Have you ever wondered about ways of identifying the problems in your service quality and finding solutions for them? In today’s service sector, service quality is the factor that brings you one step ahead. You should know the ways to find what is missing in your service quality and how to improve it.
This article covers the gap model of service quality. It will help you learn the critical gaps between your service delivery and customer expectations. It will also enable you to explore how closing these gaps enhances service quality. This will help you lay the foundations for long-term success in your business.
First things first: What is the Gap model of service quality?
The GAP Model of Service is a framework developed to identify the differences between customer expectations and perceived service.
It assesses the journey from customer expectations to service delivery. Its goal is to improve service quality by addressing the gaps through better communication. This will align the service expectations with the actual service delivery.
Gap model of service model (Gaps in the Gap Model of Service Quality)
There are five gaps identified in the GAP Model of Service Quality. Each gap defines the discrepancy between the expectations of your customer and your actual product or service quality. These service quality gaps are the knowledge gap, policy gap, delivery gap, communication gap, and perception gap. Let’s take a closer look at the model by exploring the 5 gaps in detail:
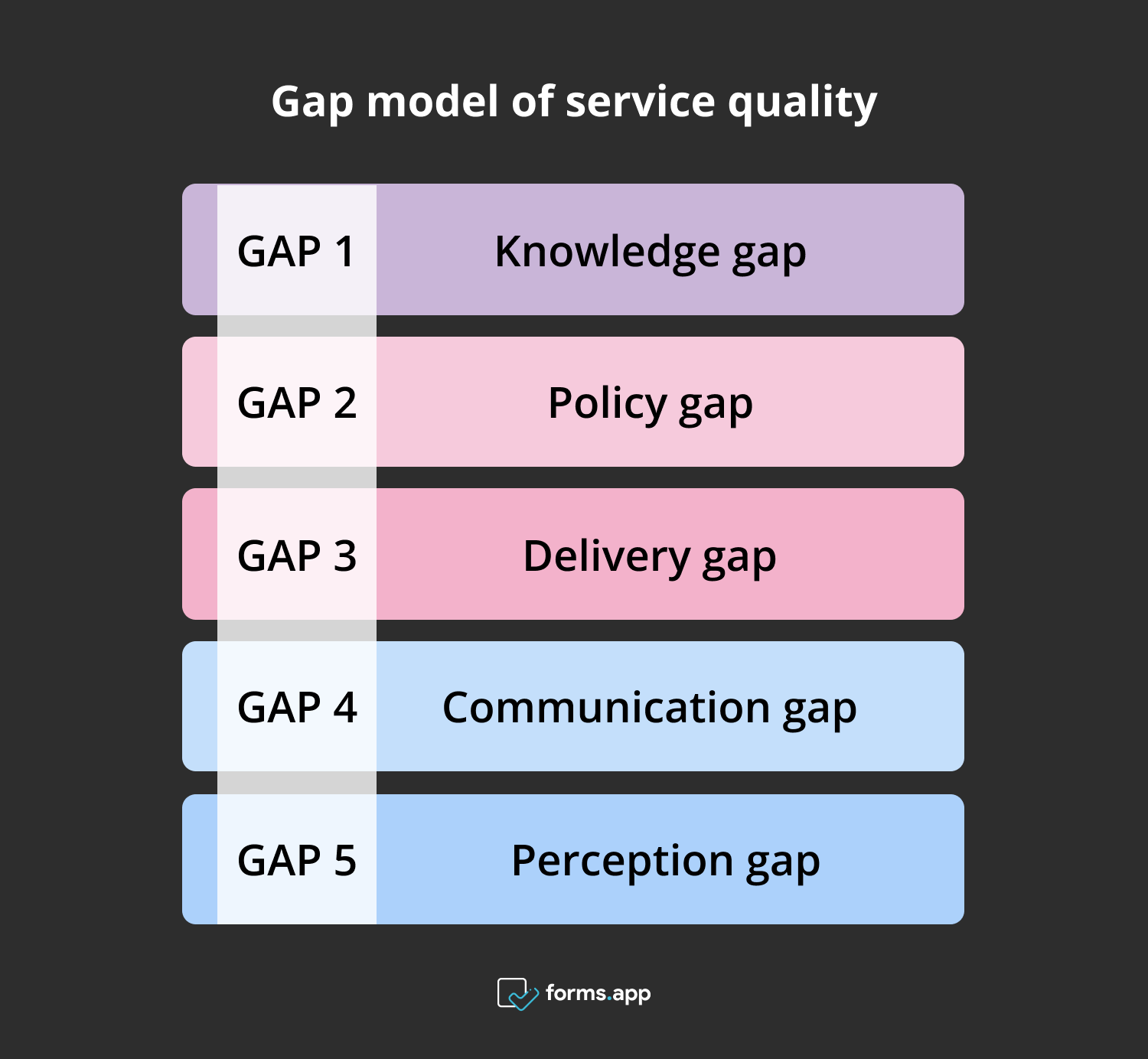
Gap model of service model
1- Knowledge gap
Knowledge gap refers to the difference in understanding between the manager (service deliverer) and the customer's expectations. You can bridge this gap by understanding the customer's needs and expectations. You can create effective communication channels, receiving customer feedback, and regular market research. This will align your knowledge with the actual expectations of the customer.
2- Policy gap
The policy gap represents the misalignment between the management’s perception of customer expectations and the actual service standard policies and specifications. Closing this gap involves refining internal policies to accurately reflect customer needs. Understand the customer complaints and make it easier to translate the customer experience into service quality specifications.
3- Delivery gap
The delivery gap reveals the disparity between specified service quality and the actual delivery of the service. It emphasizes the need to synchronize the delivery process with the delivery expectations. The solutions for this gap are simple. Make sure that your service delivery aligns with your predefined service quality specifications and meets your customer expectations.
4- Communication gap
The communication gap reflects the discrepancy between what an enterprise communicates about its services and the actual service delivery. The gap between how a company perceives its service and its service delivery can lead to many problems. Closing this gap involves aligning your marketing messages with the reality of your service delivery and enhancing transparency.
5- Perception gap
The perception gap signifies the distinction between the customer's perception of the delivered service and their initial expectations. It reveals the subjective nature of customer perception. You can close this gap by understanding your customer’s perspectives and actively seeking feedback. Also, addressing any discrepancies between the perceived and expected service will immensely help enhance your service delivery.
Examples of Gap model of service
Applying the service quality GAP model will differ in many sectors because the examples of service quality vary in each industry and business. Any company or enterprise offering products or services to any type of customer portfolio can benefit from this model.
Example #1
For example, think of a hotel. Hotel management uses customer feedback surveys and reviews them to understand guests' expectations (knowledge gap). Recognizing the need for personalized services, the hotel revised its policies and included a guest preference profile (policy gap). With updated policies, the hotel ensures its service delivery aligns with the new personalized approach (delivery gap).
The hotel updates its marketing materials to communicate enhanced personalized services and establishes clear communication for guest preference profiles (communication gap). Following all these changes, the guest can perceive a noticeable improvement in the service quality. Now, the experience offered exceeds the actual customer expectations (perception gap).
Example #2
This time, imagine a telecom company having troubles with their customers. This company recognizes that its service quality falls short (Gap 1). It embraces faster complaint resolution and enhances physical facilities (Gap 2). After this, they improve their service delivery (Gap 3).
They revise their website to reflect the changes in their service quality (Gap 4). The customer perceives the positive development (Gap 5). The company followed all these steps and ensured higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. This proves the effectiveness of this model in successfully addressing the service gaps.
Frequently asked questions about the gap model of service
As you can see, the gaps are all dependent on each other. Filling one gap generally leads to another, and the ultimate outcome is making your service quality better. However, the GAP model is not a well-known phenomenon for all. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about the GAP model of service and dimensions of service quality:
The Gap 4 refers to the Communication Gap. It represents the disparity between what a service provider communicates about their services and their actual service delivery. Essentially, it highlights the challenges faced when there is a disparity between the promises and the actual customer experience. One can close this gap by ensuring accurate marketing messages reflecting reality.
The Gap 5 is the Perception Gap. It signifies the difference between customer perceptions of the service delivered and their initial expectations before receiving it. It refers to the importance of understanding customer satisfaction and their expectations. Closing the Gap involves understanding customer expectations, setting realistic service standards, and implementing feedback mechanisms.
GAP Model analysis is a structure for assessing and enhancing service quality. It identifies five key gaps in the service delivery process. By analyzing these gaps consistently, companies can see the areas for improvement and improve their customer satisfaction. Aligning your service delivery with customer expectations will ultimately enhance your overall service quality and performance.
Certainly, gap analysis is an excellent strategy. It is a perfect way to improve your service quality. It involves assessing the discrepancies or “gaps” between your current performance and desired goals. By identifying these gaps, the companies can develop their service/product quality and marketing strategies.
This strategy will definitely help elevate customer satisfaction and achieve the management goals. As a result, the organization can ensure customer loyalty and strengthen its position in the market. This strategy also contributes to the growth of positive customer experiences for success.
To sum up
In conclusion, the GAP Model of Service Quality identifies the discrepancies between customer expectations and service quality. This model serves as a valuable guide. In it, there are a total of 5 gaps, which are dependent on each other. Bridging these gaps will lead to better customer satisfaction and service quality.
In this article, we defined the GAP Model of Service quality and all the gaps in the model. We saw examples of each gap, highlighting their dependence on each other to ultimately enhance the service quality. We also covered the frequently asked questions about this model to help understand it more smoothly. This model is a valuable tool for all businesses!
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications