In today’s competitive business landscape, companies rely heavily on models and formulas to guide their financial decisions. These tools help businesses assess their stability, growth potential, and overall financial health. Among these, financial ratios stand out as critical indicators. They provide insight into your company’s ability to meet its obligations, manage debt, and sustain operations.
Today, we will talk about one of these financial ratios, the solvency ratio formula. We will explore its definition when to use it, and why to use it. We will also see its different types and how to calculate this crucial financial metric step by step. Additionally, we will provide real-life examples from well-known companies and answer some common queries about the subject.
What is the solvency ratio?
The solvency ratio is a key financial metric to assess a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations.
It measures the relationship between a company’s total assets and its total liabilities. In simple terms, the solvency ratio indicates whether a company has enough resources to cover its debts in the long run.
The solvency ratio is calculated by dividing a company’s net income and depreciation by its total liabilities. Unlike liquidity ratios, which focus on short-term financial health, the solvency ratio gives insight into a company’s long-term stability. It helps to determine how well a company can manage its debt and continue operating with financial distress.
Understanding the solvency ratio is vital for making informed financial decisions. For instance, if your company has a low solvency ratio, it might need to rethink its debt management approach. On the other hand, a strong solvency ratio can be a sign of good financial management and can boost investor confidence in your company.
5 Solvency ratio types
Having familiarized ourselves with the concept and steps of “solvency ratio”, let’s take a look at its different types. You can select the most suitable variant and apply it to your business. The types of solvency ratio will give you a clearer idea of the subject, making you understand it better.
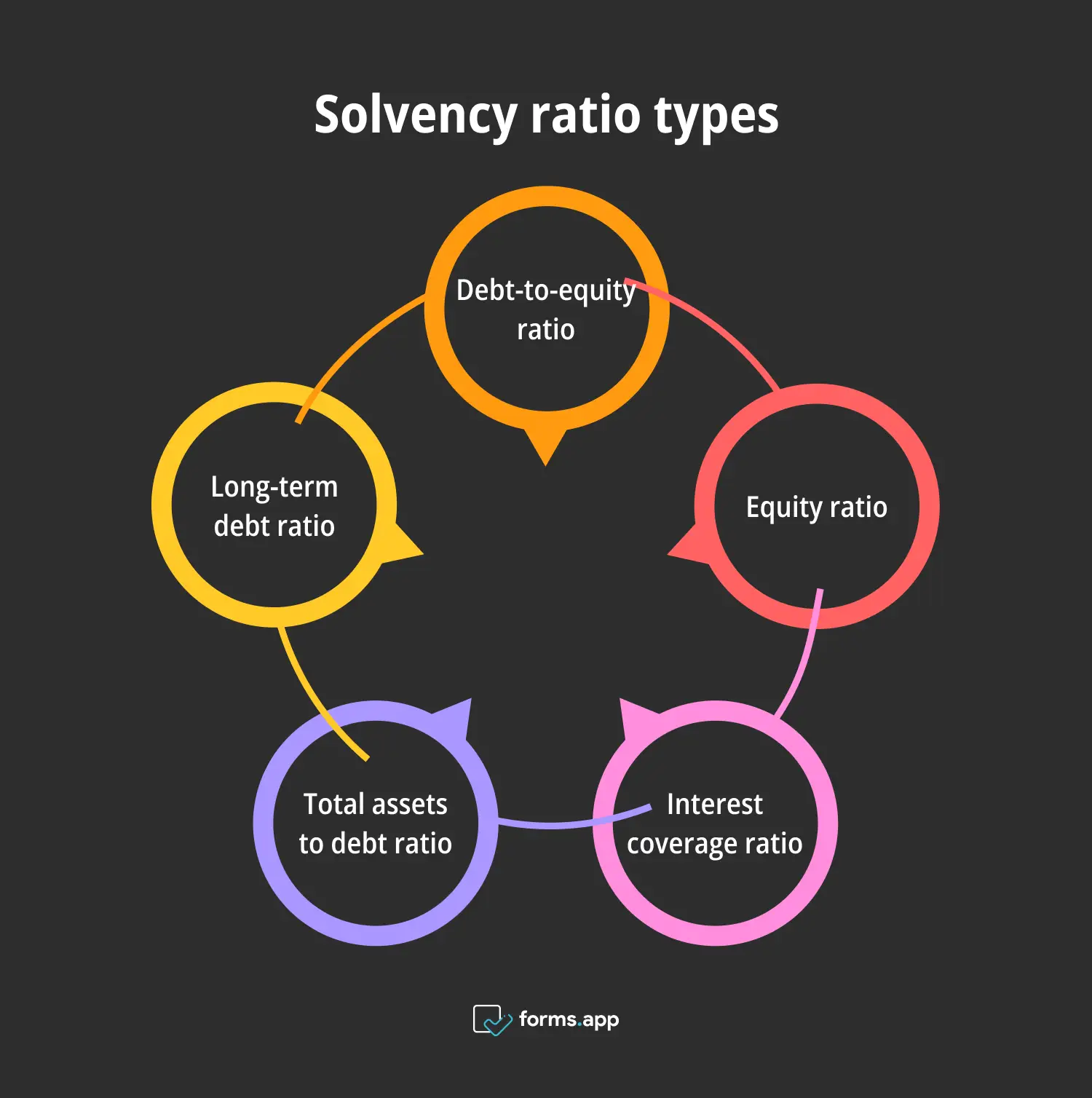
Types of solvency ratio
1- Debt-to-equity ratio
The Debt-to-Equity Ratio is one of the most common solvency ratios. It measures the proportion of a company’s total debt to its shareholders’ equity. This ratio indicates how much debt your company is using to finance the operations compared to its equity. A lower debt-to-equity ratio suggests a more financially stable company.
This means that it relies less on borrowed money. Conversely, a higher ratio may indicate higher risk, as the company is heavily dependent on debt. This ratio is particularly important for investors and lenders assessing a company’s financial leverage.
2- Equity ratio
The Equity Ratio is another important solvency metric that measures the proportion of total assets financed by shareholders’ equity. It is calculated by dividing a company’s total equity by its total assets. A higher equity ratio indicates that a larger portion of the company’s assets is funded by equity, which suggests financial stability and lower risk.
If your company has a high equity ratio, the investors will consider it less risky because it is less reliant on debt. Investors and creditors often use this ratio to evaluate the financial strength and the risk profile of your company.
3- Interest coverage ratio
The Interest Coverage Ratio measures your company’s ability to pay interest on its outstanding debt. You can calculate it by dividing your company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses. A higher interest coverage ratio indicates that your company can easily meet its interest obligations. This is a sign of strong financial health.
Conversely, a lower ratio may signal potential difficulties in meeting debt obligations, raising concerns about the company’s solvency. This ratio is particularly important for lenders and investors who want to assess your company’s ability to manage its debt burden.
4- Total assets to debt ratio
The Total Assets to Debt Ratio compares your company’s total assets to its total debt. You can calculate it by dividing total assets by total debt. A higher ratio indicates that the company has more assets than debt. It suggests a strong financial position and a lower risk of insolvency.
This ratio is useful for assessing your company’s ability to cover its debt obligations with its assets. Investors and creditors often use this ratio to evaluate the overall financial health of your company and to determine whether it is financially stable.
5- Long-term debt to capitalization ratio
The long-term debt-to-capitalization ratio measures the proportion of your company’s long-term debt relative to its total capitalization, including debt and equity. This ratio provides insight into a company’s financial structure and how it finances its operations.
A lower ratio indicates that your company relies more on equity than on debt. This suggests lower financial risk. On the contrary, a higher ratio may indicate greater reliance on debt, which could increase the company’s financial risk. This ratio is particularly important for evaluating your company's long-term financial stability and risk profile.
How to calculate the solvency ratio
We have briefly explained what the solvency ratio is and its indications. Now, let’s dive into this vital business metric and explain step-by-step how to calculate it. Understanding this part will help you understand how to use the solvency ratio effectively and help you make informed financial decisions.
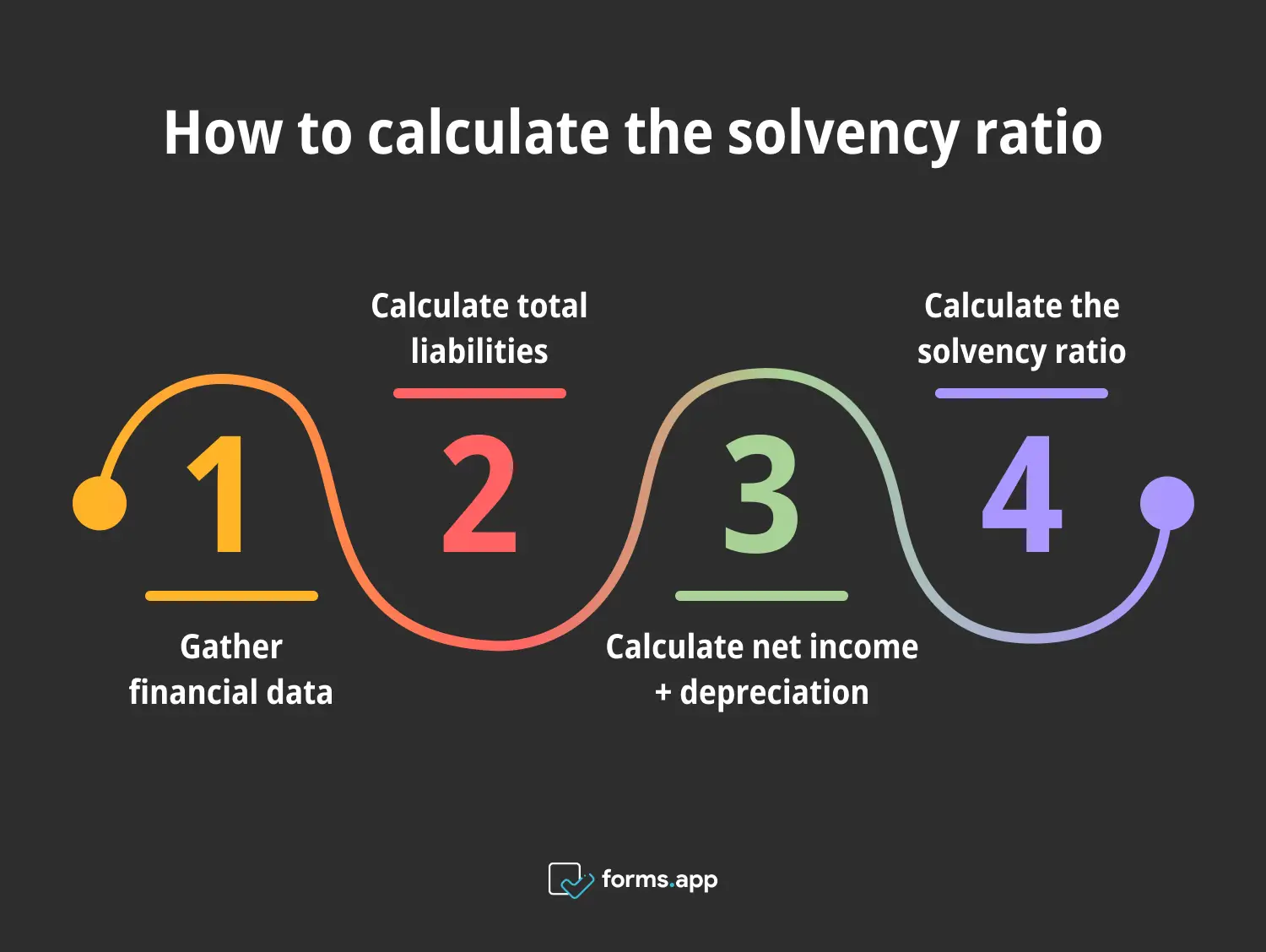
Steps to calculate the solvency ratio
Step 1: Gather financial data
The first step in calculating the solvency ratio is to gather the necessary financial data. This includes the company’s total assets, total liabilities, net income, and depreciation. These figures can be found on your company’s balance sheet and income statement.
It’s important to ensure that the data is accurate and up-to-date. Because the solvency ratio relies on precise financial information, gathering this data will give you the foundation to perform the solvency ratio calculation and assess your company’s long-term financial health.
Step 2: Calculate total liabilities
Determining the company's total liabilities is the next step in calculating the solvency ratio. Total liabilities include all debts and obligations your company owes, both short-term and long-term. You can find this figure on the balance sheet under the liabilities section.
Accurately calculating total liabilities is crucial, as this figure is a key component of the solvency ratio. Once you have the total liabilities, you can proceed to the next step in the calculation process.
Step 3: Calculate net income + depreciation
In this step, you’ll calculate the sum of the company’s net income and depreciation. Net income represents the company’s total earnings after you deduct all expenses from revenue. Depreciation is the reduction in the value of assets over time, and it is added back to net income because it is a non-cash expense.
You can find these figures can be on the financial statements. Adding net income and depreciation together provides the numerator for the solvency ratio calculation. This represents your company’s ability to generate cash flow to cover its debts.
Step 4: Calculate the solvency ratio
Finally, to calculate the solvency ratio, divide the sum of net income and depreciation by the total liabilities. The formula is Solvency Ratio = (Net Income + Depreciation) / Total Liabilities. This ratio will provide a numerical value that indicates your company’s long-term financial health.
A higher solvency ratio shows that the company is in a strong financial position and can meet its long-term debt obligations. On the contrary, a lower ratio may indicate potential financial challenges. Regularly calculating and monitoring the solvency ratio is essential for maintaining your company’s financial stability.
When to use the solvency ratio formula
We have seen the steps on how to effectively calculate the solvency ratio, as well as the different types of it. Now, let’s look at the business contexts and suitable environments in which you can use this formula. Read these “whens” carefully, as your business situations may fall under one of them.
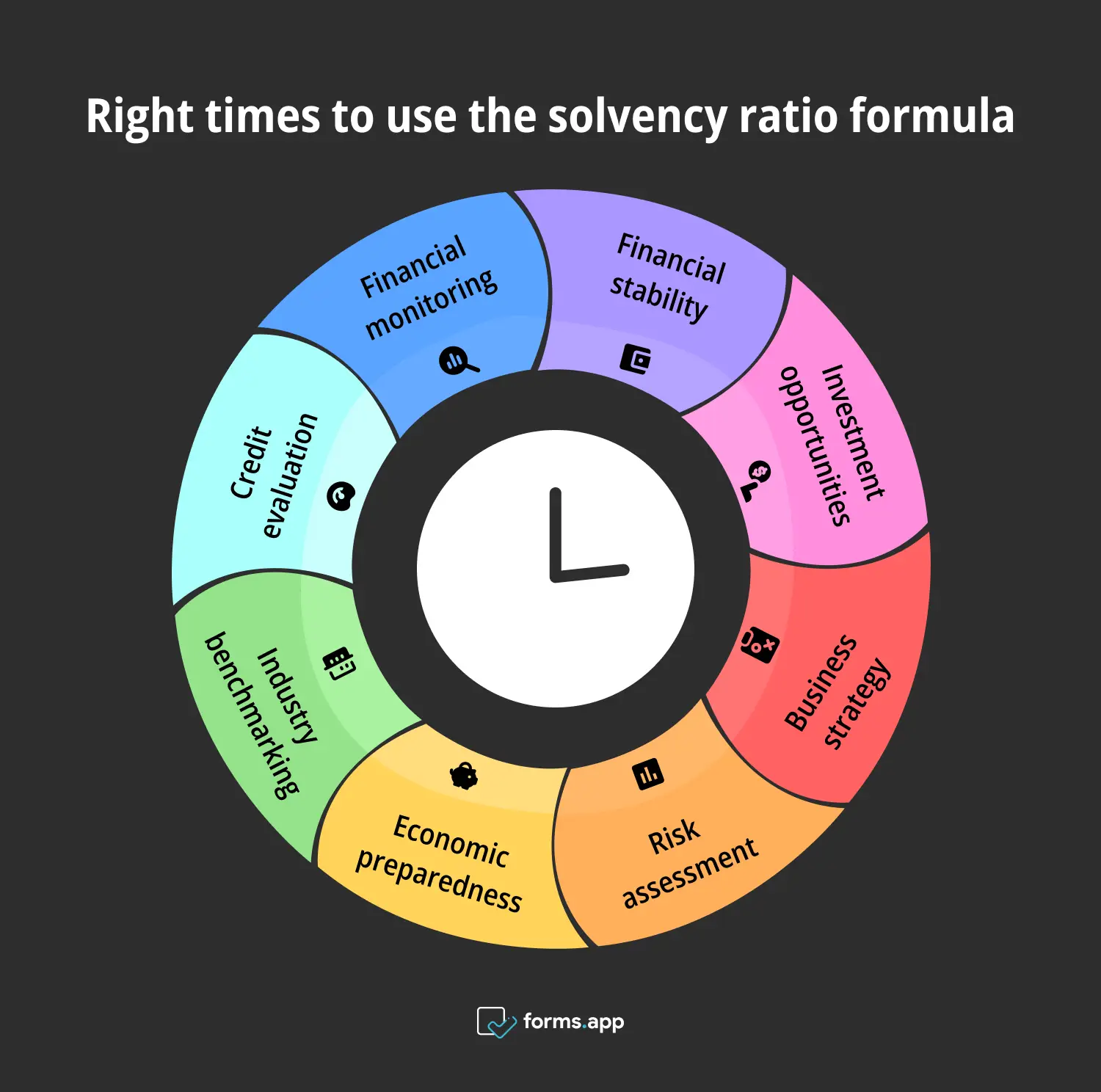
Correct times to use the solvency ratio formula
1- Assessing long-term financial stability
The solvency ratio is a key tool for assessing a company’s long-term financial stability. Unlike short-term metrics like liquidity ratios, the solvency ratio focuses on a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. Businesses and investors use this ratio to evaluate whether your company has enough resources to sustain operations over time.
2- Evaluating investment opportunities
Investors often use the solvency ratio to evaluate potential investment opportunities. A strong solvency ratio suggests that a company is financially stable and capable of weathering economic downturns or unexpected challenges. This stability makes your company a more attractive investment, as it indicates lower financial risk. Investors can compare the solvency ratios of different companies within the same industry.
3- Making strategic business decisions
For business leaders, the solvency ratio is an essential metric for making strategic decisions. Whether considering expansion, mergers, or new projects, understanding the company’s solvency ratio helps ensure that those decisions are financially sound. A high solvency ratio may signal that your company has the financial capacity to take on new initiatives without jeopardizing its long-term stability.
4- Assessing risk before taking on additional debt
Before your company decides to take on additional debt, you should assess its solvency ratio. This ratio helps determine whether your company is already carrying a high debt load relative to its income and assets. If the solvency ratio is low, taking on more debt could increase financial risk and potentially lead to insolvency.
5- Preparing for economic downturns
During economic downturns, your company should have stronger solvency ratios to be better positioned to survive and even thrive. A healthy solvency ratio indicates that your company has the financial resources to continue meeting its debt obligations even in challenging times. This resilience is crucial during periods of economic uncertainty, as it allows your company to maintain operations and avoid financial distress.
6- Benchmarking against industry standards
Comparing your company’s solvency ratio with industry standards is a valuable practice for assessing financial health. Each industry has different levels of acceptable debt and financial risk. Therefore, what creates a good solvency ratio can vary. If you benchmark against your industry peers, you can determine whether your solvency ratio is in line with your competitors.
7- Evaluating creditworthiness
Lenders and creditors use the solvency ratio to evaluate your company’s creditworthiness. A high solvency ratio indicates that your company is in a strong financial position and is less likely to default on its debt obligations. This makes your company a more attractive candidate for loans and other forms of credit. This may result in more favorable terms, such as lower interest rates.
8- Monitoring financial health over time
The solvency ratio is not just a one-time measurement. It is a tool for ongoing financial health monitoring. You need to regularly calculate and track your company’s solvency ratio. You can identify trends and proactively maintain or improve your financial stability. A declining solvency ratio might indicate potential problems, enabling you to take corrective actions before the situation worsens.
3 Examples of solvency ratio in business
We have seen different business contexts for the use of the solvency ratio. Now, let’s look at actual solvency ratio examples in businesses. Here, we will see some well-known famous companies and how their solvency ratios affect their success. If they can do it, you can too!
1- Apple
Apple Inc. is a well-known company with strong financial health. Its solvency ratio reflects this stability. With a significant amount of assets and relatively low debt levels, Apple’s solvency ratio indicates a solid ability to meet its long-term obligations. This strong financial position allows Apple to invest in innovation, expand its product line, and return value to shareholders through dividends and stock buybacks.
2- Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation, a global technology leader, also maintains a robust solvency ratio, highlighting its financial strength. The company’s significant assets and controlled debt levels result in a high solvency ratio. This financial stability allows Microsoft to invest in research and development, acquire new businesses, and enhance its product offerings. Microsoft’s strong solvency ratio also provides confidence to investors and creditors.
3- Coca-cola
The Coca-Cola Company, a leading global beverage manufacturer, is another example of a strong solvency ratio. Despite its extensive global operations, Coca-Cola manages its debt levels effectively. This results in a healthy solvency ratio. This financial strength allows the company to invest in marketing, expand its product portfolio, and maintain a competitive edge in the beverage industry.
Why to calculate the solvency ratio
At every step of the way, we have briefly touched upon the advantages of the solvency ratio and how it contributes towards your business success. Now, to understand them better, let’s see why you should use the solvency ratio in your financial assessments.
🎯 Financial stability indicator: The solvency ratio is crucial to a company’s financial stability. By comparing a company’s total assets to its total liabilities, it provides insight into whether the company can meet its long-term debt obligations.
🎯 Investor confidence: A healthy solvency ratio boosts investor confidence in a company. Investors seek companies that demonstrate financial stability and a strong ability to meet their debt obligations. A high solvency ratio indicates that a company is well-managed and capable of sustaining operations over the long term.
🎯 Improved loan terms: Companies with a strong solvency ratio are more likely to secure favorable loan terms. Lenders assess a company’s solvency ratio to determine the risk of lending money. A high solvency ratio indicates lower financial risk, making lenders more willing to offer loans with lower interest rates and better terms.
🎯 Risk mitigation: The solvency ratio helps businesses mitigate financial risk. Companies can identify potential financial challenges early by regularly assessing their solvency ratio and taking corrective actions. For instance, if the ratio indicates the company is over-leveraged, management can consider reducing debt or restructuring operations to improve financial stability.
🎯 Strategic decision-making: The solvency ratio is key in strategic decision-making. It provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, helping management make informed decisions about investments, expansions, and other long-term strategies. For example, a strong solvency ratio might indicate that the company is in a good position to take on new projects or expand operations.
🎯 Benchmarking performance: The solvency ratio is useful for benchmarking a company’s financial performance against industry peers. Businesses can gauge their relative financial health by comparing the solvency ratios of different companies within the same industry. This benchmarking process helps companies identify areas for improvement and set realistic financial goals.
Liquidity ratios: What is the difference?
Sometimes, businesses may confuse solvency ratios with liquidity ratios. Here, let’s see the difference in the liquidity ratios. Understanding the difference will enable you to select the best formula for your business and achieve positive results in your financial planning.
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity ratios are essential for evaluating a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations. Its key types are Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Cash Ratio. The current ratio measures the capacity to pay off current liabilities using current asses.
The quick ratio excludes inventory to focus on more liquid assets. The third type, the cash ratio, is the strictest version. It compares only cash and cash equivalents to current liabilities. Together, these ratios provide a comprehensive view of a company’s short-term financial health.
Difference between liquidity ratios and solvency ratios
| Aspect | Liquidity Ratios | Solvency Ratios |
| Definition | Refers to a “short-term solvency ratio formula.” | Refers to a “long-term solvency ratio formula.” |
| Purpose | Measures a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations. | Assesses a company’s long-term financial stability and ability to meet long-term debt obligations. |
| Examples | Current ratio, Quick ratio | Debt-to-equity ratio, Interest coverage ratio |
| Focus | Quickly converting assets into cash to cover immediate liabilities. | Overall financial strength and long-term debt repayment capacity. |
| Time horizon | Short-term financial health. | Long-term financial stability. |
| Usefulness | Helps evaluate the company’s ability to handle day-to-day operational expenses and short-term debt. | Provides a broader view of the company’s ability to sustain operations over the long term. |
These ratios focus on your company’s ability to quickly convert assets into cash to cover immediate liabilities. In contrast, solvency ratios assess your company’s long-term financial stability and its ability to meet long-term debt obligations. While liquidity rates concern short-term financial health, solvency ratios provide a broader view of your company’s overall financial strength.
Frequently asked questions about the solvency ratio formula
We have seen every aspect of the solvency ratio, as well as its difference from the liquidity ratio. Now, let’s look at some of the most frequently asked questions about the solvency ratio. By understanding these answers, you will get a clearer comprehension of the subject.
To calculate the solvency ratio, add the company’s net income and depreciation, then divide this sum by the total liabilities. The formula is: Solvency Ratio = (Net Income + Depreciation) / Total Liabilities. This calculation provides insight into the company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. A higher solvency ratio indicates stronger financial health, while a lower ratio may suggest potential difficulties in managing debt.
A solvency ratio of 1.5 indicates that the company has 1.5 times more income and depreciation than its total liabilities. This suggests that the company is in a relatively strong financial position and should be able to meet its long-term debt obligations. However, the ideal solvency ratio can vary depending on the industry, and it’s important to consider other financial metrics when assessing overall financial health.
A good solvency ratio generally ranges between 1.5 and 3.0, depending on the industry. A ratio within this range suggests that the company has a healthy balance between assets and liabilities and is well-positioned to meet its long-term obligations. However, what constitutes a “good” solvency ratio can vary, so it’s important to compare it with industry benchmarks and consider other financial indicators.
The solvency risk ratio is calculated by dividing total debt by total assets. The formula is: Solvency Risk Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets. This ratio provides insight into the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed by debt. A lower solvency risk ratio indicates that a company has more assets than debt, suggesting lower financial risk. Conversely, a higher ratio may indicate greater reliance on debt, which could increase financial risk.
Insurance businesses use the solvency ratio to assess the insurance parties’ financial health and ability to meet future claims. This solvency ratio formula (insurance) compares an insurer’s net assets to its total liabilities, helping to determine if the company has enough resources to cover its long-term liabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the solvency ratio is crucial for assessing your company’s long-term financial health. This ratio also provides valuable insights into your company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations and maintain financial stability. By regularly monitoring the solvency ratio, you can make informed decisions about debt management, investments, and strategic planning. Investors and creditors also rely on this ratio to make their evaluations.
This article covers the solvency ratio, when to use it, why it is used, and its different types. We have also seen how to calculate it, provided examples from well-known companies, and discussed its differences from the liquidity ratio. Last but not least, we have answered some frequently asked questions. Use this formula in your business today!
Fatih is a content writer at forms.app and a translator specializing in many text domains, including medical, legal, and technical. He loves studying foreign languages. Fatih especially likes to create content about program management, organizational models, and planning tools.
- What is the solvency ratio?
- 5 Solvency ratio types
- How to calculate the solvency ratio
- When to use the solvency ratio formula
- 3 Examples of solvency ratio in business
- Why to calculate the solvency ratio
- Liquidity ratios: What is the difference?
- Frequently asked questions about the solvency ratio formula
- Conclusion