You can carry out an online survey in a variety of methods. The survey's target audience is just as crucial as the questions you include in the survey. You may enhance your survey response rate and receive more helpful survey findings by asking the right questions to the right audience while carefully choosing the individuals to use as examples for your survey.
The ability of the researchers surveying to select the appropriate participants saves time and enables them to obtain more effective results in a shorter time. This article will explain purposive sampling, its types, advantages, and disadvantages in detail.
What is purposive sampling?
A purposive sample is a nonprobability survey system in which the experimenter depends on the researcher to select variables for the sample population. It is also known as selective, subjective, or judgmental sampling. The sample population chosen for the study is not chosen randomly but by a set of criteria. The researcher's judgment and understanding of the context are crucial to the sampling procedure.
Purposive sampling means choosing your research group deliberately based on a set of criteria.
A purposive sample is a minor part of the population that aims to reflect it rationally. Researchers can achieve these by selecting a sample that samples variances and examining the previous knowledge of the population. With sampling, all survey respondents are chosen based on criteria when researchers wish to access a specific subset of samples.
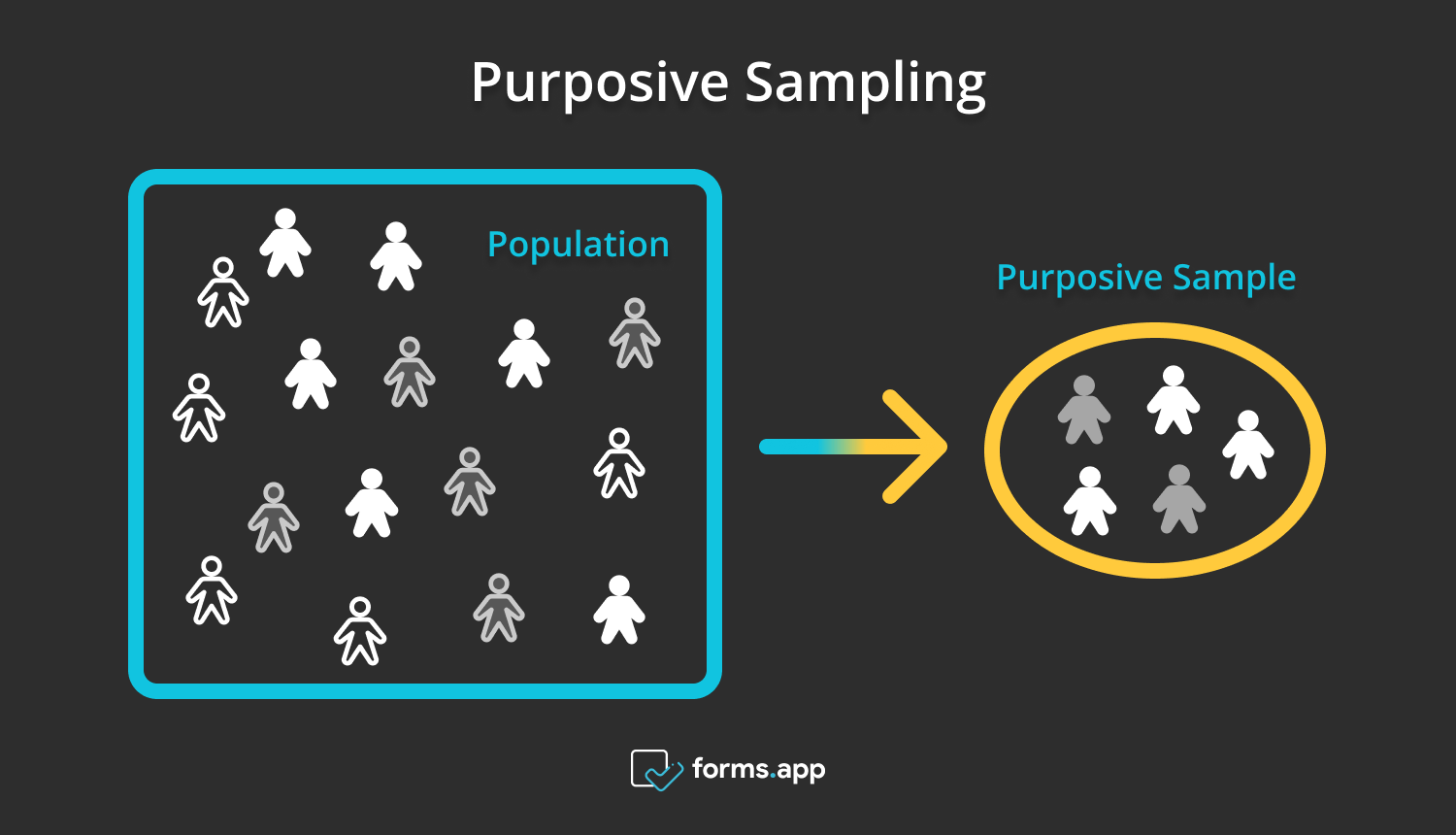
How purposive sampling works
Types of purposive sampling
Purposive sampling is a technique that requires utilizing the researchers' discretion to select a small number of people that can most effectively address their research issue. The types differ according to the objectives of the investigation. There are seven types of purposive sampling, each suitable for a different research objective.

7 types of purposive sampling
1 - Maximum variation sampling
Maximum variation sampling is also called heterogeneous sampling. It is a purposeful sampling that gathers different viewpoints on your interest. The most excellent variety of views may be recorded with it.
Maximum variation sampling's fundamental tenet is to examine a phenomenon from as many perspectives as possible to get a deeper understanding of it. This makes it feasible for researchers to collect as much data throughout their survey from many perspectives as possible.
2 - Homogeneous sampling
Researchers frequently utilize homogenous purposive sampling when conducting a study on a particular characteristic, feature, or region of interest. With an eye on how it pertains to your study topic, you should concentrate on this resemblance.
The selection of focus group members frequently involves homogeneous sampling. People investigating a particular characteristic or area of interest typically choose a group similar to each other regarding age, gender, background, or career.
3 - Typical case sampling
The researcher often chooses participants based on their propensity to behave similarly to anyone with similar traits or experiences. It enables sample comparison but not sample generalization to populations. For example, if the researcher examines the sociocultural status of low-income families, he does not consider middle- or high-income families in his research.
4 - Extreme case sampling
Extreme or deviant case sampling generally focuses on unique or unusual cases. These severe cases are beneficial because they frequently shed light on a particular occurrence and can act as lessons for future study and application.
5 - Critical case sampling
Critical case sampling is a purposive sampling strategy that is particularly helpful in exploratory qualitative research, research with constrained resources, and research where a single circumstance is crucial in describing the phenomena of interest. An information-rich example is chosen to represent the group via critical case purposive sampling.
6 - Total population sampling
Total population sampling is a purposive sampling strategy where researchers look at the entire population with a specific set of characteristics. These characteristics may be particular experiences, expertise, or talents.
7 - Expert sampling
When your study requires you to collect information from people with specific experience, an expert sampling approach is one sort of purposive sampling that is performed. Expert purposive sampling is utilized if a researcher seeks information from people with a specific area of competence.
So, how to conduct purposive sampling
The procedure of purposive sampling is relatively easy. The researcher must exclude people who do not meet a specific profile. There are seven different ways to implement the method. These methods allow you to determine the appropriate one for your research.
Examples and use cases of purposive sampling
Purposive sampling research is used in many different subjects and many various fields. In the following, we will give purposive sampling examples and use cases of purposive sampling.
Educational analysis use case
Education research frequently makes use of purposive sampling. For instance, a student feedback survey may gauge how happy students are with the educational system, how adequate the technological resources are, and how glad they are with their school supplies. Successful students studying in public schools can be targeted for this type of research.
Introducing customers to a new product use case
If a make-up company releases a new cosmetic product, its target audience is well-groomed women. It can carry out effective research about the latest product with its target audience, which is the age range and loyal users of the brand. This is a situation where the company creates a sample of people who know about that topic, that category, and brand, and it's an example of purposive sampling.
Choosing the appropriate candidate use case
You posted a job as an employer, and a bunch of job application forms came in. If you research by considering specific categories, you will have the chance to find the best candidate for your job. For example, your research by viewing criteria such as education level, age, and foreign language proficiency will lead you to the best candidate.
Advantages and disadvantages of purposive sampling
Although each type of this sampling have its advantages, there are also disadvantages. There are some general advantages and disadvantages listed below:
Advantages of purposive sampling:
- The main advantage of purposive sampling is offering many different sampling procedures that may be applied to qualitative research.
- A very efficient and low-cost way to choose samples is using purposeful sampling.
- It enables to obtain more useful data because it works with the limited sample group determined by the researcher; it can analyze all data points.
- The samples produced by this sampling technique are particularly appropriate for use in research, surveys, or experiments because there is no randomness involved.
Disadvantages of purposive sampling:
- Purposive sampling's major disadvantage is that it is vulnerable to researcher bias since researchers make subjective or broad assumptions when selecting respondents for their online survey.
- It might be challenging to persuade the reader that your decision to select the units to work with was appropriate. It is hard to convince the reader to believe in research using purposive sampling.
When to use purposive sampling?
Purposive sampling's primary objective is to pinpoint the situations, people, or groups that will be most useful in assisting you in answering your research issue. Purposeful sampling is utilized when you concentrate closely on relatively tiny samples.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a particular set of characteristics is expected of the sample group when purposeful sampling is done. The researcher can choose a precise and affordable sample by selecting individuals or points using his knowledge. The sampling strategy is accurate and suitable for research, survey, or experiment.
Researchers carefully plan how they will create a sample population using purposeful sampling. Purposive sampling looks for various participants who fit specified criteria to provide more context for a particular project. Researchers deliberately select this group because they believe they fit the description of the people they want to target this population.
Sena is a content writer at forms.app. She likes to read and write articles on different topics. Sena also likes to learn about different cultures and travel. She likes to study and learn different languages. Her specialty is linguistics, surveys, survey questions, and sampling methods.



