Some tools help your company prepare for potential disruptions in today's fast-paced business world. They identify and evaluate the effects of unexpected events on your business operations. This allows your organization to protect vital assets and sustain operations. With changing market dynamics and increased risk factors, they are essential for business resilience.
This article will explore one of these tools, the Business Impact Analysis (BIA), an essential process for your organization. We will explain its definition, why it is crucial for your business, and how to conduct it effectively. Additionally, we’ll cover real-life examples and practical insights into how BIA compares with risk assessment.
What is business impact analysis?
Business impact analysis (BIA) identifies critical organizational functions and evaluates how a disruption might impact them.
BIA assesses the effects of disruptions on processes, resources, and technology. It highlights potential losses in operations, finances, or reputation. This process helps determine which functions are most vital to maintaining continuity.
The goal is to uncover vulnerabilities, prioritize response efforts, and create a plan for rapid recovery. A robust BIA provides a roadmap for handling incidents, helping your business stay operational and minimize losses during unforeseen events. For companies today, business impact analysis is a foundational part of resilience planning.
Importance of business impact analysis
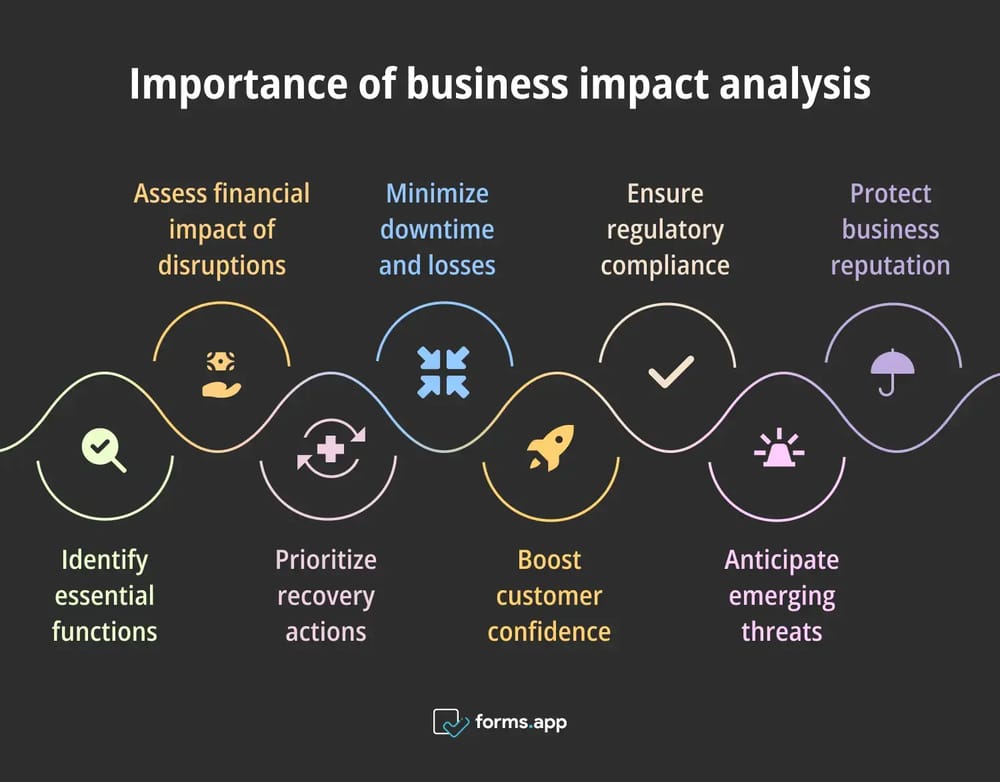
Now that we have familiarized ourselves with the concept of BIA (business impact analysis) let’s talk about its importance. This part of the article will cover why you should use business impact analysis in your operations. By using a business impact analysis methodology, you can:
Reasons why business impact analysis matters
a. Identify essential functions
A primary reason to use Business Impact Analysis is to identify the most critical functions within an organization clearly. BIA categorizes processes by importance, distinguishing core functions from those that can tolerate delays. By identifying these essential areas, you can ensure that you allocate resources wisely and direct attention to vital operations first during a disruption.
In today’s competitive landscape, knowing what is essential enables your organization to protect the operations that keep the business moving. With these insights, decision-makers can confidently focus on areas that matter most for operational continuity.
b. Understand the financial implications of disruptions
Business impact analysis helps quantify the financial impact of potential disruptions. BIA provides clear financial insight by evaluating how long various functions can be offline before disruptions affect the revenue. This information is vital for planning budgets and allocating resources. For example, a manufacturing company can determine how a supply chain interruption might result in lost sales.
These financial insights allow your business to understand the value of recovery strategies. Armed with a BIA, your company can avoid financial surprises and justify the spending on recovery measures. You can also ensure that you remain financially prepared for unexpected downtime.
c. Prioritize recovery efforts
Not all business functions require the same recovery speed, and BIA helps prioritize efforts based on importance. After assessing functions and their dependencies, BIA provides a roadmap for which areas need immediate attention. This prioritization is crucial, as it helps your business manage limited resources effectively.
For example, a retail company might prioritize its e-commerce platform recovery before internal reporting systems. With a BIA, your company clarifies which areas to address first. This ensures you allocate resources efficiently and avoid wasting time on non-essential tasks during a crisis.
d. Reduce downtime and minimize losses
Downtime can be costly, both financially and reputationally. BIA helps reduce downtime by identifying critical recovery point objectives (RPO) and establishing recovery time objectives (RTO) for action. By setting recovery time objectives for each function, BIA minimizes potential losses and accelerates recovery.
A reduced downtime strategy is invaluable in sectors where customer satisfaction depends on continuous service. BIA allows your business to prepare detailed response plans that shorten interruptions, safeguard profits, and protect customer trust. This creates a well-rounded approach to disruption management, ensuring a quick and efficient recovery.
e. Increase customer confidence
Customers place their trust in companies that demonstrate resilience and preparedness. By having a well-documented BIA, your business can show its commitment to maintaining operations even during adverse events. This proactive approach boosts customer confidence, assuring them that the company can manage challenges without compromising service quality.
Especially in industries where continuity is essential, such as finance, healthcare, and IT, a strong BIA shows customers that the business is serious about staying operational, no matter the circumstances. This reputation for reliability enhances customer loyalty and provides a competitive advantage.
f. Comply with regulatory requirements
In many industries, regulations mean a certain level of preparedness for business continuity. A Business impact analysis template assists organizations in meeting these requirements. By documenting recovery plans and operational dependencies, your company can show compliance with laws related to continuity and disaster recovery planning.
Failing to meet these regulatory standards can lead to penalties, but a BIA helps avoid such outcomes. This compliance also reinforces your company’s commitment to safety and reliability, which builds trust with clients, partners, and regulators. BIA is a vital tool for meeting legal expectations for companies operating in regulated sectors.
g. Prepare for emerging threats
BIA addresses existing risks and helps companies prepare for new threats. By analyzing potential disruptions, your business can anticipate the challenges they may face in the future. As industries evolve and new risks arise, such as cybersecurity threats or climate-related events, BIA offers a framework to address these issues proactively.
Companies can adapt their recovery plans based on emerging trends, helping them remain resilient no matter the changes. With a proactive BIA, your business can confidently face the unknown. You can stay prepared for whatever challenges come your way.
h. Safeguard business reputation
Reputation is a valuable asset, and how a company handles disruptions can significantly impact it. A BIA approach to crisis management demonstrates that your company values resilience. Your business is committed to upholding service quality by prioritizing response strategies and minimizing downtime.
This commitment to continuity fosters a strong reputation for clients, partners, and investors. Companies that handle disruptions effectively build lasting trust with stakeholders. This, in turn, strengthens the market position. Reputation management tools can help you track your brand's reputation and conducting BIA regularly ensures companies maintain credibility even in the face of adversity.
How to manage business impact analysis (step-by-step)
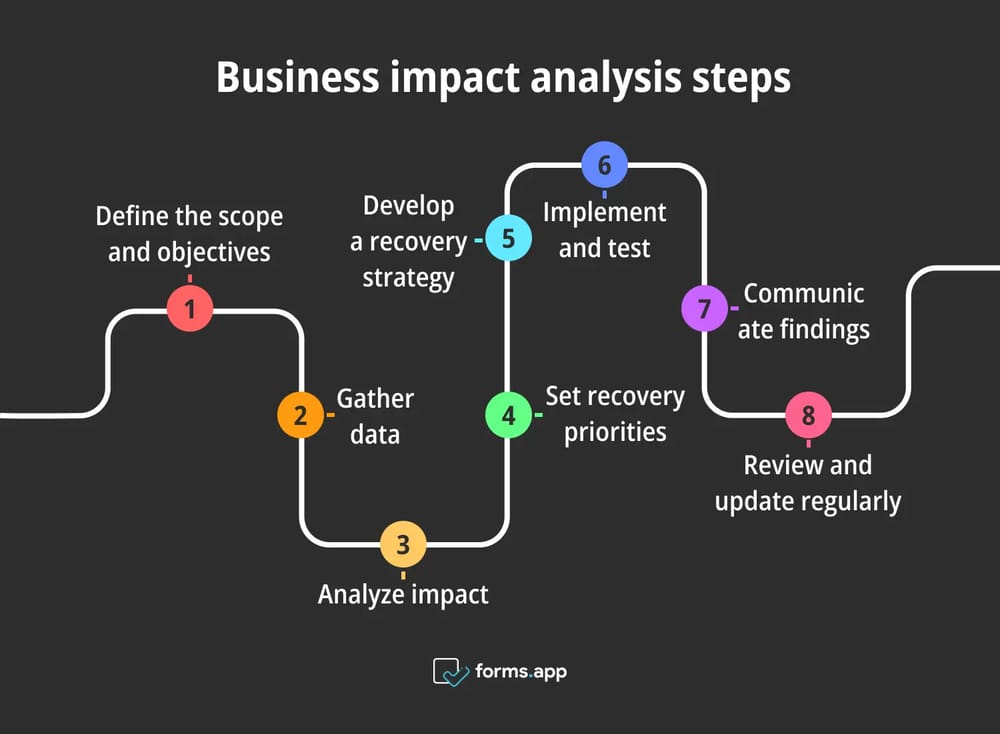
We have seen the importance of business impact and how it corresponds to your organizational structure. In this section, we will provide you with a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to manage business impact analysis. Here are the 8 steps to implement a successful BIA:
Steps for business impact analysis steps
Step 1: Define the scope and objectives
The first step in managing a business impact analysis is to define its scope and objectives. This means identifying which departments, processes, and functions the analysis will cover. Clearly defining these areas ensures that the BIA focuses on the most critical aspects of the business.
Objectives should include understanding the potential impact of disruptions and setting priorities for recovery. The clarity helps guide the entire analysis process. This ensures that it aligns with your organization’s overall resilience goals. A well-defined scope sets a solid foundation for conducting a focused and effective BIA.
Step 2: Gather data
Data gathering is a crucial part of BIA management. This step involves collecting information about each function’s operational requirements, dependencies, and risk factors. Common methods for data collection include interviews, surveys, and reviewing existing business documentation.
By gathering detailed data, your business can accurately assess each function’s potential impact in a disruption scenario. This information forms the core of the BIA. It offers insights into recovery needs and priorities. Proper data collection ensures that the BIA reflects real operational demands. This makes it a reliable tool for planning and response.
Step 3: Analyze impact
In this step, companies analyze the collected data to determine the potential impact of disruptions on each critical function. This analysis includes estimating downtime tolerance, financial implications, and operational dependencies. The goal is to understand how a disruption would affect each area and identify functions needing immediate recovery.
By assessing impact levels, your business can prioritize which functions to address first in a crisis. This step is key to creating a targeted response strategy because it pinpoints the most vulnerable areas within your organization.
Step 4: Set recovery priorities
After impact analysis, the next step is to set recovery priorities. You give functions with the highest impact and lowest downtime tolerance top priority. Setting these priorities helps businesses allocate resources efficiently. This way, you will be able to restore critical operations quickly. Recovery priorities serve as a guideline for crisis response.
This provides clarity on which functions must resume first. This prioritization allows your organization to maximize its resources, focus on essential functions, and reduce overall downtime. Establishing recovery priorities is a critical aspect of BIA management. This enables quick and organized action during disruptions.
Step 5: Develop a recovery strategy
The recovery strategy outlines specific actions to restore critical functions. This plan includes timelines, resource requirements, and step-by-step actions to bring operations back online. Developing this strategy requires input from key stakeholders to ensure it is realistic and comprehensive.
The recovery strategy is a roadmap for managing disruptions, detailing how you handle each priority function. A strong recovery plan enables your organization to act quickly and maintain service levels during a crisis. By preparing a detailed recovery strategy, your business can better manage the unexpected and maintain critical operations.
Step 6: Implement and test
Implementing and testing the BIA recovery strategy is essential for verifying its effectiveness. Regular testing through simulations and mock scenarios helps identify gaps or weaknesses in the plan. This step also allows the organization to practice and refine its response strategies, making improvements as necessary.
Testing ensures all employees are familiar with the recovery process, reducing hesitation in an actual crisis. By continuously testing and refining the strategy, your business can ensure that the BIA plan remains effective. By doing this, you will be ready to handle real disruptions confidently.
Step 7: Communicate findings
Communicating BIA findings with stakeholders is an important part of the process. This includes sharing insights with senior management, department heads, and key personnel. You can build a shared understanding of priorities and recovery strategies by ensuring that you keep everyone informed.
Transparent communication helps align all departments and strengthens organizational readiness. It also reinforces accountability, as each team understands their role in the recovery plan. Open communication ensures you integrate the BIA findings into your company’s broader risk management strategy. This will enhance overall preparedness.
Step 8: Review and update regularly
The final step in managing a BIA is regular review and updates. As your organization evolves, so do its risks and priorities. Reviewing the BIA ensures it remains aligned with the current business landscape, incorporating any new critical functions or emerging threats. Regular updates keep the BIA relevant.
This makes it a continuous part of the company’s risk management strategy. The proactive approach helps maintain business resilience. This ensures that the organization remains prepared for any disruption, regardless of changes in operations or industry dynamics.
An example scenario for business impact analysis
Now, you know how to use and maintain business impact analysis effectively. In this section, we will look at a well-known company that is using BIA and achieving positive results. This is the case of Amazon, a multinational technology company. Let’s look at a business impact analysis example:
Amazon
Amazon uses Business Impact Analysis (BIA) to prepare for high-demand periods, especially the holiday season. It analyzes the potential impacts of disruptions in its supply chain, warehouse operations, and delivery systems. This way, Amazon identifies critical functions and vulnerabilities. Through BIA, the company implemented redundancies in inventory, enhanced logistics tracking, and expanded staffing for order fulfillment.
This preparation enables Amazon to handle order spikes smoothly and maintain customer satisfaction, even during unexpected delays. The positive results are evident: minimized downtime, reliable delivery times, and strong customer trust. Amazon’s BIA-driven approach demonstrates how planning for disruptions ensures continuity and optimizes performance during the busiest times of the year.
Business impact analysis vs Risk assessment
We have covered nearly all aspects of the business impact analysis. As we have seen in its steps, it is a process similar to risk assessment and risk mitigation. It can even include a risk assessment. This section will compare business impact analysis and risk assessment to help you better understand the concepts.
Business impact analysis vs Risk assessment
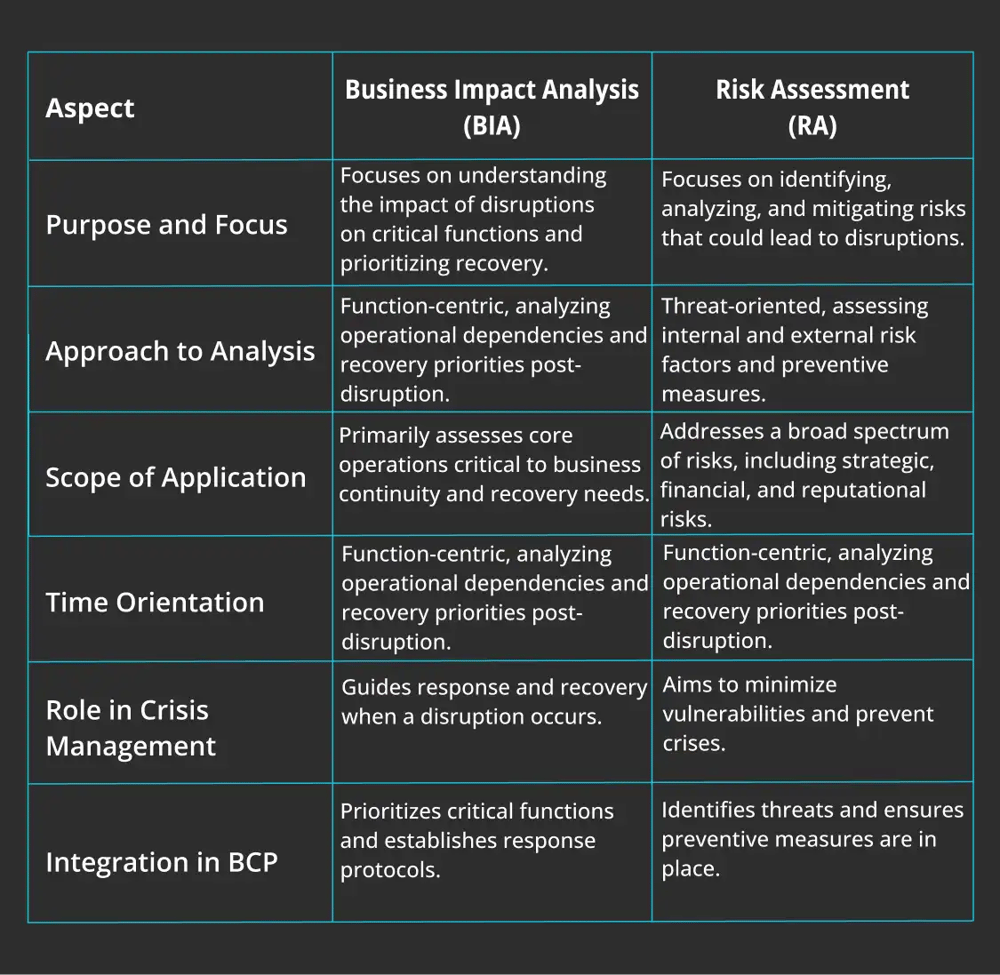
1- Purpose and focus
While both Business Impact Analysis and Risk Assessment play a role in continuity planning, their focus differs. A BIA centers on understanding the potential effects of disruptions on critical business functions and identifying which areas need urgent recovery. In contrast, a Risk Assessment evaluates potential risks that could lead to those disruptions.
It involves identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks that threaten business stability. In essence, BIA answers, “What happens if a disruption occurs?” while Risk Assessment asks, “What could cause a disruption?” Both are necessary for a robust continuity plan, but they offer different insights that complement each other.
2- Approach to analysis
BIA and Risk Assessment differ in approach. A BIA is typically function-centric, analyzing each part of the business to understand its role and impact. It evaluates operational dependencies and sets recovery priorities. Risk Assessment, however, is more threat-oriented, examining external and internal factors that could harm the business.
It assesses the likelihood and impact of potential risks, providing preventive measures. While BIA looks at the impact on functions post-disruption, Risk Assessment focuses on identifying and mitigating risks before they occur. Like BIA, risk-oriented approaches, such as risk and reward analysis, also focus on understanding potential outcomes to make informed business decisions and enhance resilience.
3- Scope of application
The scope of application for BIA and Risk Assessment also varies. BIA is generally applied to functions directly tied to business continuity, assessing impact and recovery needs across core operations. Risk Assessment has a broader application, addressing various risks, from cybersecurity to market fluctuations.
BIA focuses on operational recovery, while Risk Assessment covers risks impacting business strategy, finances, and brand reputation. Together, they create a comprehensive approach to resilience, covering operational and strategic risk elements. Integrating these scopes enhances an organization’s ability to respond to threats and maintain stability across all areas.
4- Time orientation
BIA and Risk Assessment also differ in time orientation. BIA is forward-looking but reactive, concentrating on how the organization will respond after a disruption. It prioritizes response and recovery strategies to reduce downtime. Risk Assessment, however, is preventive, aiming to identify and mitigate risks before they impact the business.
It involves proactive measures that reduce the likelihood of disruptions occurring. BIA prepares the organization for crisis response, while Risk Assessment helps prevent crises. These perspectives on time orientation complement each other, as organizations need preventive and reactive measures for effective risk management.
5- Role in crisis management
In crisis management, BIA and Risk Assessment play distinct roles. The BIA process provides a structured approach to responding when a crisis occurs, ensuring the continuity of critical functions. It guides the organization through recovery, detailing steps to restore operations. On the other hand, risk assessment focuses on minimizing the likelihood of a crisis.
Identifying vulnerabilities and implementing preventive actions aims to reduce risk exposure. Together, these roles support a holistic crisis management strategy that prepares the organization for prevention and effective response.
6- Integration in business continuity planning
BIA and Risk Assessment are integral to a robust business continuity plan (BCP). The BIA helps prioritize critical functions, while Risk Assessment identifies potential threats. They enable companies to prepare for specific impacts and safeguard their most valuable resources. Integrating these tools enhances the continuity plan by covering preventive and reactive measures.
BIA establishes response protocols, while Risk Assessment ensures necessary precautions are in place. This integration provides a comprehensive framework for resilience, allowing organizations to address threats proactively and respond effectively if a disruption occurs.
Frequently asked questions
Lastly, let’s answer some of the most frequently asked questions about the BIA. Understanding these answers will help you understand the business impact analysis more clearly. By doing so, you can use it in your organization more effectively.
A Business Impact Analysis aims to identify and assess the critical functions within an organization and understand the potential impacts of disruptions. This analysis helps prioritize recovery efforts and allocate resources to protect key operations.
The BIA's responsibility usually falls on the risk management or business continuity team. However, it involves collaboration with all departments to gather accurate data on critical functions and dependencies.
Industries that rely on continuous operations, such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, benefit significantly from a BIA. It ensures that these organizations can maintain essential services during a disruption.
Yes, small businesses can conduct a BIA, although it may require a simplified approach. Even a basic BIA can provide valuable insights, helping small businesses prioritize resources and prepare for potential disruptions.
Conclusion
A business impact analysis is a vital tool that prepares your organization to handle disruptions with minimal downtime and financial loss. Your business can protect its operations and uphold customer trust by identifying critical functions, evaluating risks, and implementing recovery plans. BIA is an essential component of a robust business continuity strategy. It offers both preventive and reactive benefits that strengthen your resilience.
This comprehensive guide covered the concept, importance, and steps of business impact analysis. We examined a well-known company case and compared BIA to risk assessment. Finally, we have answered some common queries. Embrace BIA as a proactive approach that supports continuity, reduces risks, and builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Contributors
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications