In today's fast-paced business environment, effective decision-making is paramount for success. Decision-making models provide structured frameworks that enable organizations to navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities. By employing these models, businesses can enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and adapt to ever-changing market dynamics with confidence and clarity.
This article will explore one of these effective decision-making processes, the Decision Matrix Analysis. It is a practical analysis for businesses to make informed decisions. We will cover it in detail, and examine its steps, suitable environments, and advantages and disadvantages. Now, let’s dive into this valuable framework:
First things first: What is the decision matrix analysis?
Decision Matrix Analysis is a systematic tool that is used to evaluate multiple options against a set of criteria to facilitate informed decision-making.
It involves creating a matrix where options are listed as rows and criteria are listed as columns.
Each option is then scored based on how well it meets each criterion, with scores typically ranging from 1 to 10 or categorized as low, medium, or high. Criteria are often weighted to reflect their relative importance, and the scores are multiplied by these weights to calculate a total score for each option.
Once all options have been evaluated, the option with the highest total score is chosen as the preferred choice. The analysis helps streamline complex decision-making processes by providing a structured framework for assessing options objectively. It allows decision-makers to consider multiple factors simultaneously, prioritize criteria based on their significance, and ultimately select the option aligning with the desired outcomes.
Decision matrix analysis steps
The Decision Matrix analysis tool is a systematic approach that allows individuals or teams to evaluate various options against predefined criteria. This process typically involves seven key steps, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the options at hand and facilitating a well-informed decision-making process. Let's delve into these steps in more detail:
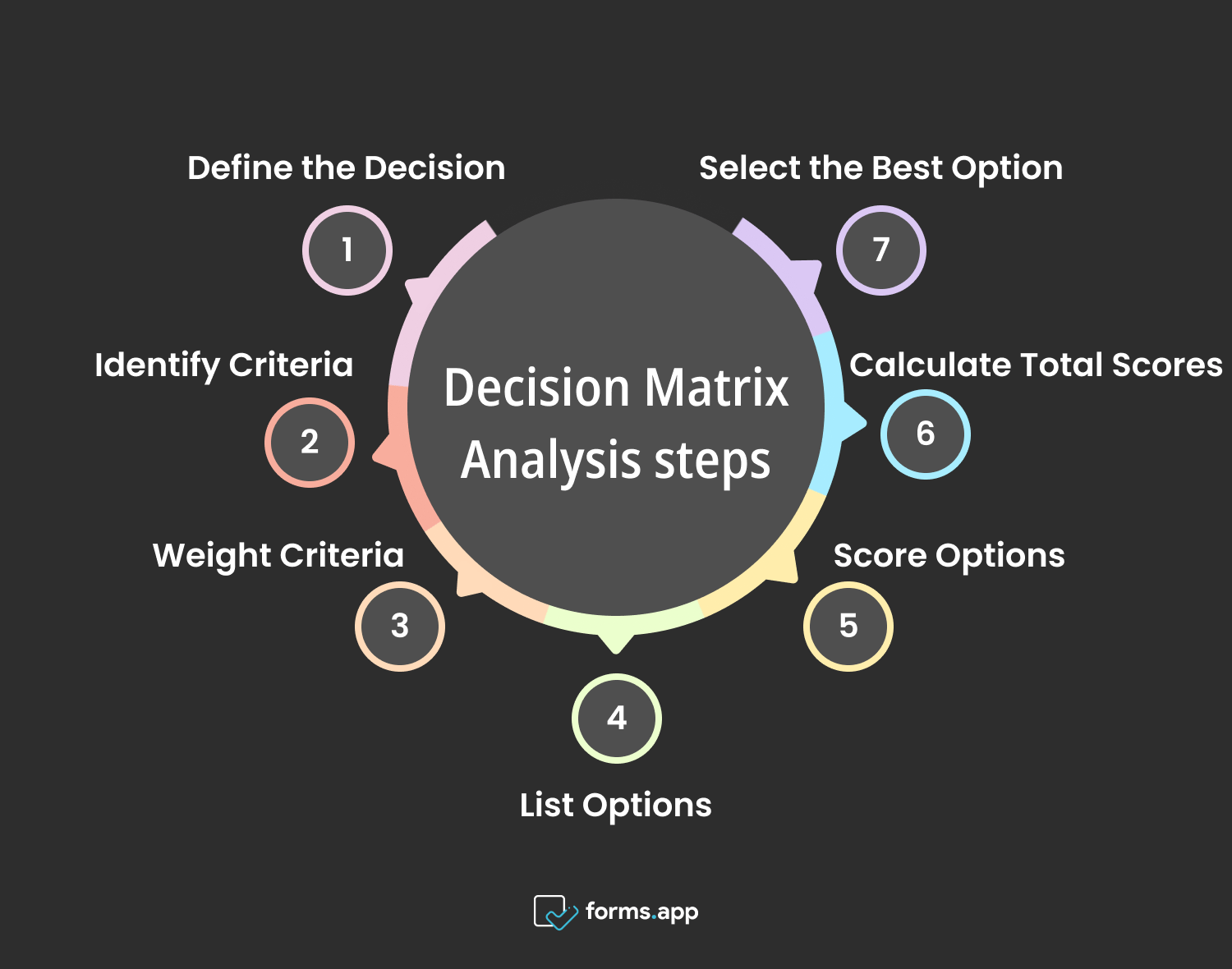
Steps for Decision Matrix Analysis
1- Define the Decision
In this step, the decision to be made is clearly defined, along with its purpose and scope. It's essential to understand the problem or opportunity at hand to ensure that the decision-making process remains focused and aligned with organizational objectives. This will also prevent disruption at the beginning of the process.
Example: Imagine a company needs to choose a new supplier for a critical component. The decision is defined as selecting the supplier that offers the best balance of quality, cost, and reliability to meet production needs for a specific period.
2- Identify Criteria
After defining criteria, decision-makers assign weights to each criterion to indicate their relative importance. These weights reflect the decision-maker's priorities and help ensure that more critical factors have a greater impact on the final decision. This step is essential to the model as it determines the way of implementation.
Example: In a car-buying scenario, a buyer might assign a higher weight to safety ratings and fuel efficiency if these factors are especially important while giving less weight to interior features.
3- Weight Criteria
In this step, weights are assigned to each criterion based on their relative importance or priority. This ensures that more critical factors have a greater influence on the final decision. This way, you can act in accordance with the weighted decision matrix.
Example: The vehicle company determines that the product quality is the most critical factor, so it assigns this factor a weight of 40%. Price and delivery time are also important but less so, so they are weighted at 30% each.
4- List Options
All available options or alternatives are identified and listed. These could be different suppliers, products, strategies, or courses of action. You brainstorm potential solutions or choices to address the issue at hand. Generate diverse ideas without judgment, exploring various perspectives and possibilities.
Example: The company compiles a list of potential suppliers based on recommendations, online research, and industry referrals. By listing options, it makes it easier to pick the best strategy in an option-based manner. It also prioritizes creativity and quantity by aiming for a wide range of options.
5- Score Options
Each option is evaluated against each criterion, and scores are assigned based on how well it meets each criterion. Scores can be numerical or qualitative, depending on the nature of the criteria. You can evaluate each potential solution or choice against predetermined criteria or factors.
Example: The company scores each supplier on product quality, price, delivery time, reputation, and customer service, using a scale of 1 to 10. This gives them a specific order among the listed options for their strategy. This step helps prioritize tasks or options and informs the decision-making process.
6- Calculate Total Scores
The scores for each option are multiplied by the corresponding weights of the criteria and then summed to calculate a total score for each option. You can aggregate the scores assigned to each option in the previous step to determine the overall ranking or preference.
Example: The weighted scores for each criterion are multiplied by the assigned weights and then summed to calculate a total score for each supplier. This data-driven approach facilitates informed decision-making and enhances the likelihood of selecting the most suitable solution.
7- Select the Best Option
Finally, the option with the highest total score is selected as the preferred choice. This option best aligns with the desired outcomes and objectives of the decision. Consider the aggregated scores, weigh any additional factors or considerations, and trust your judgment to select the optimal option.
Example: Based on the total scores, the company selects the supplier with the highest score as the preferred choice for the component. In this decision matrix example, the company approached the decision-making process with an evaluative and quantitative approach and made an informed and optimal decision for its strategy.
When to use the decision matrix analysis
The Decision Matrix is a tool to use in many cases and situations. This quantitative and evaluative analysis helps businesses to set and implement important criteria. Let’s look at some of the suitable cases in which you can use this decision-making tool:
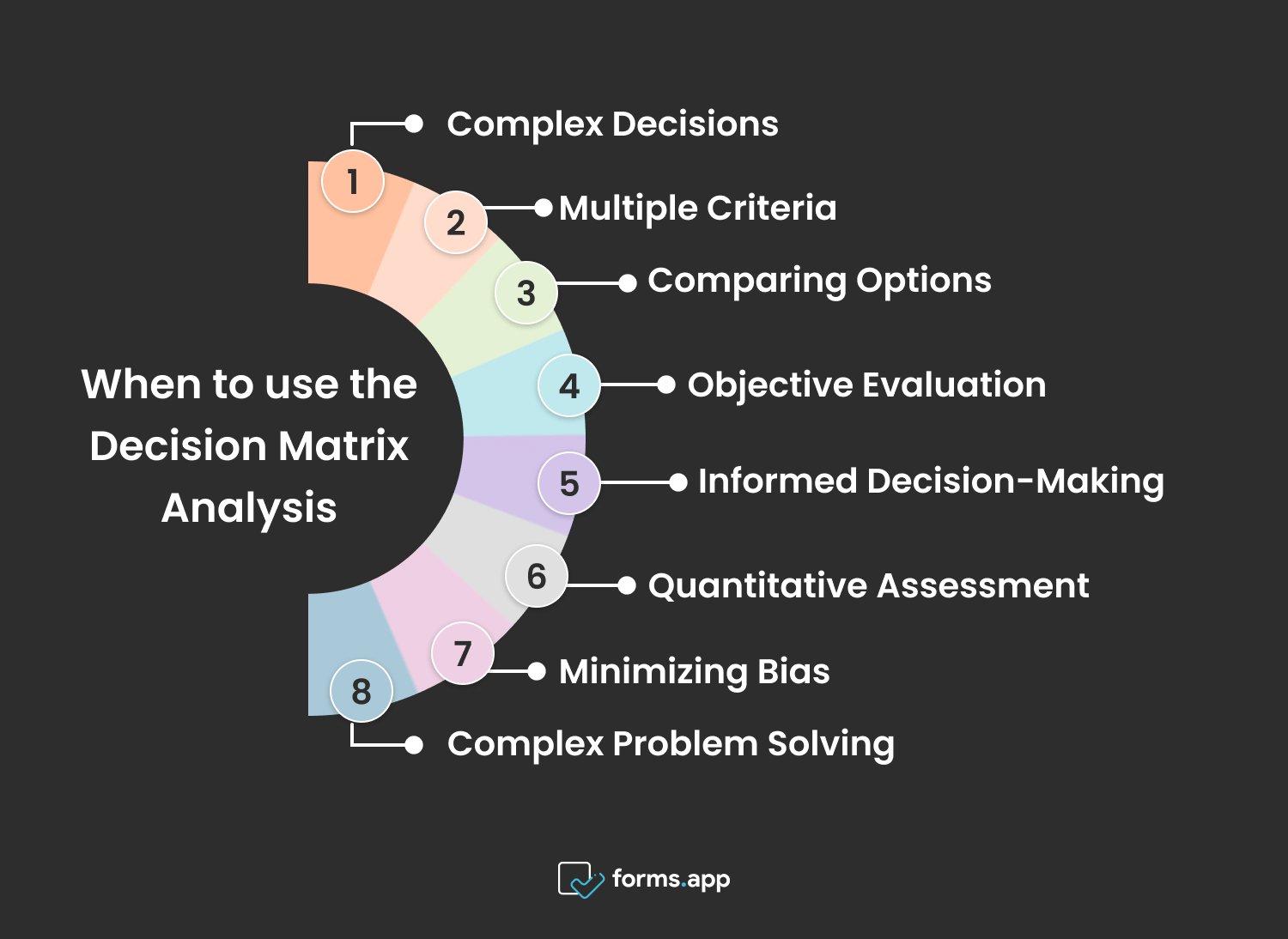
Right times to use the Decision Matrix Analysis
- Complex Decisions: Decision matrix analysis is ideal for tackling complex decisions where multiple factors and options need consideration. It provides a structured framework for evaluating choices and prioritizing actions based on predetermined criteria.
- Multiple Criteria: It's beneficial when you need to evaluate options against several criteria or factors simultaneously, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of each option's strengths and weaknesses.
- Comparing Options: Decision matrix analysis facilitates systematic comparison of options by considering their performance across various criteria. This allows for objective evaluation and helps in identifying the most suitable solution or course of action.
- Objective Evaluation: By assigning weights to criteria and scoring each option accordingly, decision matrix analysis enables objective evaluation of options based on their alignment with organizational goals and priorities.
- Informed Decision-Making: Decision matrix analysis provides a structured approach to decision-making, ensuring that choices are based on thorough analysis and consideration of relevant factors. This leads to more informed and effective decisions.
- Quantitative Assessment: It allows for a quantitative assessment of options, enabling a more data-driven approach to decision-making. By assigning numerical scores to criteria, decision matrix analysis facilitates objective comparison and prioritization of options.
- Minimizing Bias: By providing a structured method for evaluating options objectively, decision matrix analysis helps minimize bias in decision-making. This ensures that decisions are based on merit rather than personal preferences or opinions.
- Complex Problem Solving: Decision matrix analysis is effective for addressing complex problems where there are multiple interrelated variables to consider. It provides a systematic approach to problem-solving, allowing for thorough analysis and evaluation of potential solutions.
Advantages of using the decision matrix analysis
You can create a decision matrix and benefit from many advantages. You can add weight to important criteria and make decision-making easier for yourself and your team members. Let’s see those advantages in detail and understand how this analysis can make our jobs easier:
- Structured Evaluation: Decision matrix analysis provides a structured framework for evaluating options, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered systematically and comprehensively, leading to more informed and thorough decision-making processes.
- Objective Comparison: It enables objective comparison of options by assigning numerical scores to criteria, allowing decision-makers to assess each option's performance based on quantitative data rather than subjective opinions or biases.
- Clarity and Transparency: Decision matrix analysis offers clarity and transparency in decision-making by clearly outlining the criteria used for evaluation and providing a transparent process for scoring and ranking options, enhancing accountability and understanding among stakeholders.
- Efficiency and Time Savings: By streamlining the decision-making process and organizing information in a structured manner, decision matrix analysis saves time and improves efficiency, allowing decision-makers to focus on evaluating options and making informed choices more quickly.
- Risk Mitigation: It helps in identifying and mitigating risks associated with different options by considering factors such as potential drawbacks, uncertainties, and adverse consequences, enabling decision-makers to make more risk-aware decisions.
- Facilitation of Group Decision-Making: Decision matrix analysis facilitates group decision-making by providing a systematic and objective approach that allows for collaboration and consensus-building among team members, leading to decisions that reflect collective input and agreement.
- Prioritization of Criteria: It allows decision-makers to prioritize criteria based on their importance and relevance to the decision at hand, ensuring that the evaluation process focuses on factors that have the greatest impact on the desired outcomes.
- Optimization of Resource Allocation: Decision matrix analysis aids in optimizing resource allocation by identifying options that offer the best value or return on investment, helping organizations make strategic decisions that maximize the use of available resources.
How can forms.app can help?
The inclusion of a "selection matrix" form field in forms.app offers significant advantages for people who want to use Decision Matrix Analysis. This feature enables users to systematically evaluate various options against pre-defined criteria, fostering a structured approach to decision-making.
By inputting relevant criteria and weighting factors, respondents can efficiently compare options, facilitating informed decision-making processes. This streamlined method empowers users to prioritize choices based on quantitative assessments, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of decision-making efforts. forms.app will help you create online surveys with quantitative and evaluative approaches like the Decision Matrix analysis.
Frequently asked questions about the decision matrix analysis
So far, we have covered many aspects of the Decision Matrix analysis, including its definition, steps, suitable environments, and advantages. We will now look at answers to some of the most frequent questions asked about this practical and valuable model:
The Decision Matrix involves several steps: defining the problem, identifying criteria, weighting criteria, listing options, evaluating options against criteria, calculating scores, and making a decision based on scores. These steps guide users through a systematic evaluation process, ensuring thorough consideration of factors and options before reaching a decision.
The seven steps to effective decision-making, aligned with the Decision Matrix, include problem definition, criteria identification, criteria weighting, option listing, option evaluation, score calculation, and decision-making based on scores. By following these steps, individuals can methodically assess options and make informed decisions that align with their goals and priorities.
The process of Decision Matrix Analysis entails defining the decision problem, identifying relevant criteria, assigning weights to criteria, listing available options, evaluating options against criteria, scoring options, and selecting the option with the highest score. This structured approach enables decision-makers to objectively assess choices, prioritize preferences, and ultimately make sound decisions based on thorough analysis.
Key points to take away
In conclusion, the Decision Matrix Analysis is a structured, quantitative, and evaluative model for decision-making. It helps teams, project managers, and many other people to add weight to the factors and make the optimal decision in many cases and situations.
In this complete guide, we have discovered all aspects of the Decision Matrix Analysis, including its steps with examples. We have also seen its suitable environments, advantages as well as some answers to the frequently asked questions about it. Now, it is time for you to create your own decision matrix template and make more informed decisions.
Fatih is a content writer at forms.app and a translator specializing in many text domains, including medical, legal, and technical. He loves studying foreign languages. Fatih especially likes to create content about program management, organizational models, and planning tools.