Businesses regularly look for ways to analyze their potential to thrive strategically in the market. Either by increasing their existing advantages or benefiting from the opportunities, the goal is always to get better and eventually have a competitive position. This need to seek a new strategic plan to bring out the ‘superpowers’ leads businesses to use analysis tools.
Like SWOT analysis, the VRIO model serves as another strategic framework for organizations to find what makes them unique and valuable for a competitive advantage. In this article, we will look at the VRIO framework, how it works, its pros and cons, and when best to use it.
First thing first: What is the VRIO framework?
VRIO framework is a type of analysis that organizations use to examine the available resources, advantages, and capabilities internally.
This framework helps businesses identify their strengths for a sustainable, long-term competitive advantage.
The VRIO framework
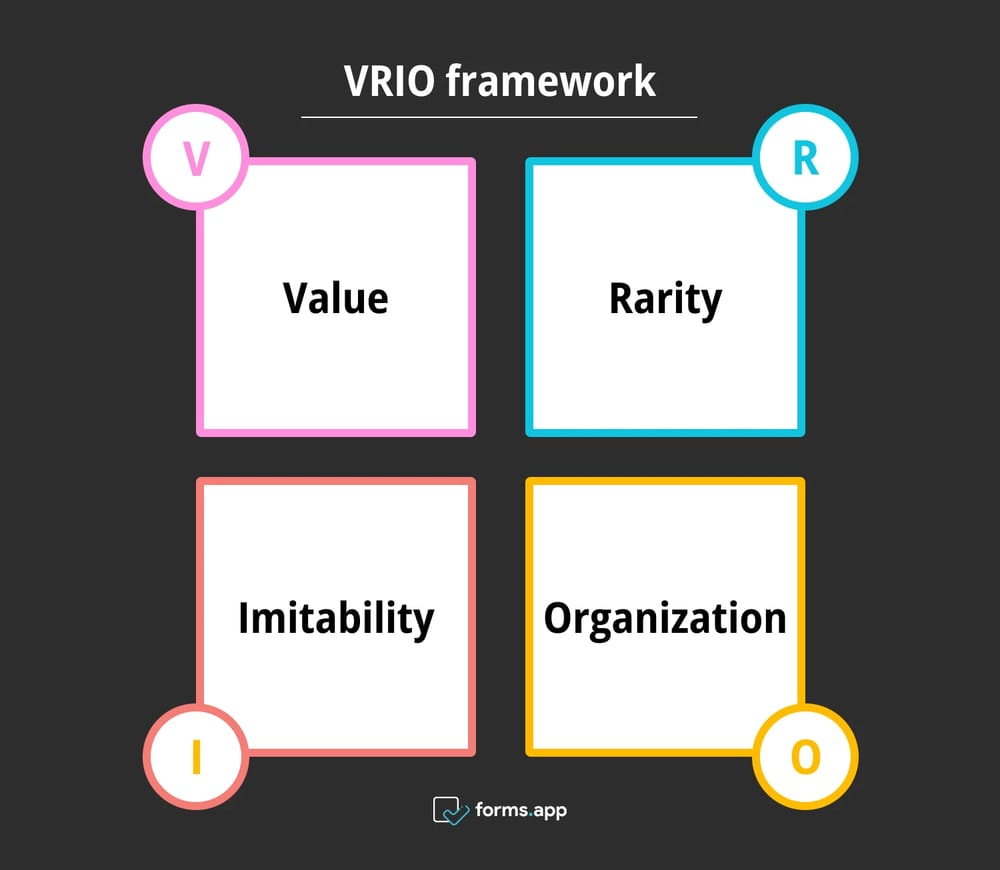
VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organisation, which forms the VRIO model for internal analysis. VRIO framework suggests that for a business to have a competitive advantage, one of the resources must be valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized. Let’s have a look at these elements individually:
VRIO framework
1. Value
Value refers to the valuable resources of a business that add value to the company. A valuable resource creates pivotal benefits and advantages for the business that represent its strengths, just like an invaluable resource creates a competitive disadvantage. To achieve competitive parity, a resource should be valuable. You can consider if the resource benefits your target audience and aligns with your business strategy and objectives.
2. Rarity
Rarity is about the rare resources that a business possesses. If your resource is valuable and unique, it can give you a competitive advantage. However, it comes with pros and cons. If a resource is uncommon, it can also be short-lived, as the competitors would not miss the chance of imitating it, making it a temporary competitive advantage. Consider whether competitors lack your rare resource and how unique it is in your industry.
3. Imitability
Imitability refers to a resource that is difficult to imitate by other companies. When your resource or capability is inimitable and organized, it becomes the strength of the company. However, if it is not as unique or rare, it could be easily copied by others, which makes it imitable. This creates a temporary competitive advantage for the business. Make sure to have a resource that requires specialized knowledge or technology, which makes it unique only to you.
4. Organization
Organization is about how organized your company is with its resources. When you combine all the big fours, including value, rarity, inimitability, and organization, it creates sustainability and a long-term competitive advantage for the company. An organized company also means it can exploit the resources and capability for strategic management. Think about whether your company uses strategic planning processes effectively and efficiently.
Examples of the VRIO framework
As we covered above, the VRIO framework works the most efficiently only when four of its elements are used all together to keep the standards, efficiency, and effectiveness safe and secure for the competitive advantage. Many well-known brands can manage using the VRIO framework adeptly, including Coca-Cola, Google, Apple, and many other popular brands. Let’s have a look at a couple of VRIO formulation examples.
A. Coca-Cola
There is no doubt that Coca-Cola is a famously successful company that has managed to keep its VRIO at high standards at all times. Being one of the most recognized and valuable companies in the world, Coca-Cola created a strong brand name and a competitive advantage for decades.
Value: To create a valuable company, Coca-Cola used smart advertising campaigns and marketing strategies that made the brand and the product precious.
Rarity: As we already know, Coca-Cola has a secret formula that is completely unique to them only. It is kept so well-secured, creating a significant competitive advantage for the brand.
Imitability: While there are similar companies that try to replicate Coca-Cola’s brand and products, it is difficult for them to create the exact same taste as the secret formula, which makes it impossible to create an identical product.
Organization: Coca-Cola has a solid organizational framework with its famous and successful marketing campaigns. Also, with its distribution network, it gains a competitive advantage in the sector.
B. Apple Inc.
Apple is another highly popular company that has enormously succeeded in the tech world and beyond. With its user-friendly features, sleek design, and high-quality products, it has created a strong name in the sector.
Value: Apple’s unique design, the ecosystem that fosters interconnectedness, and user-friendly functions make it a valuable product in the market.
Rarity: Designers and engineers working for Apple are some of the most talented and skillful in the world. The company creates products using an innovative approach that is unique to the company, which results in signature products.
Imitability: Apple’s products are difficult to replicate because of years of work and research put into the brand’s development and design. Even though the competitors try to copy the product, they cannot copy the user-friendliness and quality.
Organization: Apple is a big company that focuses on constant innovation and development, which takes a strong organizational structure. This approach helps to create products that are highly in demand by the customers.
VRIO framework example is used by many other well-known companies in the world, similar to the SWOT analysis examining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. No matter the size of your organization, the VRIO framework can help you identify and bring out the strengths and advantages of your resources.
Below, you can see an example of a VRIO framework template that ticks the boxes.
VRIO framework example
Advantages & Disadvantages of the VRIO framework
Just like any other analysis framework, the VRIO model also has its pros and cons. Although it is one of the most popular frameworks to leverage the internal resources and capabilities of an organization, it does have its own limitations, which might need some additional support. Let’s have a look at these advantages and disadvantages together.
Advantages:
➕ The VRIO framework helps identify the core strengths of a company that can be vital for a long-term competitive advantage.
➕With its structured method, it evaluates the internal resources and capabilities to gain a competitive position in the market.
➕The framework helps companies gain insight into the significance of their resources that outshine their competitors.
➕VRIO helps optimize resource allocation by channeling investments into resources and capabilities.
➕It enhances understanding of an organization’s competitive position and the opportunities to improve it.
Disadvantages:
➖ The VRIO framework can provide an oversimplified analysis by solely focusing on the internal factors and overlooking the external ones.
➖The analysis can be too subjective depending on who is conducting it.
➖It provides a quick view of a business's resources and capabilities only for a particular time period and fails to capture dynamic market changes.
➖It focuses too much on the internal factors that it overlooks the external factors such as market trends and changes or customer preferences that could have a big impact on the business and strategy.
➖Performing a VRIO analysis can be time-consuming in a fast-paced business environment.
When to use the VRIO framework
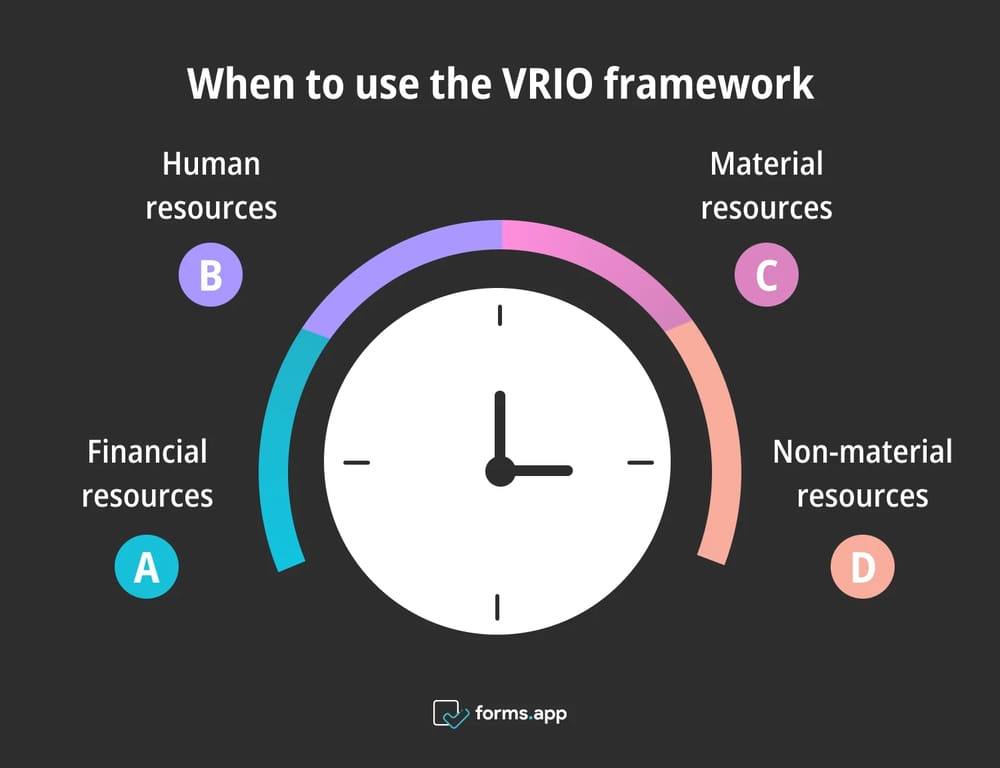
To use the VRIO framework and conduct an effective analysis, you will first need to identify your tangible and intangible resources. These can be financial resources, human resources, material resources, and non-material resources. Let’s have a look at what these may include.
Correct times to use the VRIO framework
1. Financial resources:
Tangible: Cash reserves, investment capital, lines of credit
Intangible: Financial reputation
2. Human resources:
Tangible: Employees, management team, specialized workforce
Intangible: Skills, expertise, company culture
3. Material resources:
Tangible: Inventory, machinery, raw materials
Intangible: Patents, production processes
4. Non-material resources:
Tangible: Brand logos, packaging
Intangible: Brand reputation, customer loyalty, intellectual property
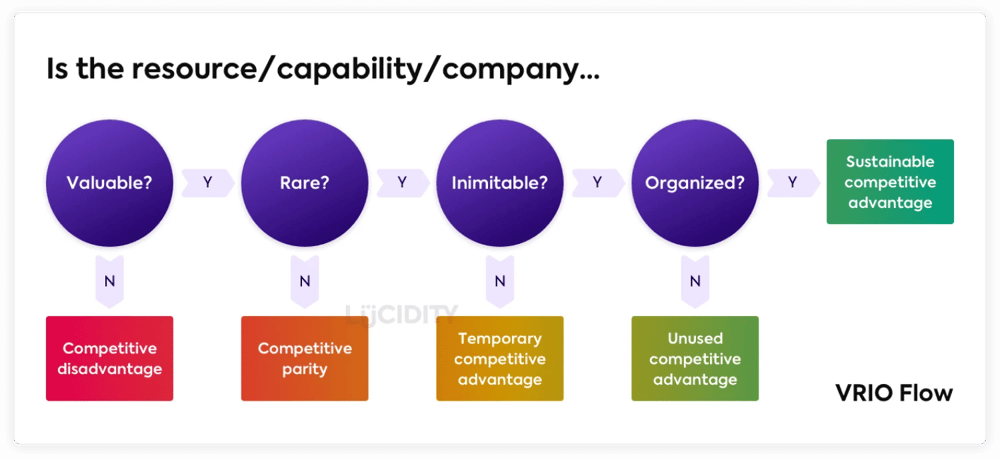
Once you have identified your resources, evaluate each resource through the VRIO framework and categorize them based on their characteristics. You can classify each resource into one of the categories, which include competitive parity, temporary competitive advantage, unused competitive advantage, or long-term competitive advantage.
Categorizing your resources into groups will give you a clear picture of your competitive advantages and whether they are short or long-term advantages. The analysis of each resource can then follow this. This analysis aims to find resources that can be elevated into a higher category.
For example, an organization might possess a valuable and rare resource, like a unique invention. According to the VRIO analysis, this invention is classified as a temporary competitive advantage, which may be because a competitor can easily replicate it. Upon further analysis, they identify an opportunity to elevate this temporary advantage through obtaining a patent. As a result, this resource would move into a higher, more valuable category.
Frequently asked questions about the VRIO Framework
So far, we have already explained the VRIO framework with examples of each of its elements. Yet, you might still have some questions related to this popular analysis model. Below, you can find answers to some of the most common questions.
When both analysis tools are used strategically to identify and analyze the organization’s potential for success, these analysis types focus on different parts of the business. VRIO’s primary focus is the internal resources and factors to maintain a competitive advantage. SWOT, on the other hand, serves a broader analysis by identifying both internal and external elements.
The VRIO framework was first invented by Jay B Barney in 1991, and he originally called it VRIN.
It is expected to use the VRIO analysis at least once a year to achieve a consistent strategic route and stay competitive.
Final words
In this article, we talked about the VRIO framework and its four elements, including Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organisation, how big companies use it to keep a competitive advantage in the market, the advantages and disadvantages of the VRIO analysis, and when to use this model.
Unlike the SWOT analysis, VRIO solely focuses on the internal factors that affect a business’ growth and competitive position. It is a tool to help you identify and analyze your resources and capabilities to develop and sustain a competitive advantage in the sector.
forms.app, your free form builder
- Unlimited views
- Unlimited questions
- Unlimited notifications