When performing survey research, it is challenging for researchers to get data from the entire population. This issue highlights the need to gather a sample to conduct the research. The researcher should pick a sampling frame from which to draw a model after precisely specifying their target population.
A sampling frame lists all the units from which the sample was drawn. The sample frame can be specified for many research designs, whether qualitative or quantitative surveys. This article will explain the definition of the sampling frame, examples, and frequently asked questions about the frame of sampling.
What is a sampling frame?
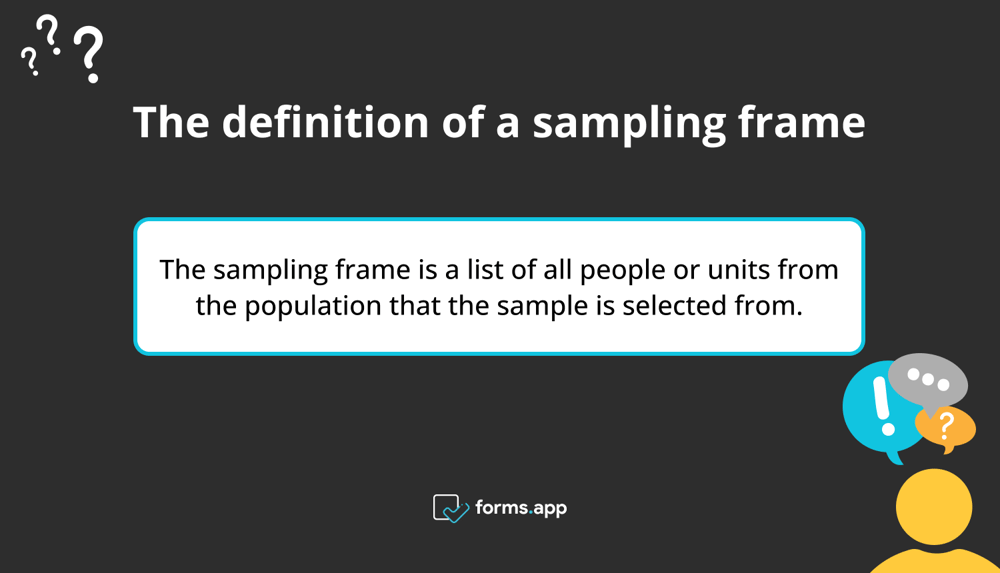
A sampling frame is a list of every element in your population. It is a comprehensive list of everyone or anything you wish to learn. In a simple random sampling, every unit from the sampling frame has an equal probability of being drawn and appearing in the sample. This collection of units is called the sampling frame. The frame of the sample and the population of interest should, ideally, match.
The definition of a sampling frame
Utilizing the sample frame in research, you may classify and code information on segmentation characteristics that are already known. To collect a sample, you must have a supply or list of every member of the target population and a method for choosing the sample. Any source that has the knowledge required to research every member of the intended audience is acceptable.
Types of a sampling frame
A sample frame needs to be current and applicable. The sampling frame in statistics comes in two different varieties. They consist of list frames and area frames. Typically, an area frame is used to start the survey, followed by a list frame.
1 - Area frames
Frames for area sampling encompass a vast geographic region. These regions often encompass enormous areas, are well-defined and mapped, and contain population statistics. Area frames often include a whole country, with national census data as the initial reference point.
2 - List frames
A list frame is a frame that includes a list of the intended audience. There may be more elements found after looking through the census list. This data may serve as the foundation of a list frame.
3 sampling frame examples
After choosing a frame of sampling, a sampling technique may be used to select a sample. It is not always feasible or practical to study every member of a population. Here 3 sampling frame examples:
1 - For example, researching people who frequently drive, ride a bike, or stroll about the neighborhood is a goal of road safety research. When recruiting participants, contacting individuals in each sample is more straightforward when there are three frames of sampling of people who drive, cycle, or walk. This ensures that each sample group has an equal number of participants.
2 - Another example is the whole Italian population is your target demographic. In such a situation, you may choose a subgroup of people for your research using information from a census, a phone book, or an electoral register.
3 - If your frame of the sample consists of 1500 individuals, you may choose 150 randomly from the group (for instance, using a random number generator) and invite them to participate in your study.
Frequently asked questions about the sampling frame
A sample frame is a list or source that contains all of the people in your target demographic and should not include any people who are not included in it. There are frequently asked questions about the frame of sampling.
Sampling frame vs. population
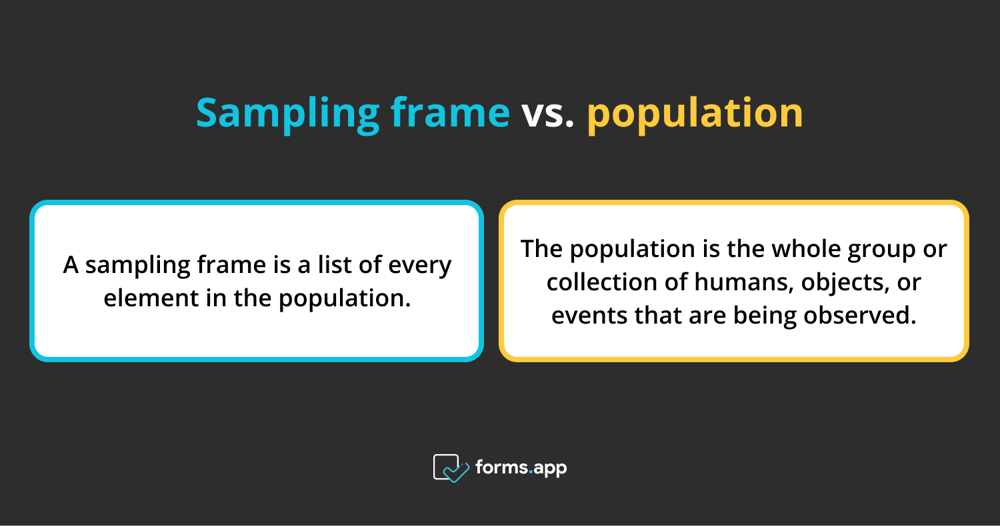
The sampling frame is a list of all people or units from the population that the sample is selected from. In contrast, the population is the whole group or collection of humans, objects, or events that are being observed.
The difference between sampling frame and population
Sampling frame vs. sample
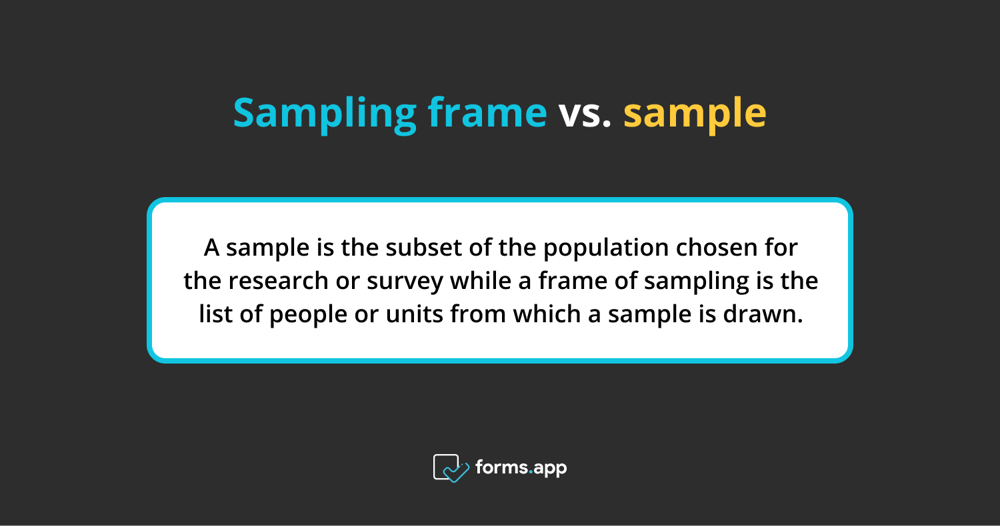
The database of every member of your target population is a frame of the sample. Your population is probably big; therefore, it’s either not feasible, or you can’t pay to include everyone in your study. A sample is the subset of the population chosen for the research or survey, and a frame of sampling is the list of people or units from which a sample is drawn.
The difference between sample and sampling frame
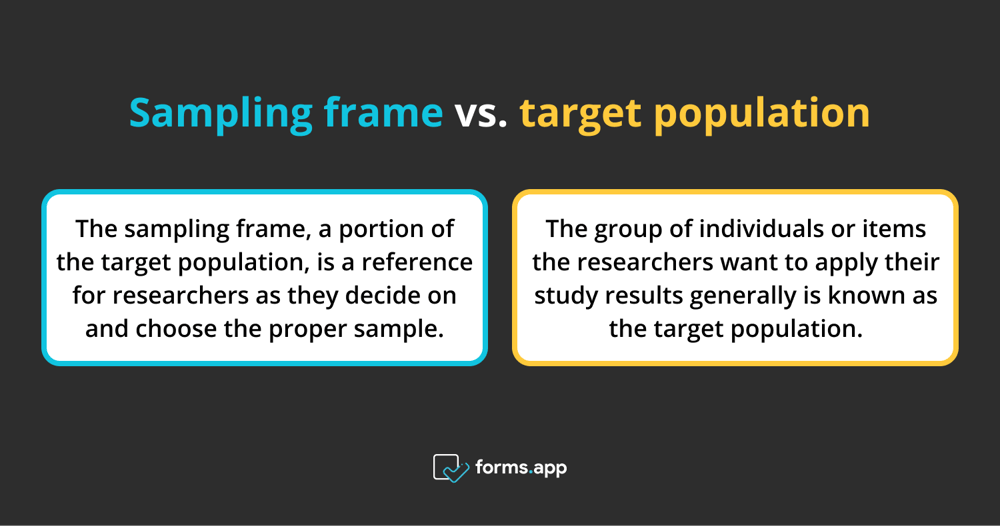
Sampling frame vs. target population
The sampling frame, a portion of the target population, is a reference for researchers as they decide on and choose the proper sample. It describes the list of people, homes, and other things that researchers have access to or can utilize to select a sample from. The group of individuals or items the researchers want to apply their study results generally is known as the target population.
The difference between sampling frame and target population
How does the sampling frame affect the results?
The population or list from which the sample is taken is known as the sampling frame. Because it decides who is included in the sample, the sampling frame impacts the outcomes.
- The sample will only be representative of the population if the frame of sampling is, and the findings might be skewed.
- The findings of a survey to ascertain the opinions of a particular age group may be biased if the frame of the sample does not cover every person in that age group.
- To reduce mistakes and sampling biases, a thorough frame of sampling that reliably identifies the population from which the sample is collected is necessary.
- The frame of sampling can influence the sample size, selection process, and distribution of sample units, which can impact the accuracy and precision of the findings.
- The sample may contain people who are ineligible and result in over-coverage if the frame of sampling includes people or units who are not a part of the interest.
Wrapping it up
In conclusion, the sampling frame is a set of sampling units from which a sample is chosen. It is crucial for selecting the target population’s constituents. It gives detail for locating and identifying the units.
While a sample frame clearly describes every member of the population and how to reach them, your target population is the broad notion of the group you are evaluating. Because some techniques, like stratified random sampling, need it, it could also contain demographic data for each individual.
In this article, we have shared the definition of the sampling frame, examples, and frequently asked questions about the sample frame. Reading this article will give you detailed information about the sampling frame.
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications