional fluctuations depend on.
Does
This stage shows the actions that the user takes including what they do and how they do it. You can map out each step that the user takes which is useful to understand the customer journey and to see how they make a decision depending on qualities and features, pros and cons. These steps will also clarify the areas of struggle and confusion regarding the product/service the user intends to get.
Because of the complexity of human thoughts and emotions, it is not always easy to find solutions or pinpoint the actual needs depending on the process, as it tends to alter and fluctuate any time. This is the reason why user experience and behaviour should be observed and followed at all times by the help of empathy mapping sessions.
Why do you need empathy mapping?
Empathy maps are designed to organise user segmentation and help designers understand and prioritise customer needs, expectations and goals in details. The four quadrants that we listed above are essential aspects to see the complexity of needs and respond with a relevant solution.
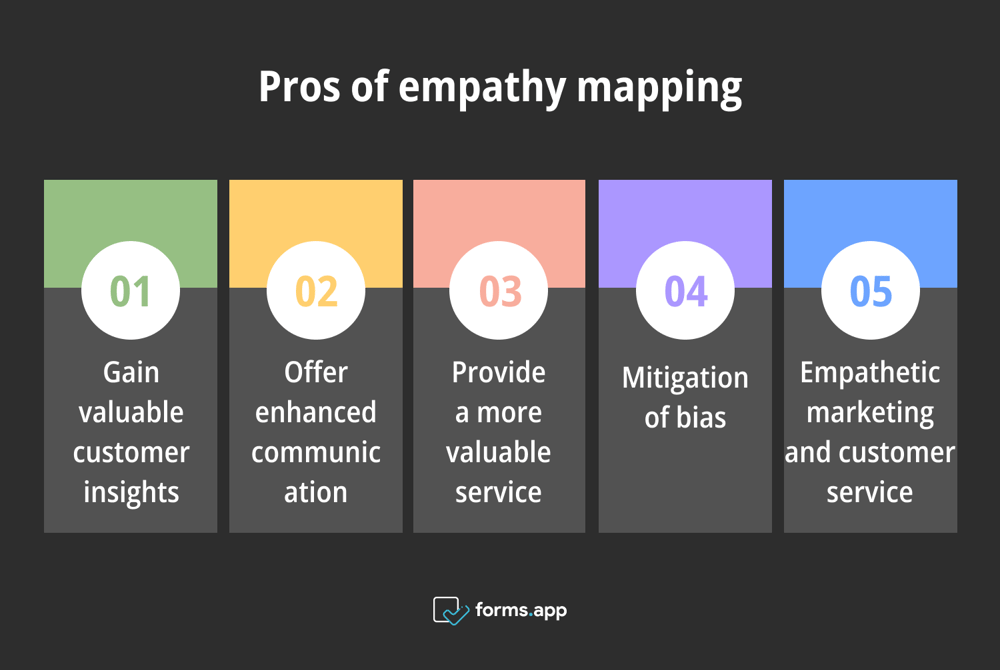
Benefits of empathy mapping
They are also great tools for UX designers to communicate information in an organised way. You can have your customers create their own empathy map, or conduct user interviews, surveys, or other instruments for data collection.
There are five key factors that emphasize why empathy maps are important including gaining valuable customer insights, offering enhanced communication, providing a more valuable service, mitigation of bias, and empathetic marketing and customer service.
1. Gain valuable customer insights
UX designer teams can gain detailed information from the user’s perspective, preferences, and struggles by using empathy maps. Designers can use this opportunity to understand the users’ motivations and can find solutions that resonate with the customers, which can also help with business growth and development.
For example, when designing a new app, you can use an empathy map to understand the frustrations and preferences of the users. This can help designers to provide the customers with a more user-friendly and intuitive interface making the user experience smoother and more enjoyable.
2. Offer enhanced communication
UX designers are not the only team members using empathy maps; developers, marketers, and shareholders collaboratively contribute for effective communication and optimised product or service. Shared understanding of users’ thoughts, preferences, feelings and behaviours encourage teams to work towards a common goal.You can personalize communications and offer customers a tailored service that is more personalized and unique by collaborating with the other team members. For instance, you can personalize communications through the needs and preferences of a customer buying a dress from your store sending them customized emails with recommendations based on their past purchases, style, and taste.
3. Provide a more valuable service
Empathy maps help you understand what your target audience is exactly looking for in a product or service they receive from you. This means you can create and upgrade a product that aligns with the customer’s preferences and desires, making it as valuable as possible to meet the customer’s needs.
For example, by analyzing the pain points, needs and goals of a customer using a mobile app who experiences confusion and frustration, you can provide them with a simplified version of app features to make their experience easier and more comfortable. This results in a satisfied customer who will want to purchase your products again in the future.
4. Mitigation of bias
Through empirical evidence, customer profiles, and user insights, you can mitigate bias by grounding design decisions. At this point, empathy maps can help team members focus on the emotions and behaviors of their audience to update or change the features of their products accordingly.
For instance, when designing a website for an older demographic, empathy maps can help with narrowing down the preferences of an older generation and highlight the diverse needs and preferences in order to build a more specified product to their demands.
5. Empathetic marketing and customer service
Businesses can provide their customers with more empathetic marketing campaigns that align with their expectations on an emotional level. Marketing teams can use the information related to users’ aspirations, fears and desires to create their messages and tailor interactions to build trust and long-term customer relationships.
For example, having an unsatisfied customer who is unhappy with the product they purchased from you, you can provide them with an empathetic solution by acknowledging their thoughts and feelings, providing assistance and following up with them to keep in contact making sure they are happy with the service they receive.
How to create your own empathy maps
To be able to create your customized empathy map, you need to follow a few steps. These include identifying your target audience, clarifying your objectives, completing the empathy map, team collaboration, and implementing insights.
a. Identifying your target audience
In order to have a clear empathy map and better understand your users, you need to know who you want to empathise with. This will help you detail the information you want to use when creating the empathy map. Once you have clarified this, it will be easier to collect data on this particular target audience.
b. Clarifying your objectives
It is important to know the purpose of creating an empathy map. Defining the goals and results will help with the mapping process. Before you start building your empathy map, make sure why you want to create one. Make a list of the reasons as this will help with creating clear paths and finding relevant solutions to your goals.
c. Completing the empathy map
Once you have a clear picture of your target audience and goals, you can start adding information using sticky notes, diagrams, texts, and/or images to plot your empathy map. You can use the four quadrants to fill in the map with the data and information you have collected about your users.
d. Team collaboration
Following the completion of the map, you can share it with the other team members to receive feedback. According to their reviews, you can make necessary changes and edits to the details you have on the map to better fit the user experience.
e. Implementing insights
You can create an action plan to apply what you have learned and created into practice. This will pinpoint the areas where you can deliver optimized customer value with the quickest outcomes. It is also essential to be updated with any change in need or expectation of the target audience. In case of a change, you may need to change the map to suit their needs accordingly.
An empathy map example
Below is an example of an empathy map to clarify what you would expect from a simple empathy map of an individual user.
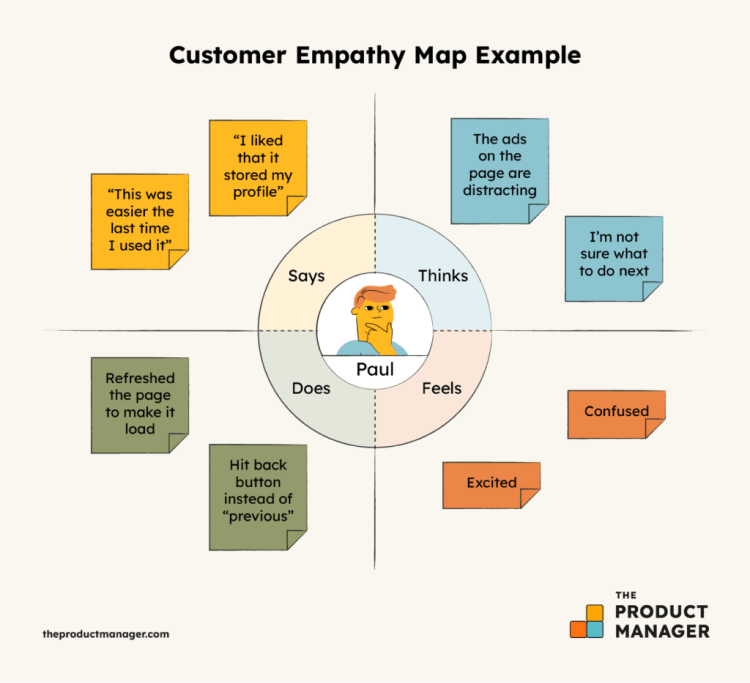
An example Customer Empathy Map of The Product Manager
Free empathy mind map templates
Some of the popular websites, like Miro and Figma, offer free empathy mind map templates that you can try out. Here are the visual examples of some of the templates from both websites.
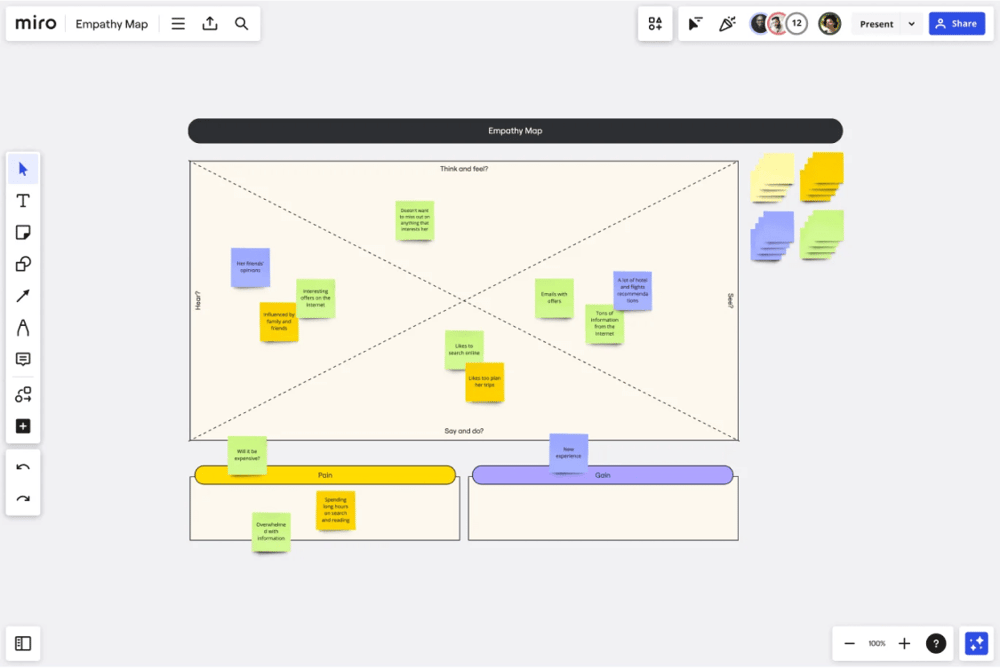
An example Empathy Map of Miro
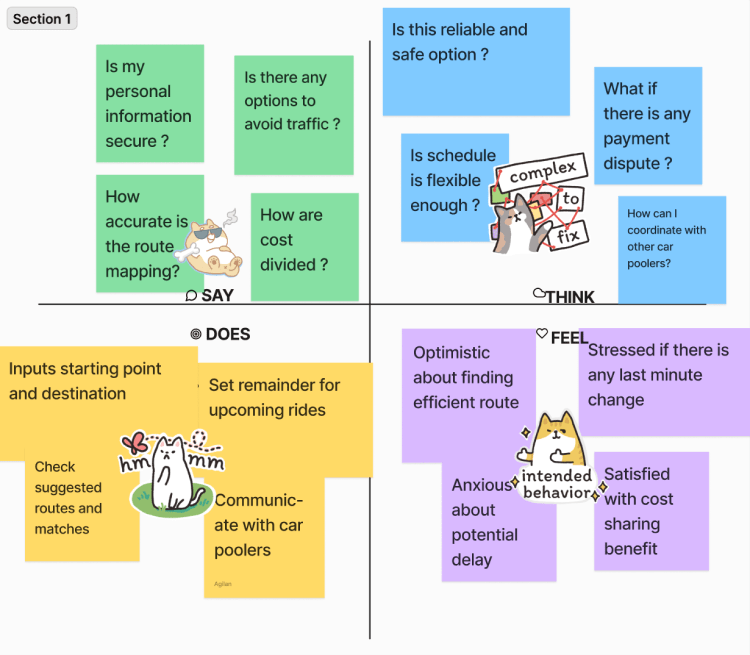
An example Empathy Map of Figma
When do you need to use an empathy map?
You need an empathy map to:
- improve user experience (UX): This will help improve the user design by visualizing the key areas of what your user wants and needs.
- launch a new product: This will help you figure out how a new product can create value.
- refine customer experience: This will help identify the areas of development considering the user segmentation.
Essential tools to use when creating an empathy map
Thanks to widespread online resources, now there is a variety of practical, as well as creative ways and tools to make your own empathy map. Below, we have listed some of the most popular tools which you can explore and choose the best for your unique empathy map.
A. Tools to learn about users and their feelings
- Hotjar: This is a useful tool that allows you to analyse behaviour and empathise with your audience.
- forms.app: This is a great tool to use to collect data by creating variety of online forms, surveys, quizzes, and more.
- Google Analytics: This tool is useful to collect insights and data of the visitors of your website, and to track website performance.
- Google Cloud Natural Language: This tool provides sentiment analysis, and extracts insights of users’ emotions and behavior.
B. Tools to actually create a visual empathy map
- Miro: Miro offers infinite boards and drawing tools to organize your maps, and allows you to co-create them.
- Figma: As diverse as it is, Figma is a utile tool to create detailed maps, and also allows you to work on them collaboratively.
- Mural: Mural offers a variety of options to create different sorts of maps and allows you to share them with your colleagues for teamwork.
- Creately: Creately is an easy-to-use tool to create your diagrammes, charts, and maps.
Frequently asked questions about empathy mapping
So far, we have presented the fundamentals of creating an empathy map, its importance for both businesses and users, how you can prepare an empathy map template, useful websites with diverse functions and features to make your own empathy map or just to find further information on. Check out some of the popular questions asked about empathy maps below:
The four aspects, also known as the four quadrants, are sees, thinks, does, and feels.
It refers to the target audience of a certain product or service.
While empathy maps refer to the individual user identifying specific points, persona refers to the summary of users focusing on entire user journeys.
Key takeaways
Empathy mapping is a great tool for product development, customer satisfaction, and paying close attention to your users’ needs. By understanding what matters to your customers, you can provide a more satisfying, user-friendly service to keep long-term and trustworthy relationships with your audience.
In this article, we clarified the definition of an empathy map, its importance in user experience, the four key aspects, and how to create an empathy mind map with examples and templates. Empathy maps help designers identify significant points and individual user experiences by creating a personalized map.
- What is an Empathy Map?
- What are the 4 aspects of an empathy map?
- Why do you need empathy mapping?
- How to create your own empathy maps
- An empathy map example
- Free empathy mind map templates
- When do you need to use an empathy map?
- Essential tools to use when creating an empathy map
- Frequently asked questions about empathy mapping
- Key takeaways
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications