In statistical analysis, sampling is the process by which researchers select a predetermined number of observations from a larger population. Choosing a method is an essential step for researchers. Depending on whether the study is qualitative or quantitative and the results they hope to obtain, researchers employ a variety of sampling techniques.
One of the essential types of sampling is probability sampling. Knowing when to apply a specific sampling technique can be helpful when conducting your research or evaluating a study’s findings. This article will explain the definition of probability sampling, its types, and examples in all detail.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling is the process of selecting a sample from a population when the selection is based on the randomization principle, also known as chance or random selection. Each study subject will have the same chance of being chosen through probability sampling. To apply the study's findings to a larger population, probability sampling’s objective is to obtain a sample representative of the larger population.
Probability sampling is randomly selecting a small sample of people from a large population and then predicting that all their responses will represent the entire population. The essential prerequisite for probability sampling is that each person in your population has an equal and known chance of being chosen.
Types of probability sampling
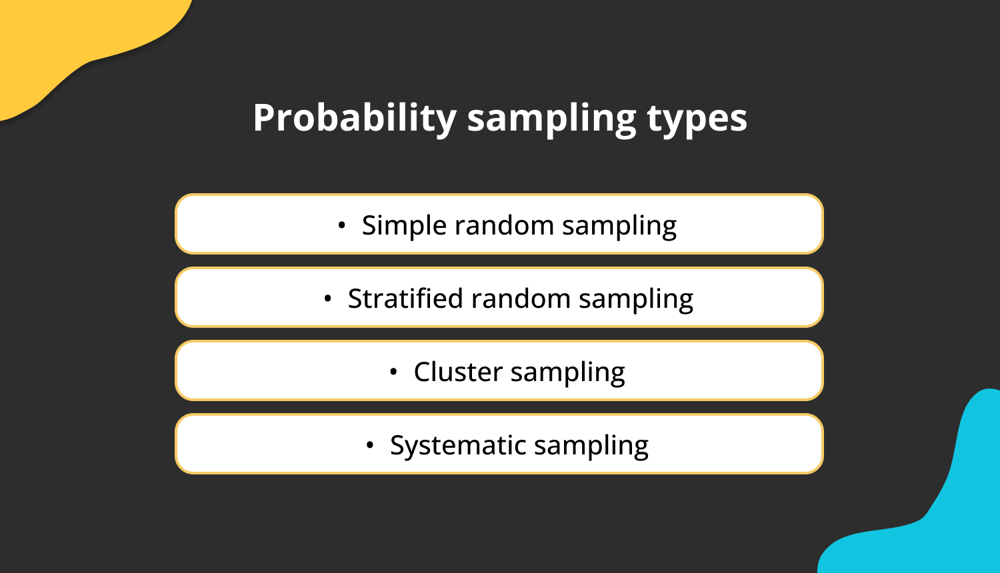
Probability sampling types
When selecting a probability sample design, the purpose is to minimize the sampling error of the estimates for the most significant survey variables while minimizing the survey’s time and cost. The characteristics of the survey frame, for example, can affect that decision due to operational constraints. Here are the probability sampling types:
- Simple random sampling: Each sampling unit within a population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample in simple random sampling. As a result, there is an equal chance of choosing any potential sample. You must list every unit in the survey population to select a simple random sample. This method is helpful when the population is diverse, and you want to ensure that the sample represents various subgroups.
- Stratified random sampling: A sample is randomly chosen from one or more strata or population subgroups. Each subgroup is distinguished based on a shared trait, like gender, age, or religion. By doing this, you can ensure that your sample population adequately represents each subgroup. Stratified random sampling is helpful when the population is heterogeneous.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is the process of dividing the target population into groups. The sample is then drawn from one of these groups at random. When researching sizeable, dispersed populations, cluster sampling is a helpful strategy. It usually involves already-existing groups that share some characteristics. This method can benefit a population spread over a large area.
- Systematic sampling: When using systematic sampling, units are chosen at regular intervals beginning at a random point, drawing a random sample from the target population. This method involves picking a random starting point and picking every nth person in the population.
You should divide your sampling frame into several intervals before beginning your systematic sample. These are calculated by dividing the population size by the desired sample size. Then, using simple random sampling, pick one unit from the first interval. The position of the unit chosen in the first interval determines the selection of the following units from other breaks.
Probability sampling vs. nonprobability sampling: What is the difference?
Probability sampling and non-probability sampling are the two main subcategories of sampling techniques. In probability sampling, each participant has a fixed, known chance of being a part of the sample. In nonprobability sampling, there is no set probability that any given person will be a part of the sample.
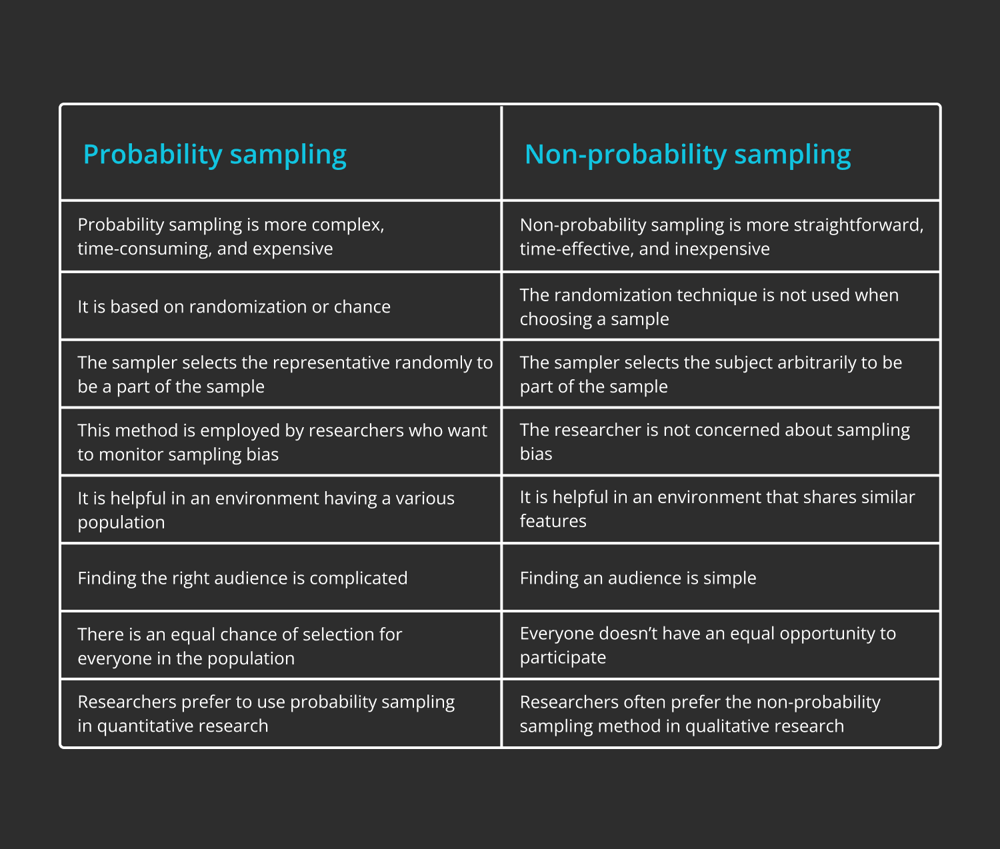
Probability sampling vs. nonprobability sampling
When to use probability sampling?
Probability sampling is the best method for quantitative studies when using statistical analysis to make generalizations about a large population. This sampling method can be used by researchers to gather representative data when it would be too difficult or expensive to survey the entire population. Here are some cases to use this sampling method:
- When the population is diverse: In most cases, populations are diverse. A sample that accurately captures the diversity of the population can be made by researchers using probability sampling. Researchers widely prefer this method because it enables them to produce samples that accurately reflect the population.
Let’s say you want to know which country Italian students prefer for higher education. Probability sampling allows the selection of a sample that closely represents students’ gender, socio-economic backgrounds, and ambitions among the student population.
- When you want to minimize the sampling bias: Sampling bias happens when some population units are more likely to be selected than others. An inaccurate representation of the population is the result. With probability sampling, each population unit has an equal chance of being chosen for the sample because the units are selected at random. Probability sampling produces more accurate results because it offers a fair population representation.
- To produce a reliable sample: Probability sampling aids in creating a precise population sample for researchers. If the sample is accurate, researchers can confidently draw conclusions about the larger population using tried and true statistical methods. Researchers use proven statistical techniques to create a precise sample size and collect data with high definition.
Advantages and disadvantages of probability sampling
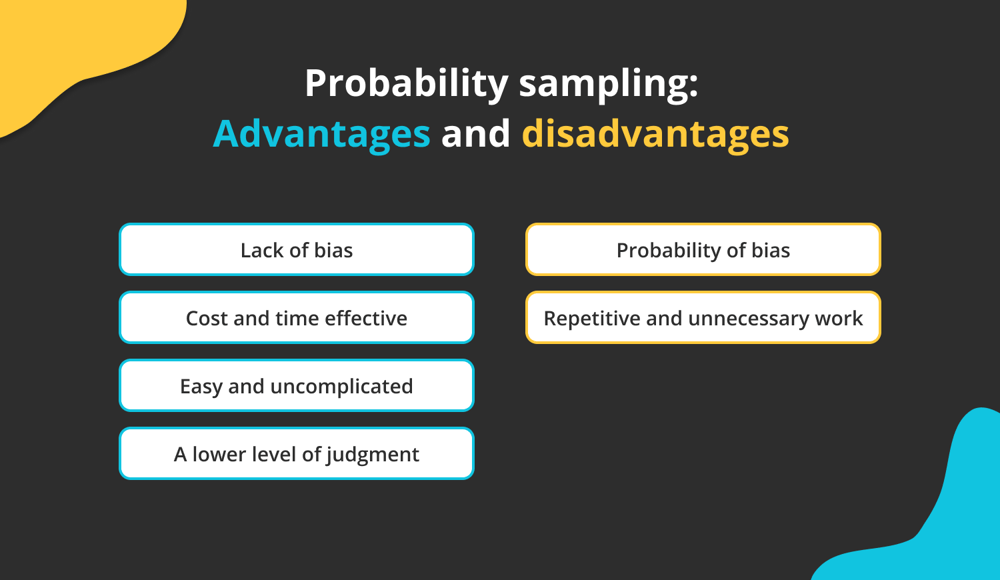
Probability sampling: Advantages and disadvantages
Each probability sampling technique has different benefits and drawbacks. This sampling reduces the possibility of systematic bias. This ensures your results represent the population and lowers the probability of overrepresentation. You can validate your results using statistical methods like confidence intervals and margins of error.
Advantages of probability sampling:
- Lack of bias: With this sampling, systematic errors, and sampling bias are less likely to affect your research population. Any evidence of bias should be removed by probability sampling. The vast population group’s members all have an equal chance of being chosen because the individuals who make up the smaller subgroups of the more significant number are chosen randomly. Most of the time, this produces a balanced subset with the best chance of accurately representing the larger group.
- Cost and time effective: The researcher can save time and money using this data collection method. By first giving the test numbers, this technique enables the selection of a larger sample by randomly selecting data from a large sample.
- Easy and uncomplicated: Since probability sampling is a simple sampling method, it doesn’t require a complicated procedure. It is a quick and efficient technique. Thus, the time saved can be applied to data analysis and conclusion-making.
- A lower level of judgment: Using a random trend when allocating the number to a population item makes the probability sampling procedure more effective and reliable. Highly reliable data are produced by probability sampling.
Disadvantages of probability sampling:
- Probability of bias: Although sampling bias is less likely to happen with this sampling method, it is still possible. The representation of the entire population is skewed if your sample isn’t wide enough.
- Repetitive and unnecessary work: Due to the repetitive tasks necessary to distribute the numbers and gather the data, there is a chance that the surveyor will grow bored, which would reduce the system's effectiveness. Data quality may be impacted if the researcher selects similar research variables.
Conclusion
In conclusion, probability sampling is a statistical analysis technique that ensures a representative sample is chosen from a large population. This sampling method uses randomization as a criterion for selecting a sample size. In probability sampling, each research unit has an equal chance of being selected.
Probability sampling predicts that all of the responses from the randomly chosen small group of individuals (the sample) from a large population will represent the entire population. There are different types of probability sampling. You can select one of them which is appropriate to your study. Besides its disadvantages, probability sampling has many valuable advantages. From this article, you learned the definition of probability sampling, its types, and examples so that you can select and use probability sampling methods in your study any more.
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications