In the fast-paced business world, making informed decisions is crucial for success. There are essential tools for evaluating potential opportunities and threats. By understanding these tools, businesses can make strategic choices that maximize gains while minimizing losses. They can learn how these powerful analyses can elevate their decision-making process.
Today, we will explore one of these models, the Risk and Reward Analysis, in-depth. This comprehensive guide will cover its fundamental concepts, steps to conduct the analysis, real-world examples, advantages and disadvantages, suitable environments for its application, and frequently asked questions. Let’s explore this essential tool to enhance your business decision-making and strategic planning.
What is the Risk and Reward analysis?
Risk and Reward Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the potential risks and rewards associated with a business decision or project.
This analysis helps organizations to identify, assess, and balance the possible outcomes, ensuring informed decision-making. It is crucial for managing uncertainty and maximizing opportunities while minimizing potential downsides.
Risk and Reward Analysis involves a systematic approach to understanding the potential impacts of different scenarios. By weighing the risks against the expected rewards, businesses can make more calculated decisions that align with their strategic goals. This method is widely used across various industries to enhance project management, investment decisions, and overall business strategy.
A template for Risk and Reward analysis: Business Plan
A Risk and Reward Analysis template provides a structured framework to systematically evaluate potential risks and rewards associated with a decision or project. This template ensures that all aspects of risk management and reward evaluation are considered, facilitating a comprehensive analysis. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key components typically included in a Risk and Reward Analysis template:
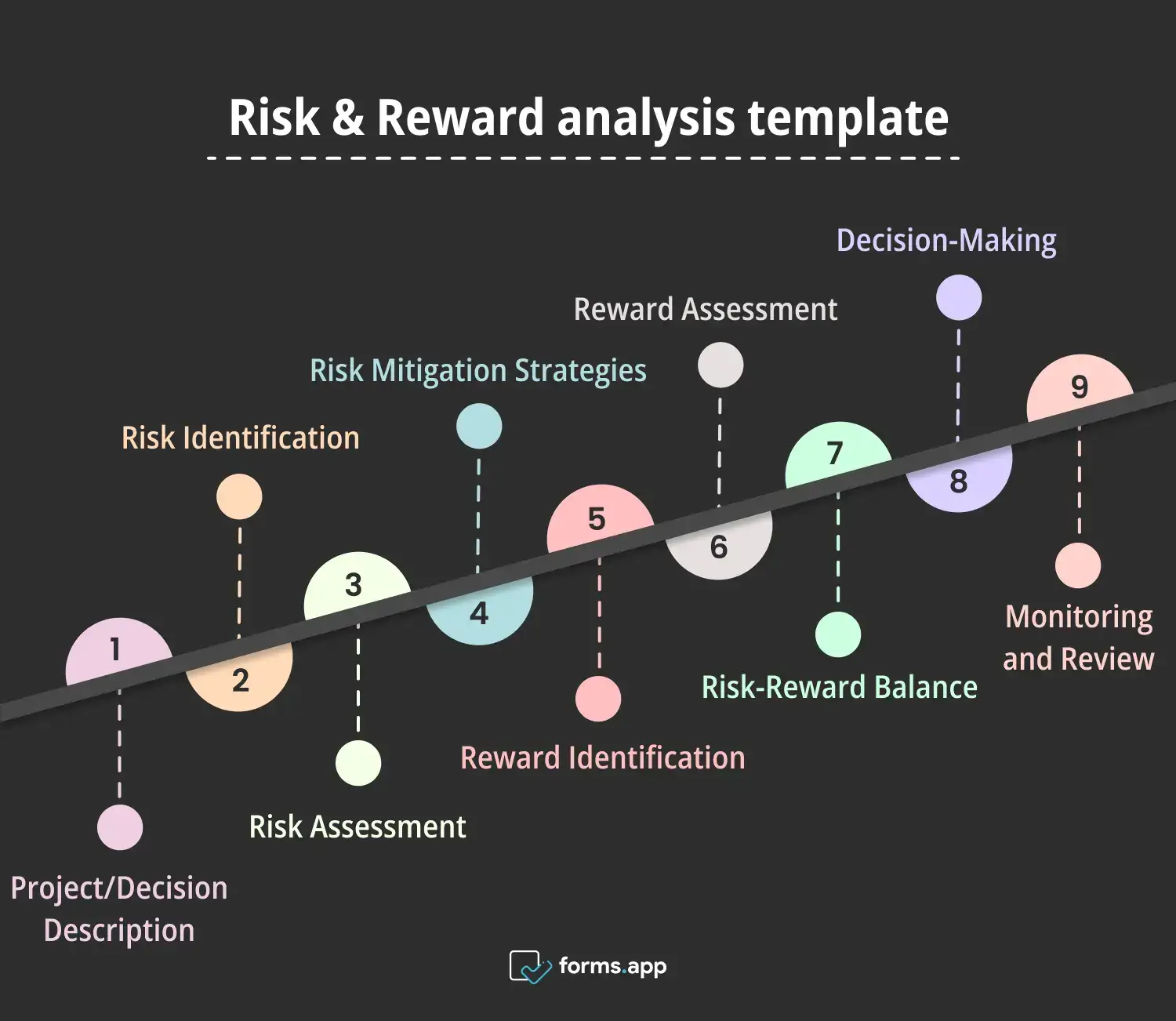
Risk and Reward analysis template for your business plan
1- Project/Decision Description
The project description section outlines the specific project or decision under consideration. It includes a brief summary of the objectives, scope, and expected outcomes. Clearly defining the project ensures that all stakeholders understand the context and purpose of the analysis. Thus, you can start implementing this model better.
2- Risk Identification
In this part, all potential risks are identified and listed. Risks could be internal or external factors that might negatively impact the project. Examples include financial risks, operational risks, market risks, and regulatory risks. Each risk should be described in detail to understand its nature and potential impact.
3- Risk Assessment
This involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of each identified risk. A common method is to use a risk matrix that categorizes risks based on their probability (e.g., low, medium, high) and impact (e.g., minor, moderate, severe). This assessment helps prioritize risks based on their significance.
4- Risk Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation strategies are developed to minimize or manage the impact of each identified risk. This could include contingency plans, risk transfer (e.g., insurance), or risk avoidance measures. Documenting these strategies ensures that there are proactive plans in place to address potential issues.
5- Reward Identification
This section lists the potential rewards or benefits of proceeding with the project or decision. Rewards could include increased revenue, market share, cost savings, or strategic advantages. Clearly identifying the rewards helps in balancing the analysis by considering the positive outcomes.
6- Reward Assessment
Similar to risk assessment, this part evaluates the likelihood and magnitude of the identified rewards. It may involve financial projections, market analysis, and scenario planning to estimate the potential benefits. This assessment helps quantify the expected returns from the project.
7- Risk-Reward Balance
In this component, the identified risks and rewards are compared and analyzed together. This helps in understanding whether the potential rewards justify the risks involved. The analysis might include a risk-reward ratio or a decision matrix to visually represent the balance.
8- Decision-Making
Based on the comprehensive analysis, a recommendation is made on whether to proceed with the project or decision. This section summarizes the key findings and provides a rationale for the recommendation. It might also include alternative options or next steps based on the analysis.
9- Monitoring and Review
Finally, this section outlines the process for ongoing monitoring and review of the risks and rewards. It ensures that the analysis remains relevant and updated as the project progresses or as new information becomes available.
How to use the Risk and Reward analysis in business
Transitioning to the practical application of risk and reward analysis, let's explore the essential steps for its effective use in business decision-making. By following these steps diligently, organizations can mitigate risks, capitalize on opportunities, and maximize their chances of success.
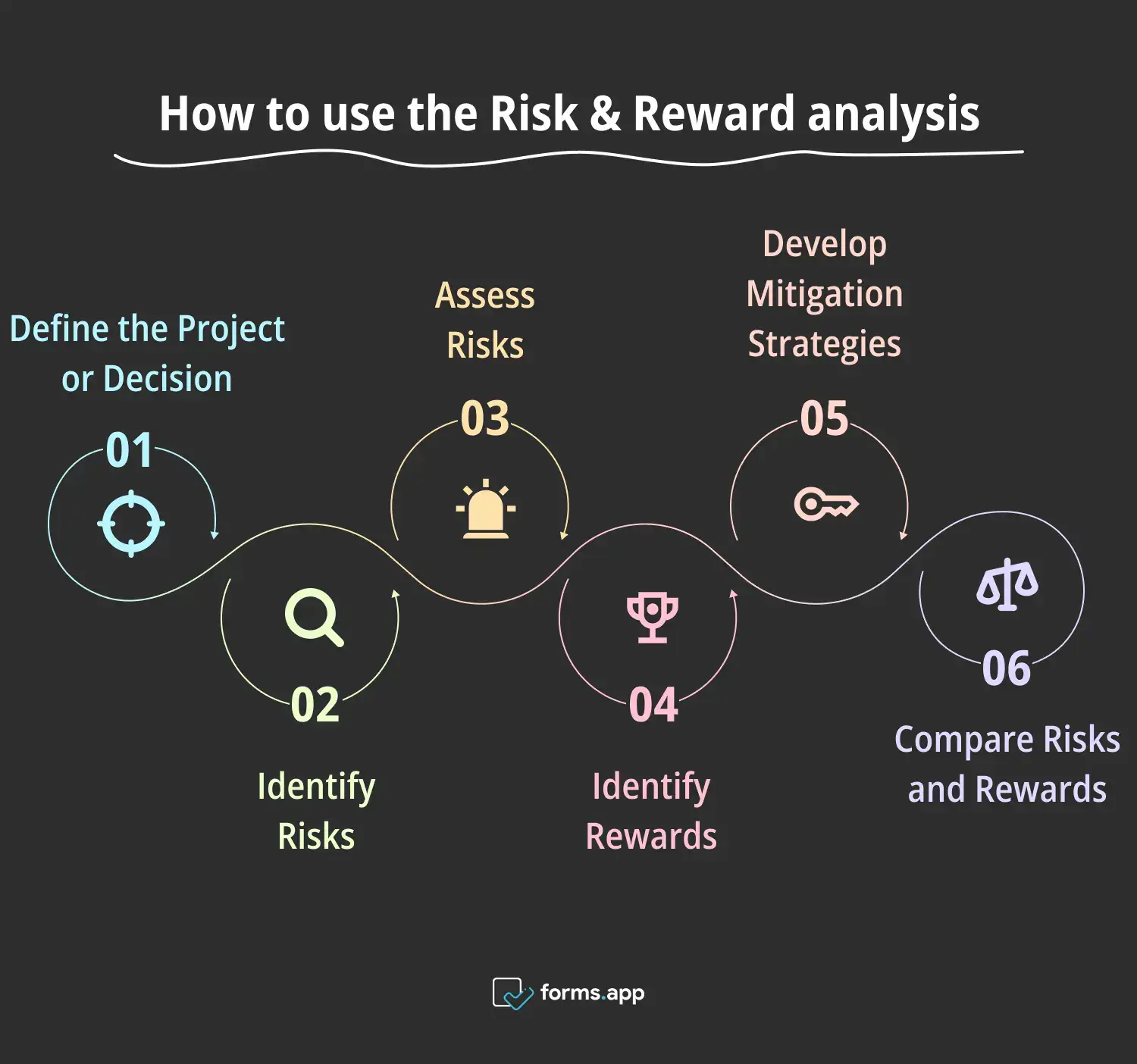
Steps for Risk and Reward analysis
📖Define the Project or Decision
Start by clearly outlining the project or decision that requires analysis. This includes setting specific goals, identifying key objectives, and understanding the scope and context. A well-defined project ensures that all stakeholders have a common understanding and provides a solid foundation for the risk and reward analysis.
🕵🏻Identify Risks
List all potential risks associated with the project. These can be internal (e.g., operational issues, financial constraints) or external (e.g., market fluctuations, regulatory changes). Use brainstorming sessions, historical data, and expert input to ensure comprehensive risk identification. Detailed documentation of each risk helps in the subsequent assessment and mitigation stages.
🚨Assess Risks
Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each identified risk. Use qualitative methods (e.g., risk matrix) or quantitative methods (e.g., statistical models) to categorize risks. This assessment helps prioritize risks, focusing on those with the highest potential to affect the project. Understanding risk severity guides the development of appropriate mitigation strategies.
🏆Identify Rewards
Determine the potential rewards or benefits of the project. These could include increased revenue, market expansion, cost savings, or competitive advantage. Use data analysis, market research, and forecasting to quantify the expected benefits. Clearly articulating the rewards helps balance the focus on both risks and positive outcomes.
🔑Develop Mitigation Strategies
For higher risks, create strategies to mitigate or manage its impact. This could involve contingency planning, risk transfer through insurance, or process improvements. Effective mitigation strategies reduce the likelihood or severity of risks, enhancing the chances of project success. Documenting these strategies ensures a proactive approach to risk management.
⚖️Compare Risks and Rewards
Conduct a comprehensive comparison of the identified risks and rewards. Use tools like risk-reward ratios or decision matrices to visualize the balance. This analysis helps determine whether the potential rewards justify the risks involved. Based on this comparison, make informed decisions on whether to proceed, adjust, or abandon the project. This step ensures a balanced and strategic approach to decision-making.
Example of the Risk and Reward analysis
In this scenario, we’ll examine Company X, a medium-sized manufacturing firm. It decides to expand its product line to capitalize on emerging market trends. Using risk and reward analysis, the company identifies potential risks, such as supply chain disruptions and market competition, alongside rewards, such as increased revenue and brand diversification.
Through thorough assessment, Company X quantifies the likelihood and impact of each identified risk, prioritizing mitigation strategies to minimize supply chain vulnerabilities and enhance competitive positioning. By investing in robust inventory management tools and fostering strategic partnerships, the company mitigates supply chain risks while leveraging its strengths to seize market opportunities.
As a result of implementing risk and reward analysis, Company X experiences smoother product launches, reduced operational disruptions, and accelerated revenue growth. By adopting a proactive approach to risk management and capitalizing on market rewards, the company establishes itself as an innovative player in the industry, driving long-term success and profitability.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Now, let’s move on to examine the advantages and disadvantages of risk and reward analysis and delve into its strengths and limitations. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing the use of this analytical tool in various business scenarios.
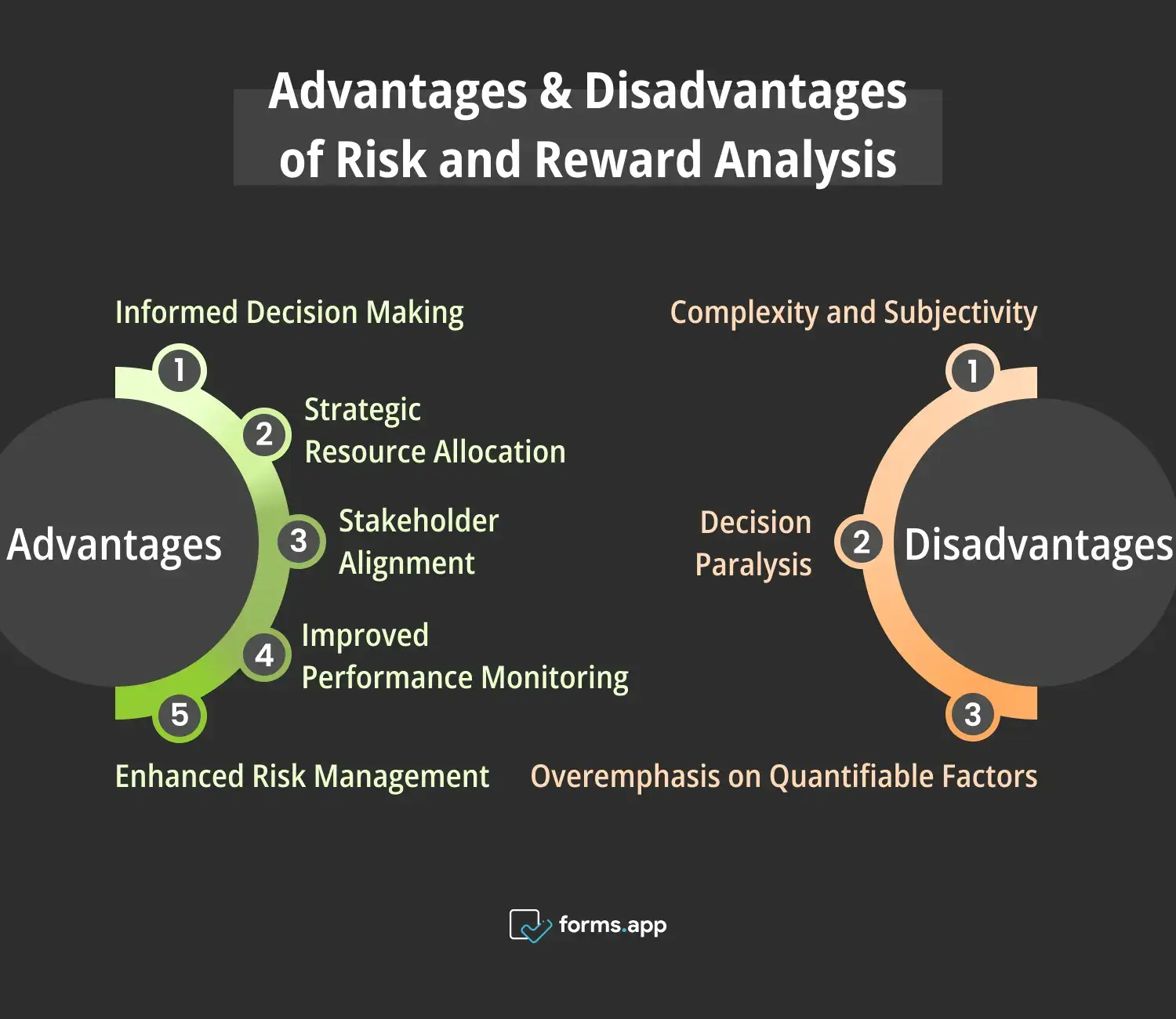
Pros & Cons of Risk and Reward analysis
Advantages of Risk and Reward Analysis:
👍🏻Informed Decision Making: Risk and reward analysis enables businesses to make informed decisions by providing a structured framework to assess potential outcomes. By evaluating both risks and rewards, organizations can weigh the benefits against potential drawbacks, leading to more strategic and well-informed choices.
👍🏻Strategic Resource Allocation: This model helps in strategic resource allocation by directing investments toward opportunities with favorable risk-reward profiles. By prioritizing resources based on potential returns and associated risks, businesses can optimize their allocation strategies to maximize profitability and mitigate potential losses.
👍🏻Enhanced Risk Management: Risk and reward analysis facilitates proactive risk management by identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to business objectives. By systematically evaluating risks and rewards, organizations can develop risk mitigation strategies to minimize negative impacts and capitalize on opportunities effectively.
👍🏻Improved Performance Monitoring: Through ongoing risk and reward analysis, businesses can continuously monitor their performance and adapt strategies as needed. By tracking key metrics and evaluating risk-reward trade-offs over time, organizations can identify emerging risks or opportunities and make timely adjustments to optimize outcomes.
👍🏻Stakeholder Alignment: Risk and reward analysis promotes stakeholder alignment by providing a transparent and objective evaluation of potential outcomes. By involving stakeholders in the analysis process, businesses can ensure alignment of goals and expectations, fostering trust and collaboration across the organization.
Disadvantages of Risk and Reward Analysis
👎🏻Complexity and Subjectivity: Risk and reward analysis can be complex and subjective, requiring comprehensive data and expert judgment to accurately assess potential outcomes. The subjective nature of risk assessment may introduce bias or uncertainty, leading to challenges in determining the true risk-reward profile of a decision.
👎🏻Overemphasis on Quantifiable Factors: Risk and reward analysis may overemphasize quantifiable factors such as financial metrics, overlooking qualitative aspects that could influence outcomes. By focusing solely on measurable criteria, organizations may fail to account for intangible risks or opportunities, leading to incomplete assessments and suboptimal decisions.
👎🏻Decision Paralysis: In some cases, extensive risk and reward analysis can lead to decision paralysis, where organizations become overwhelmed by the complexity of factors to consider. This can result in delays in decision-making and missed opportunities, especially in fast-paced or competitive environments where agility is essential.
When to use Risk And Reward Analysis?
We will explore the optimal scenarios for employing risk and reward analysis. Let's uncover the key situations where this strategic tool can yield valuable insights. Identifying these contexts will enable organizations to leverage the benefits of risk and reward analysis effectively in their decision-making processes.
Right times to use Risk & Reward analysis
⏰Strategic Planning: Risk and reward analysis is essential during strategic planning processes to evaluate potential initiatives or investment risks. By assessing the risks and rewards associated with different strategic options, organizations can prioritize initiatives. They can have long-term objectives and be risk-tolerant.
⏰Project Evaluation: This analysis is valuable when evaluating new projects or initiatives to determine their feasibility and potential impact on business objectives. By conducting a comprehensive risk and reward assessment, organizations can identify potential risks and rewards early in the project lifecycle and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
⏰Investment Decisions: Risk and reward analysis is crucial for return on investment decisions, whether in financial markets, new technologies, or business expansion opportunities. By evaluating the potential risks and rewards of investments, organizations can make informed decisions that maximize returns while mitigating potential losses.
⏰Product Development: When developing new products or services, it's important to assess the amount of risks and rewards associated with innovation and market entry. Risk and reward analysis can help organizations identify potential market risks, competitive challenges, and opportunities for differentiation, informing product development strategies and investment decisions.
⏰Performance Evaluation: Risk and reward analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of existing initiatives, projects, or investments. By comparing actual outcomes to projected risks and rewards, organizations can assess the effectiveness of their strategies and identify areas for improvement or adjustment.
⏰Change Management: During periods of organizational change or transformation, risk and reward analysis can help assess the potential risks and rewards associated with change initiatives. By understanding the potential impacts on stakeholders, processes, and outcomes, organizations can develop change management strategies that mitigate risks and optimize rewards.
Frequently asked questions about the Risk and Reward analysis
To address common queries surrounding risk and reward analysis, let's look at the frequently asked questions. We will provide clarity on determining risk and reward, understanding risk-reward ratios, and practical examples illustrating their application in various contexts. It will enhance your comprehension and facilitate informed decision-making processes.
Risk and reward are determined by assessing the potential benefits of an action against the likelihood and magnitude of potential losses. This involves analyzing factors such as market conditions, competition, financial metrics, and strategic objectives to quantify the potential risks and rewards associated with a decision or investment.
An example of risk and reward is investing in the stock market. The risk is the possibility of losing money due to market fluctuations, economic downturns, or company performance. The reward is the potential for earning returns through capital appreciation, dividends, or other investment gains if the market performs favorably.
The 1.5 risk-reward ratio refers to a trading or investment strategy where the potential reward is 1.5 times greater than the potential risk. For example, if the risk of a trade is $100, the potential reward would be $150. This ratio is used by traders and investors to assess the potential profitability of a trade relative to the level of risk.
A 3 to 1 risk-reward ratio means that the potential reward of a trade or investment is three times greater than the potential risk. For instance, if the risk of a trade is $100, the potential reward would be $300. This ratio indicates that the potential payoff outweighs the potential loss, making it an attractive opportunity for investors.
Key points to take away
To conclude, risk and reward analysis is a crucial tool for decision-making in various domains, including finance, business, and investing. By carefully assessing potential risks and rewards, organizations and individuals can make informed choices that maximize opportunities while minimizing potential losses. Understanding the balance between risk and reward is essential for achieving long-term success and achieving strategic objectives.
In this comprehensive guide to risk and reward analysis, we explored the definition of risk and reward and the psychology of risk vs. rewards. We also covered the risk and reward relationship, its steps, examples, advantages, and suitable applications. Now equipped with this knowledge, you can confidently apply risk and reward analysis in their decision-making processes. Balance risk and reward effectively, and make informed choices that lead to success and sustainable growth.
Fatih is a content writer at forms.app and a translator specializing in many text domains, including medical, legal, and technical. He loves studying foreign languages. Fatih especially likes to create content about program management, organizational models, and planning tools.
- What is the Risk and Reward analysis?
- A template for Risk and Reward analysis: Business Plan
- How to use the Risk and Reward analysis in business
- Example of the Risk and Reward analysis
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- When to use Risk And Reward Analysis?
- Frequently asked questions about the Risk and Reward analysis
- Key points to take away