You know you're not talking to your friend like you're talking to a grocery store cashier, or communication with your family is different from communication with strangers. The field of discourse is interested in these situations as context and human relations.
The language you use carries traces of you and reflects your identity, but this process of language use mostly manifests itself subconsciously. It is at this point that discourse analysis lends you a helping hand to explore the world of discourses.
What is discourse analysis?
Discourse analysis (DA) is a type of analysis that examines how language is used in a social context using a variety of research methods.
People use different languages and speak according to different vocabularies in different social environments. This not only constructs discourse but also shapes culture by regulating social relations. Therefore, discourse analysis does not only examine sentences or expressions; it also tries to describe the structural process of language and language use.
Discourse analysis types
Discourse analysis includes different methods in terms of focusing on communication and language use. To share the most common of these with you:
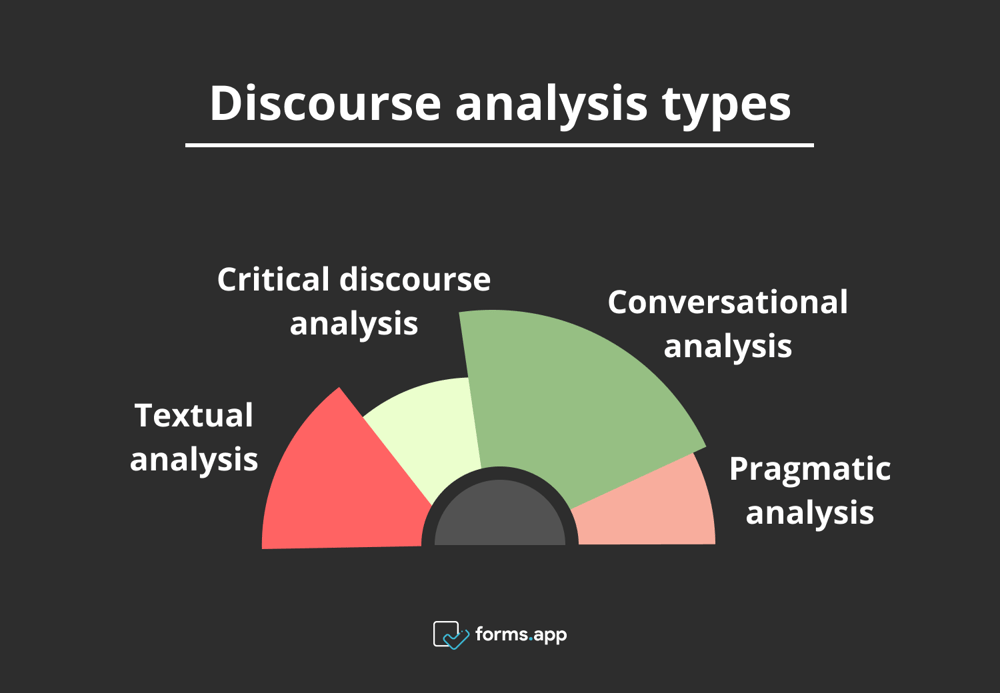
Types of discourse analysis
Textual analysis
Textual analysis examines the written part of the discourse. Although it is generally used to describe the linguistic features of written texts, you can also examine the transcript of any conversation. With this method, researchers can reveal word choices, style of expression, use of expressions and idioms, formal or informal language, and cultural reflections in any text.
Critical discourse analysis (CDA)
The focus of critical discourse analysis is the language usage in the construction of power relations. They are interested in the reflection of social order in language and what can be done to understand these social variables. Examining the language usage of teachers toward students, bosses toward their employees, and politicians toward the public can be given as examples of this.
Conversational analysis
This analysis studies daily conversations. Many factors of speech are taken into consideration. For example, what is your speaking and listening frequency, how much body language do you use, or how much eye contact do you make? All of these are important factors that determine the course of communication and the construction of social relations.
Pragmatic analysis
Pragmatics, as a branch of linguistics, is the study of language in context. Rather than examining words simply, their meanings and messages in the real world are examined along with their dimensions. For example, saying someone's name while getting angry and shouting someone's name with joy are two situations that have the same meaning in the literal sense of the word but have different consequences in the pragmatic sense.
How to use discourse analysis
There are many methods by which you can perform discourse analysis. Still, as in any analysis, the analysis has two stages: data collection, that is, the initial stage, and data evaluation, that is, the analysis stage.
Initial Stages
First of all, the purpose and scope of the research are determined. This is the basis for the data to be collected and the methodologies to be chosen. If your foundation is strong, the structure you build on will also be strong.
You should find the source that best suits your research question. Social media posts, user comments, news articles, scientific articles, interviews, or surveys are well-known qualitative data sources. But again, these options should not be chosen randomly. Not every social media or newspaper is the same and may not fit your goals for your research. Factors such as who uses these environments and texts also need to be examined.
Finally, make the data you have collected ready for analysis. If you are going to perform your analysis on a computer, if your data is a hard copy, you will need to convert it to a soft copy.
Analysis Stages
Know your data. Data is far from being simple; there are many social, cultural and historical factors in its background. This changes the use, choice, source and target of language.
Analyze the structure of the text. Outline the text, and identify key concepts. Sort out the elements that make up the meaning and start coding. For this, you need to read the text well and rearrange it so that it is not overlooked.
Now that everything is ready, all that remains is to understand the discourse expressions. Analysis is made by taking into account many features such as the accuracy, consistency, style, tone, etc. of an expression. Discourse analysis is completed by determining the general characteristics and situational structure of the speech. What follows is post-analysis and enters the interpretation part.
When to use the discourse analysis
Discourse analysis may have different needs depending on which research field you are in. Because there are many different fields, such as linguistics, sociology, psychology, and education. But in general, if you ask when to use a discourse analysis, the following can be said:
- To understand how language reveals power relations
- To understand the impact of language in creating social identity
- To examine the cultural transmission of language
- To describe the construction of language and the foundations of this construction
- To better understand groups such as customers, employees, students, etc., by analyzing their language usage
- To reveal the purposes of different language usages
Approaches to discourse analysis
Discourse analysis can be examined as two main methods and their subbranches. The first method deals with language use, and the second one deals with socio-cultural studies.
- Structuralism: As its name suggests, it is an approach that helps examine the structure and form of the language in a text. Examines the text and describes the language in areas such as grammar rules, syntax, and semantics.
- Sociolinguistics: It deals with the social dimension of language. It is generally preferred by researchers who want to study topics such as power hierarchy, social norms, taboos, and identity.
Example of discourse analysis
For example, a politician is speaking at an election rally. In the speech, he promises to his voters about the economy. These promises include tax regulations, factory openings, and job creation. The politician speaks in a persuasive language, using rhetoric rather than simple expressions. He very often presents counterexamples and criticizes his opponents.
Now, if you want to perform a discourse analysis on this political speech:
- Select one of his speeches and transcript it in detail, describe his tone, stress, and pause.
- Examine word choices and sentence structures. For example, he may have used too many interrogation sentences and overly emphasized development and future themed words.
- Then, try to understand the context, taking into account the politician's views, the ideology of the party he belongs to, and the target audience.
- If you want to examine how the politician establishes power relations with language, apart from his use of language, you can look at his linguistic attitude about himself and his opponents.
- Ultimately, you can interpret the politician's communication and the effectiveness of his speeches and make inferences about the public's opinion of him or the impact of his speeches on the outcome of the election.
Advantages of discourse analysis
The benefits of discourse analysis may vary depending on the purpose you use it for, but in general terms, the benefits are as follows:
- It supports a wide range of qualitative analyses, such as content analysis and textual analysis
- It reveals the underlying meanings of words, phrases, and sentences
- It can provide an interdisciplinary working environment with many specializations in humanities and social sciences
- It allows you to understand power dynamics in cultural, social, and economic dimensions
- It can reveal themes and patterns and the relationships between them in any discourse or text
Frequently asked questions about discourse analysis.
You can take a look at the FAQ below to read answers to questions directly related to discourse analysis.
For example, examining how the comments on an election bill by the right and left parties are reflected on television screens or news headlines is a discourse analysis.
The four main types of discourse analysis in any qualitative research are textual analysis, conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and pragmatic analysis.
Discourse analysis is evaluated within various theoretical frameworks. These include structuralism, sociolinguistic, critical, and pragmatic theories. Structuralism focuses on describing structures in language and language use. Sociolinguistics examines the social dimension of language and interpersonal relationships.
Critical theory, on the other hand, reveals the power hierarchy and social inequalities in the discourse. Finally, pragmatics aims to explore the role of context and experiences in ensuring or implementing communication. As a result, these theories help understand and simplify the complex structure of communication.
Identity, context, and power elements are the major concepts of discourse analysis.
- Identity: What you say is your identity. When commenting on a person, you are primarily interested in what they say and how they say it. That's why discourse analysis is used to examine the identity of individuals and groups.
- Context: When, where, with whom, why, and in what sense the language is used creates the context. This brings with it the difficulty of examining the sentences simply. Discourse analysis helps this by examining the importance and function of the context.
- Power: Another dimension of discourse is social power relations. It is a fact that people use different languages depending on some social factors such as age, position, and socio-economic status. Discourse analysis helps describe and understand this social attitude.
Discourse analysis is a topic that became popular in linguistics, especially in the 1950s by Zellig Harris. It aims to reveal the secrets of human language by describing the scheme of speech. It also serves as a bridge between social sciences as an interdisciplinary field of study.
The main purpose of discourse analysis is to systematically examine and understand deep and surface language usage structures. It examines the social structures of communication and speech within contexts and relationships of meanings. It tries to understand what effect the features of language have on people and cultures.
Final words
This article has been prepared to provide an introduction to discourse analysis and detailed information about the subject. For this purpose, first of all, a definition of discourse analysis was provided in the introduction. Then, the types you can use in research were mentioned.
Afterward, the method of using discourse analysis was explained step by step. When you may need it is explained in another topic. Two main approaches were then presented. Finally, examples of discourse analysis and advantages were explained. Thus, the article touched upon many useful points and made you informed about discourse analysis in research.
Contributors
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications