Understanding everyone is challenging in a world where people have different narratives and experiences. People's comments and stories are different from mathematics in nature, and naturally, it is necessary to make sense of them with a different method. This method is qualitative data analysis.
This article will discuss data analysis in qualitative research, with examples showing when and how to use it and its types. In the last section, there is also the FAQ section, where you can find answers to the questions you have in mind. You can start reading the article without further ado.
What is the qualitative data analysis?

Qualitative data analysis is the research method for any data set that doesn't have numerical data.
It is used to make sense of the meanings and patterns of various texts, images, videos, and audio. Examining people's feelings, experiences, and thoughts is at the forefront.
Companies constantly use this analysis to examine qualitative data and improve themselves. Qualitative research design starts with collecting the necessary data from different channels. The necessary data can be obtained from interviews, messages, comments, petitions, complaints, support requests, etc.
When to use qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is a valid and effective type of analysis that you can use whenever you need it. Of course, sometimes companies need this more. You can understand what these times of need generally are by looking at the examples below:
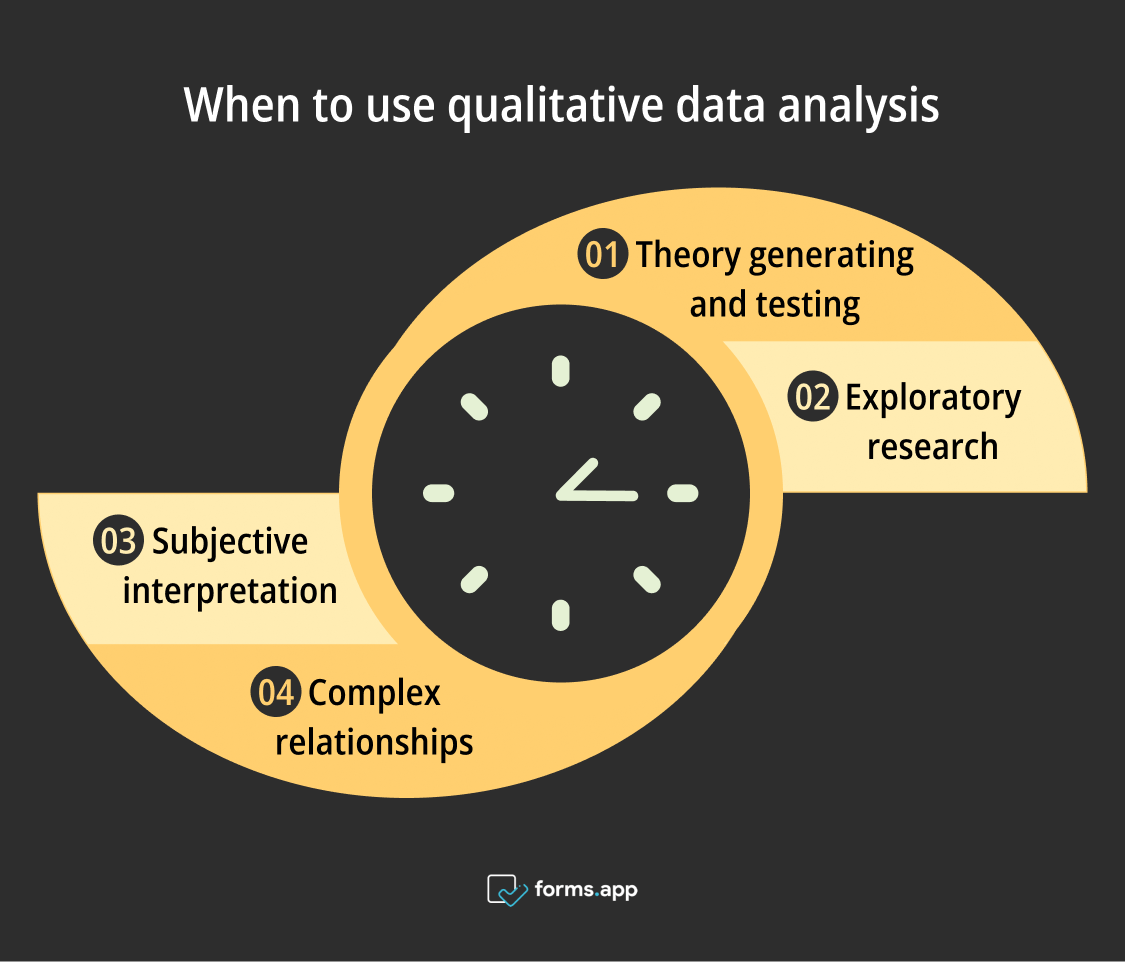
Right times to use qualitative analysis
⏰Theory generating and testing
Qualitative analysis provides the ideal working environment for testing any of your hypotheses. With the reports it provides, you can understand the framework and concepts of the subject you are focusing on in more detail. Or you can ask it to present you with any hypotheses using programs supported by artificial intelligence.
⏰Exploratory research
This analysis can be used in the early stages of any research or project. In general terms, it creates an environment for determining the variables and taking steps towards more advanced studies.
⏰Subjective interpretation
You use this analysis to understand people's subjective opinions. It interprets people's experiences by examining them with different methods.
⏰Complex relationships
Unlike quantitative data, discovering and measuring qualitative data is a difficult and complex task. This analysis collects data from subjective texts and reveals complex relationships.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative data is subject to different interpretations due to its nature and content. It may be necessary to examine your data using different methods that are in line with the purpose of your research process. These methods are:

Methods of qualitative analysis methods
1. Content analysis: It is a method of systematically examining any visual, audio, or written text. It identifies patterns and meaningful parts in content. Then, the specific content of the data is revealed.
2. Thematic analysis: It analyzes the theme in qualitative data and turns it into actionable insight. It reveals the main theme by focusing on particularly recurring images, ideas, and concepts in any text.
3. Discourse analysis: Discourse analysis is the study of language usage from many different dimensions. It enables a deep understanding of a narrator's oratory skills and identity and identifies the meanings and relationships in their speech.
4. Narrative analysis: It is a method of examining how people describe an event, their own views, and how they construct meaning. Businesses conduct this analysis to learn about customers' feedback and opinions about their brands and to improve themselves.
Types of qualitative analysis
Analysis of qualitative data is one of the cornerstones of many businesses and organizations. It continues to be preferred both because it is a wide-ranging research field and because of the solutions it offers. That's why different types of analysis are often used to support it. But, here, only various kinds of qualitative data will be presented to you:
Surveys, interviews, and focus groups
These are the most basic data collection methods. Especially thanks to the internet, it is possible to reach large audiences through surveys. Interviews, on the other hand, are more like one-on-one conversations and are one of the frequently used methods to learn people's opinions.
Focus groups, on the other hand, are where members of a certain group interact with each other to evaluate and discuss a topic. The data that emerges as a result of these discussions has the value of qualitative data.
Textual, visual, and auditory data
In this qualitative type, you benefit from various sources. These may again be interviews, website comments, social media posts, speeches, etc. It can be documents and narratives. Examining these data formats is a detailed task. Because the language and visuals used by the speakers contain subjective narratives, mastery of analysis will be required to make sense of these details.
Observations
This method is more skillful than the other two methods. The researchers need to make sense of the interactions and behaviors happening around themselves with their observation skills. Then, they need to bring their field notes to a consistency that can be analyzed and separated into datasets for the qualitative study.
Examples of qualitative analysis
Qualitative data is very rich in examples. It is easy to understand because it is widely experienced in everyone's life. It may be easy to understand, but it may not be easy to make sense of it. For now, only general qualitative data analysis examples will be given. These can be considered the first steps of qualitative data analysis.
- I did not like the features of this product in general.
- Every time I use this product, it irritates my skin.
- The simplicity and usefulness of this product is amazing!
- I was hesitant at first when buying it, but then I became addicted to it.
- You cannot sell this product with this kind of color and design. It's too bad!
Case analysis
A local patisserie wants to expand its business and take better care of its customers. For this, qualitative data analysis was decided. A survey is being prepared with open-ended questions where customers can describe their experiences. Customers are asked their opinions about the services offered by the patisserie, employees, menus, pricing, etc.
There are common patterns and themes in the data collected from these surveys. In light of these patterns, the patisserie can make new decisions about its business; for example, it can increase the menu diversity or reduce the prices of the products. Ultimately, the patisserie ensures customer satisfaction with this analysis.
Qualitative data analysis vs. Quantitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis and quantitative data analysis are two very different types of analysis in terms of research methods and the data they deal with. The main reason for this is that quantitative data contains numerical and objective realities, while qualitative data contains non-numerical and subjective realities. Apart from this, you can take a look at the differences in the list:
- Qual. D.A. deals with texts, images, video, and audio, but Quan. D.A. deals with formulas, counts, and measurements.
- Qual. D.A. uses methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, but Quan. D.A. uses methods such as experiments, surveys, and scales.
- The analysis techniques Qual. D.A. uses mostly thematic, content, discourse, and narrative analysis, but Quan. D.A. uses analysis techniques such as regression, correlation, and descriptive analysis.
- Qual. Data results may vary from sample to sample and are often based on generally accepted facts. However, Quan. D.A. can be applied to wider audiences, and its measurements are more objective.
Frequently asked questions about the qualitative analysis
This article explained qualitative data analysis in general terms. However, frequently asked questions can help you to get more detailed information and read the parts you are more curious about.
Les plus connues sont l'analyse thématique, l'analyse du discours et l'analyse du contenu. Dans le cadre de la recherche, il est possible de mener différents entretiens et d'examiner le retour d'information, les commentaires et les critiques des utilisateurs. En fonction de l'objectif de votre recherche, vous pouvez prendre des dispositions pour un groupe spécifique ou pour des groupes dont la répartition démographique est très différente.
Les principales différences résident dans le fait que l'analyse qualitative examine des données non numériques et que l'analyse quantitative examine des données numériques. Par conséquent, les méthodes de collecte et d'analyse des données diffèrent. Alors que l'analyse qualitative se concentre davantage sur les expériences et les comportements, la recherche quantitative se concentre sur les modèles, les fréquences et les statistiques générales.
Imaginez que vous êtes une entreprise possédant une marque de smartphone. Vous souhaitez étudier l'accueil réservé par le public à votre nouveau produit. Vous pouvez créer une enquête de recherche et y inclure à la fois des questions qualitatives ouvertes et des questions quantitatives d'évaluation.
Par exemple, "De 1 à 10, quelle note donneriez-vous à ce produit ?" L'analyse des données quantitatives permet d'examiner une telle question. En revanche, "Qu'est-ce qui vous attire dans ce produit ?" Vous pouvez examiner une telle question à l'aide d'une analyse de données qualitatives.
L'objectif de l'analyse qualitative est de révéler les schémas des données non mathématiques, leurs relations entre elles et leur signification. Elle est également utilisée pour générer et tester des hypothèses dans divers domaines, tels que la finance, l'éducation, la santé et la science.
L'objectif premier de l'analyse qualitative est de comprendre le comportement et les pensées humaines et de révéler les relations significatives. Elle permet de voir des structures profondes qui ne sont pas perceptibles à première vue. Elle permet de comprendre n'importe quel sujet dans son contexte détaillé et d'interpréter les phénomènes sociaux. De cette manière, vous pouvez créer des théories à partir de ces déductions et conclusions et fournir un soutien et une base pour les actions que vous jugez nécessaires.
Final words
Qualitative data is a never-ending process. It is a method of keeping up with changes and times. It is a vast information sea for every small or large business to improve themselves and their relationships with their customers. It allows you to solve problems if there are problems, make predictions if you have plans, and test if you have hypotheses.
This article is divided into four main parts. In the first part, the definition of qualitative data is given, and then when it would be appropriate to use it is explained. Various types of analysis are mentioned, and finally, the article is finished with qualitative data examples. Now, you are ready to analyze qualitative data perfectly.
Atakan is a content writer at forms.app. He likes to research various fields like history, sociology, and psychology. He knows English and Korean. His expertise lies in data analysis, data types, and methods.



 6 minutes de lecture
6 minutes de lecture