Decision-making is a vital process in today’s businesses. It defines the policies and actions of the institutions and corporations. Today, decision-makers often seek a guide to navigate the challenges of steering their organization. There are various decision-making models to come up with more effective decisions. They will come in handy in the fast-paced and ever-developing business world.
In this article, we will discover the RAPID decision-making model. It is a structured framework offering clarity and effectiveness. The expression “RAPID” is an acronym for distinct roles for individuals in the decision-making process. It is also an adjective for the model describing the dynamism for making swift and sound decisions.
What is the RAPID decision-making model?
The RAPID decision-making model in business is a decision-making framework developed by Bain Company.
It outlines the specific roles in the decision process. It ensures that the decision-makers hear all the sounds at the right time. The model involves assigning clear responsibilities to each role/individual. This way, the managers will be able to make more beneficial decisions for the sake of their organization.
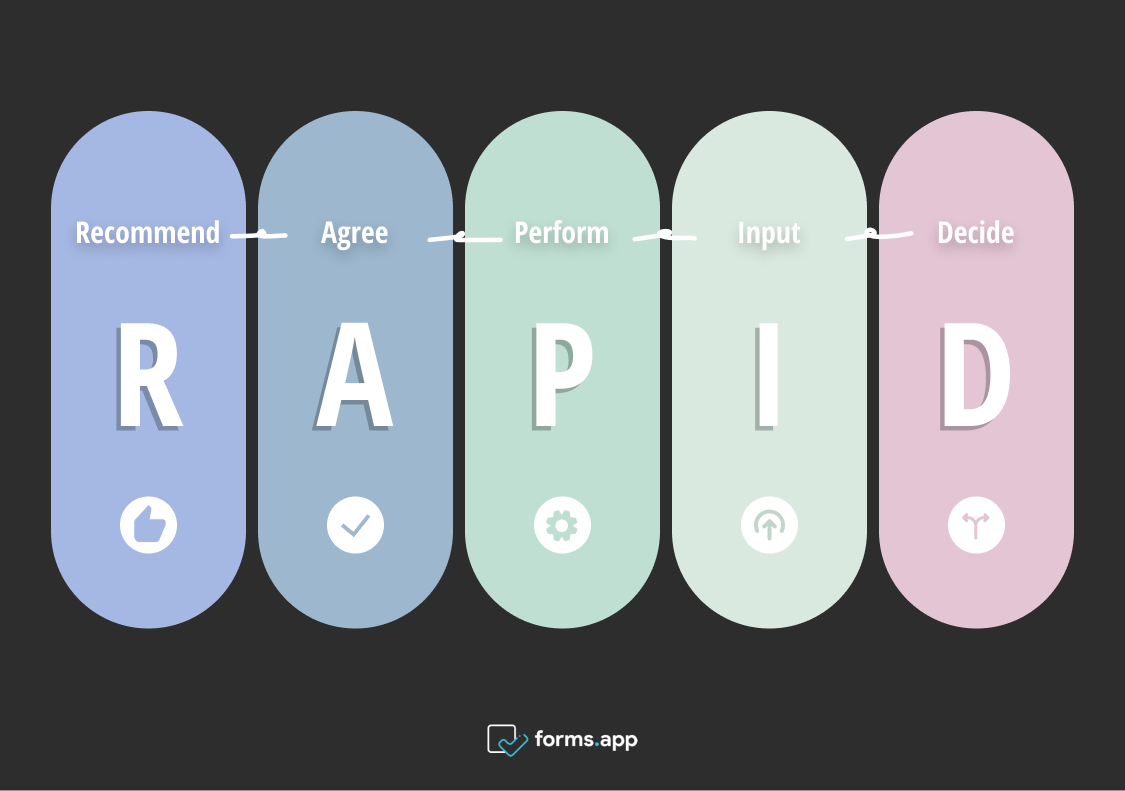
RAPID decision-making model
The acronym RAPID stands for Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, and Decide. These are the roles/responsibilities assigned to address challenges in the decision-making process. They make it easier to make more effective and accountable decisions. The model will also help eliminate uncertainty, improve communication, and enhance transparency within the organizations. This rapid framework is beneficial in complex organizational environments.
The RAPID decision-making model
The RAPID framework consists of five key roles and courses of action. The word “RAPID” can give the impression that it is all about speed. However, the purpose of RAPID is about a collaborative journey toward a well-informed final decision. Now, let’s delve into the acronym.
💡Check our article to learn about the Gap model of service quality.
1- Recommend (Recommender role)
The Recommender is accountable for suggesting a particular course(s) of action. This role involves analyzing information, considering alternatives, and proposing good ideas. The person in this decision-making role should be able to assess situations and offer sound advice. They also need to possess communication skills.
2- Agree (Agreer role)
Agreers are individuals or groups who give approval for the decision to proceed. They review the recommendation, share their insights, and ultimately agree or disagree with the recommended action. The person in this role needs to have effective communication skills and a comprehensive understanding of the potential decision.
3- Perform (Performer role)
The Performer is the person performing or testing the decision. This role includes implementing the chosen plan/action. It often requires specific skills or expertise related to the execution phase. The “perform” role also entails proficiency in translating decisions into tangible decisions and outcomes.
4- Input (Input role)
The Input Providers contribute information or insights into the decision-making. Multiple people can assume this role. They offer relevant data, perspectives, and context that can influence the recommendation and the ultimate decision. It requires strong logical and communication skills, as well as a willingness to share valuable input.
5- Decision (Decision-maker role)
The Decision-maker is a single person or a group with the authority to make the final decision. This role involves considering recommendations, assessing input, and ultimately choosing the best course of action. Also, the person(s) should have leadership and strategic thinking skills. They can be CEOs, department heads, team leaders, or project managers.
Together, these roles establish a clear and cooperative structure. They ensure the organizations tackle each aspect of the decision-making process transparently and with a sense of responsibility. This systematic approach promotes efficiency, minimizes uncertainty, and fosters a good environment for effective decision-making.
Advantages of the RAPID decision-making model
The RAPID decision-making process offers several advantages for corporations, project teams, managers, and leaders in complex structures. This model not only applies to large and complex organizations or corporations. It is also useful for a small company or team looking for rapid actions and changes. The advantages of this rapid model of decision-making are:
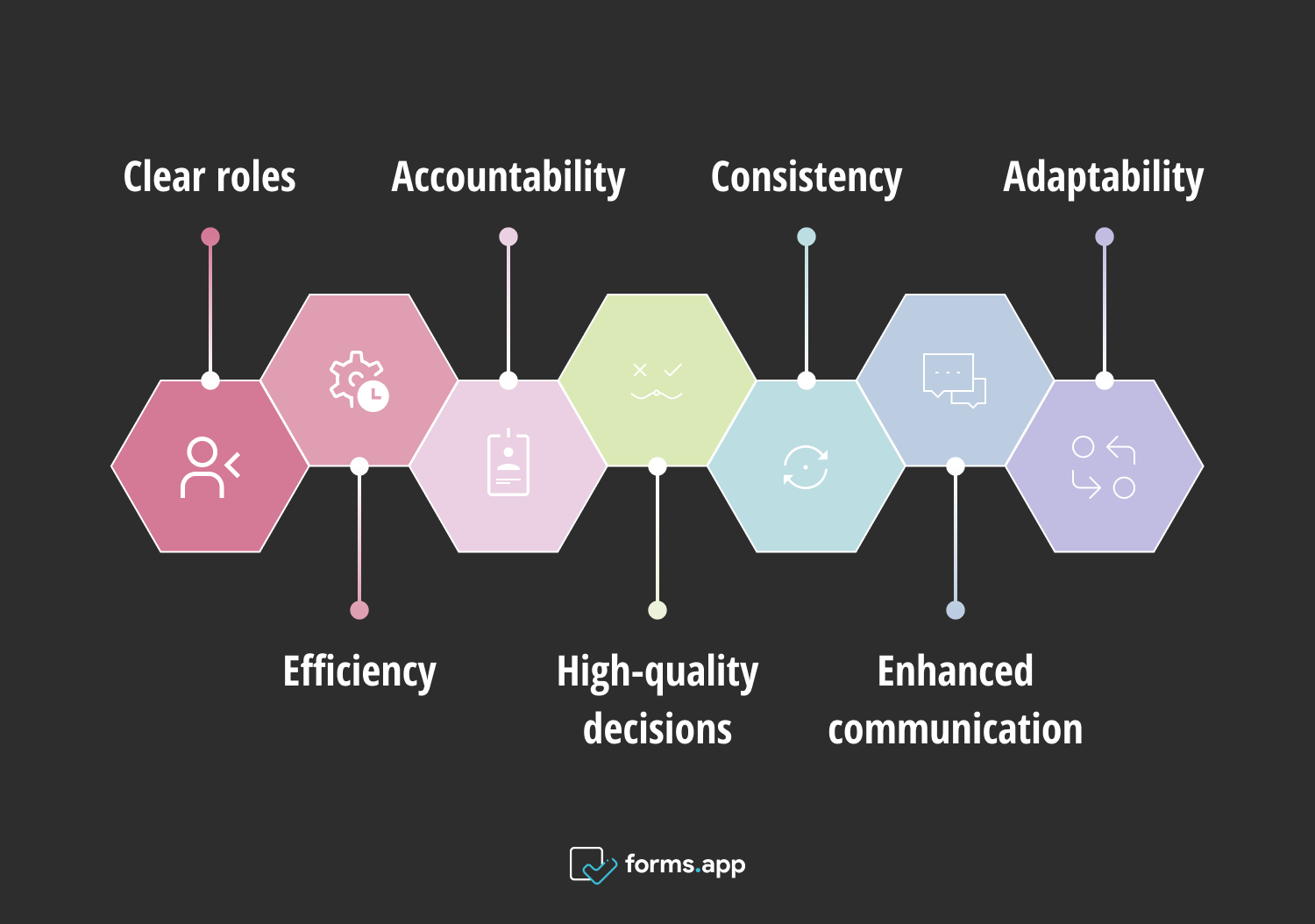
Pros of the RAPID decision-making model
- Clear roles: The model will outline the responsibilities for each role clearly.
- Efficiency: It eliminates unnecessary steps. It focuses on the essential actions when decision-makers need to make a complex decision.
- Accountability: It enhances the ownership and responsibility of the people in the decision-making process.
- High-quality decisions: It ensures informed decisions and a rapid process by minimizing unnecessary delays
- Consistency: It provides a standardized approach for different situations
- Enhanced communication: It enables the team to identify team members to consult or inform at the right time.
- Adaptability: It adapts to the specific needs and dynamics of different decision-making scenarios.
Examples of the RAPID decision-making model
So far, we have covered the RAPID decision-making model with all its aspects and advantages. Any corporation, organization, or institution wanting to enhance its decision process can apply this model. They can assign decision-making roles to persons or teams in line with their preferences. Let’s look at a scenario to get a clearer picture of the model:
1 - Cosmetic company launching a new product
Imagine a cosmetics company wanting to launch a product line. First, the marketing team recommends a specific product line and identifies end-users, market trends, and potential competitors. Then, the finance team agrees after they have assessed the cost of the production and the potential revenue from the new product.
The product development team creates prototypes, performs product testing, and ensures the quality and safety of the cosmetics. Upon this, the regulatory team provides input to ensure that the new cosmetics product conforms to all relevant regulations. Lastly, the executive team makes the final decision on launching this new product. They can do it thanks to the contribution from the other teams.
2- Tech company nearing a merger
For another example, let’s examine a tech company looking at merging with another company. The merger is a long and complicated process requiring delicate work. Firstly, the strategic planning team recommends the merger, highlighting the potential for beneficial growth and market advantages.
Then, the financial team agrees after analyzing the financial situation of both companies. The integration team performs the merging plans and ensures a smooth transition. The legal team provides input by reviewing the contracts and considering regulatory matters. Finally, the board of directors makes the final decision and makes the merger official.
Frequently asked questions about the RAPID model
We have established a comprehensive understanding of this framework with examples. We know that RAPID is an acronym involving five decision-making roles, which enhance collaboration and decision processes. Now, let’s look at some of the frequently asked questions about the RAPID model.
RAPID and RACI are both decision-making frameworks. But, their focuses differ from each other. RAPID stands for Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, and Decide. However, RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed. It defines roles and responsibilities within a project.
RAPID focuses on the decision-making process itself and outlines the specific roles and responsibilities for a final decision. RACI, on the other hand, emphasizes broader roles and responsibilities within a project or process. It identifies the persons for responsibility, accountability, consultation, and information.
The five decision-making models involve contributions from various scholars and researchers across disciplines. They come from different theories and perspectives in the fields of psychology, economics, and management. These five models of decision-making reflect diverse approaches to understanding and explaining how individuals or organizations make decisions:
- Rational Decision-Making
- Intuitive Decision-Making
- Incremental Decision-Making
- Normative Decision-Making
- Bounded Rationality
The D.A.I model for decision-making stands for Data, Analysis, and Insight. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach. It involves collecting information (data) and thorough examination (analysis). It also requires the generation of a deeper understanding for informed decisions (insight).
The most common type of decision model is Rational Decision-making. This approach involves a systematic and logical process. It includes analyzing relevant information and options to make an optimal decision. It also reflects diverse ways for individuals and organizations to navigate between choices.
Conclusion
To sum up, the RAPID Decision-making model consists of five roles to help make high-quality decisions. The roles of recommender, agreer, performer, input provider, and decider enable teams and companies to enhance communication and transparency for more effective decisions.
In this article, we have covered the RAPID Decision-making Model with all of its aspects and advantages. We have seen what a useful tool it is with various examples. Last but not least, we have answered some of the most frequently asked questions about the model. Now, you are ready to use it in your business!
Fatih is a content writer at forms.app and a translator specializing in many text domains, including medical, legal, and technical. He loves studying foreign languages. Fatih especially likes to create content about program management, organizational models, and planning tools.