Just as you can see the distance you want to reach when you use Google Maps, you can adapt a very similar system to see the distances between data points. If you are wondering how to do this mapping, the answer is multidimensional scaling.
Multidimensional scaling is a statistical tool that takes into account the similarities and differences in the data and places them on a new plane according to their distances. The purpose of this article is to provide you with a multidimensional scaling tutorial. To learn more, let’s start with the definition!
What is Multidimensional scaling (MDS)?

Multidimensional scaling (MDS) is a statistical technique used in data analysis to reduce the number of dimensions in high-dimensional data.
By doing so, the data are visualized for easier analysis and interpretation. MDS's area of use is quite wide: it is used to make critical decisions in market research, psychology, sociology, geography, health, education, and biology.
When to use the Multidimensional scaling
Multidimensional scaling visualizes complex data, making it useful in various times and situations. It is ideal for understanding critical points before, during, and after any research. When doing any research, there may be exact times when you might need to use it:
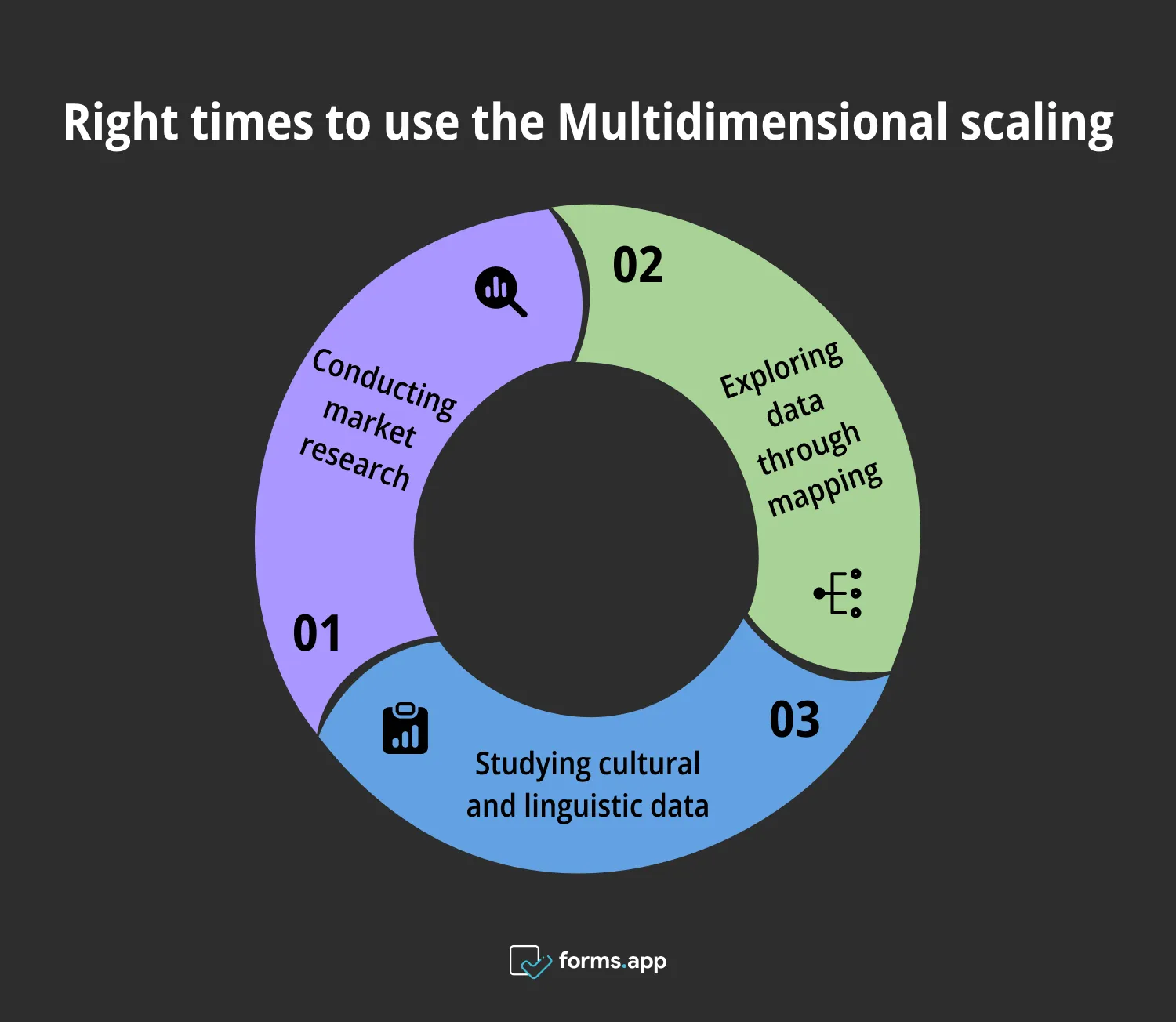
Correct times to use the Multidimensional scaling
⏰ When conducting market research: In this respect, MDS becomes very valuable during market research when knowledge of consumer perception and preference is required. It can visualize the similarities between products, services, or companies, showing their position in the competitive atmosphere. Businesses can use this insight to adjust marketing strategies and provide better service to their customers.
⏰ When exploring data through mapping, MDS visualizes complex data and reduces it to a lower-dimensional space. This allows one to see more easily the patterns and relationships in that dataset. It can also conserve relative distances of data points, which helps one see the underlying structure.
⏰ When studying cultural and linguistic data: MDS is used especially in sociology academic research, culture, and language studies because it facilitates geographical classification. It places the characteristics and patterns of cultures and languages at distances by considering the similarities and differences between them. Thus, it is an effective tool for cross-cultural studies.
Multidimensional scaling types
There are several types of multidimensional scaling that you can choose depending on the purpose of your research. Here, the three most commonly used types (metric, non-metric, and classical multidimensional scaling) will be explained:
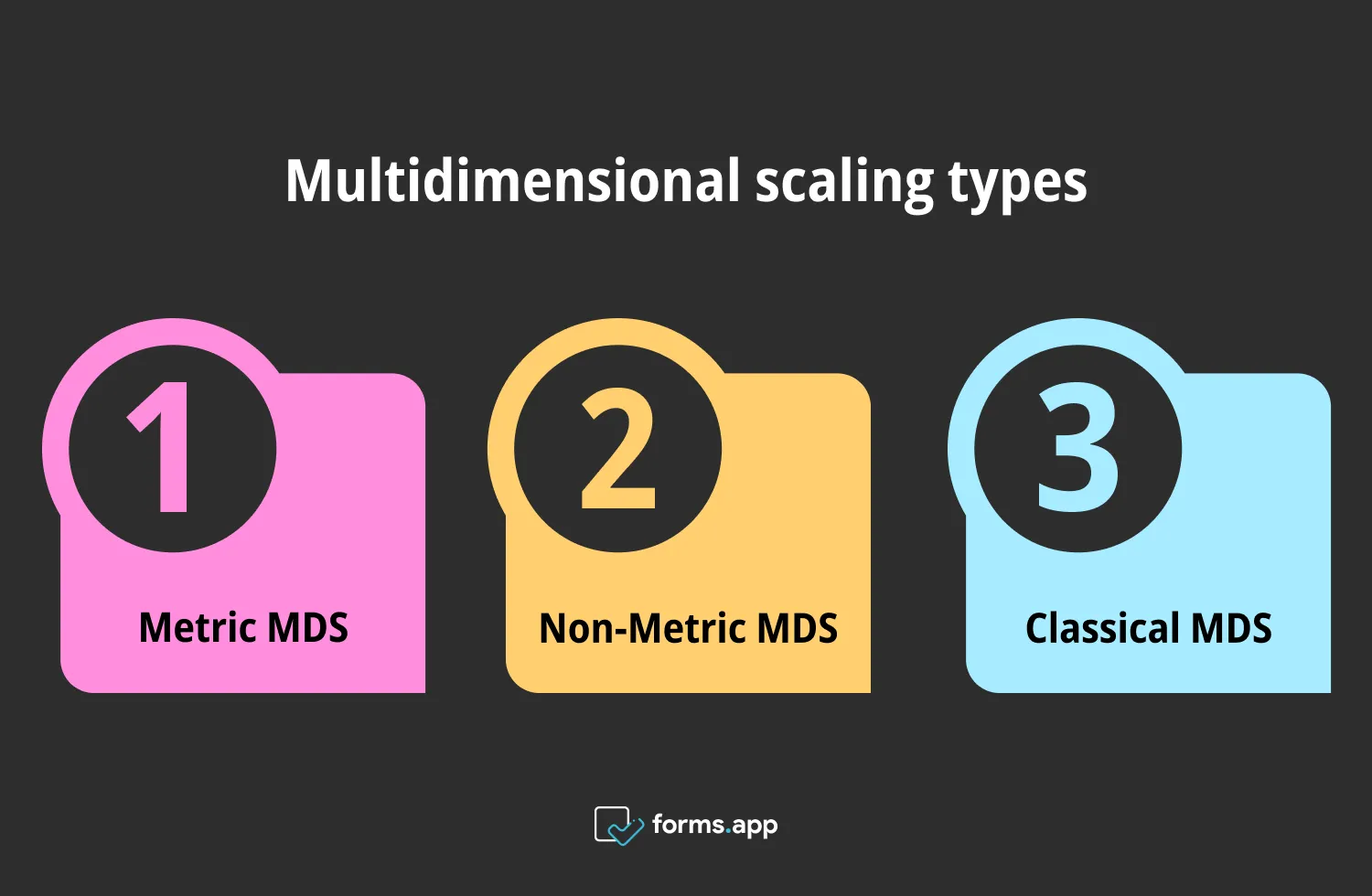
Types of multidimensional scaling
1. Metric MDS: This type extends the optimization process to include different loss functions and input matrices with specified distances and weights. It reduces a cost function known as "stress," typically minimized through a method called stress majorization.
2. Non-Metric MDS: This technique is mostly used in examining qualitative data and understanding non-Euclidean relationships. It optimizes a "stress" function by taking into account a statically increasing function.
3. Classical MDS (Torgerson Scaling): This method is used to generate a coordinate matrix using an input matrix of dissimilarities between item pairs, aiming to minimize strain. It can be used when the data has Euclidean distance. Thus, it ensures that the distances are transferred as they are when transferring them to the new space.
Examples of Multidimensional scaling
Here, multidimensional scaling examples of its usage from two different areas will be given. It is recommended that you read these examples carefully, as they can be a guide in your analyses.
1. Linguistic study
Assume that there is a researcher who wants to create a map of dialects of a language based on their similarities and differences. The researcher uses the MDS technique in the following steps:
- Select linguistic features and measure a distance matrix for the dissimilarities between dialects. Set up language configuration in a lower dimensional space.
- Continuously readjust the positions of the dialects to preserve the original dissimilarities. This will minimize the stress function. Repeat the process until the stress function converges.
- Finally, visualize the set-up to show linguistic patterns and relationships.
2. Brand perception
Assume that there is a company that seeks to learn customer perception about their brand in the market environment. To visualize customer comments and their position in the market with MDS using survey data, it performs the following steps:
- Start collecting a distance matrix, which expresses consumer perceptions about the similarity or dissimilarity of various brands. Place the brands in a lower dimensional space.
- Adjust brand positions with repetitive actions, and this will minimize the stress function. Then, spatial relationships that reflect consumer perceptions will emerge. Continue adjustments until the stress function is stabilized.
- Finally, marketing strategies should be developed according to the resulting brand map.
Advantages of Multidimensional scaling
Multidimensional scaling has different benefits depending on which research area you use it in. For example, its benefit in the field of sociology is to be able to examine social structures on a visible and understandable level. Apart from that, it has generally such advantages as:
➕ Reduces the dimensionality of data while retaining essential information.
➕ It can test your hypotheses, provide resources for more complex analyses, and be an important basis for decision-making.
➕ It is applicable across various fields and data types thanks to its versatile nature. So you can use it in any research area without a problem.
➕ It can be used to reveal hidden structures in complex data sets and to show relationships between data points.
Frequently asked questions about the multidimensional scaling
This article gives a rough description of multidimensional scaling. Still, if you want to ask a critical point about which you are curious, you can check the frequently asked questions below.
Es gibt mehrere Zwecke für multidimensionale Skalierung (MDS), die Sie nutzen können. Ihr Hauptzweck ist es, Datenpunkte zu visualisieren, die hauptsächlich im zweidimensionalen Raum liegen. Dabei versucht sie, die Distanz zwischen den Datenpunkten so gut wie möglich zu erhalten.
Es wird verwendet, um Datenpunkt-Werte besser zu beobachten und Muster und Beziehungen zu visualisieren. Es ist besonders nützlich, um komplexe Beziehungen in Tabellen zu verstehen und Sie vor dem Verlieren unter den Datenpunkten zu bewahren. Somit spielt es eine wichtige Rolle bei der Suche nach Lösungen für Probleme wie Marktforschung im Geschäftsbereich.
Non-metrisches Multidimensionales Skalieren (NMDS) und Multidimensionales Skalieren (MDS) sind statistische Techniken, die verwendet werden, um die Beziehungen zwischen Datenpunkten in einem reduzierten-dimensionalen Raum zu visualisieren und zu erkunden. Allerdings unterscheiden sie sich in der Anordnung der Datenpunkte. NMDS ist eine flexible Methode, die Sie verwenden können, wenn es keine direkte lineare Beziehung zwischen den Unähnlichkeiten und Entfernungen gibt. Es zeigt nicht die genauen Entfernungen, sondern erhält die Rangfolge. Andererseits zeigt MDS deutlich die metrischen Entfernungen zwischen Datenpunkten. Wenn Sie eine geeignete Kartierungstechnik benötigen, um lineare Unähnlichkeiten darzustellen, sollten Sie MDS verwenden.
Der Schlüssel zum multidimensionalen Skalierungsalgorithmus besteht aus folgenden Schritten:
- Zunächst erstellen Sie eine Unähnlichkeitsmatrix. Sie repräsentiert die paarweisen Abstände zwischen den Datenpunkten.
- Beginnen Sie mit der Konfiguration der Datenpunkte im niedrigdimensionalen Raum.
- Verschieben Sie dann die Datenpunkte im Raum, um die Stressfunktion zu minimieren, und wiederholen Sie diesen Vorgang mehrmals.
- Verbessern Sie diese Konfiguration weiter, bis die Stressfunktion konvergiert.
- Beenden Sie den Prozess, wenn Sie die Konvergenz erreicht haben, und beenden Sie die Konfiguration für die Visualisierung und Interpretation.
Hauptkomponentenanalyse (PCA - Principal Component Analysis) und Multidimensionale Skalierung (MDS - Multidimensional Scaling) sind beide Datenvisualisierungsmethoden, die zur Erkundung komplexer Datensätze verwendet werden. Sie unterscheiden sich jedoch in Bezug auf die Eingabe von Daten, Linearität und Darstellung der Ergebnisse. Im Gegensatz zu MDS erfordert die PCA-Methode quantitative Daten, um eine Struktur aufzubauen.
PCA wird verwendet, um Daten in linearen Beziehungen in linearer Form darzustellen, aber für MDS ist es nicht erforderlich, dass die Daten linear sind. Bei der Visualisierung von Daten bereitet PCA einen Graphen gemäß neuer Variablen vor, die als Hauptkomponenten bezeichnet werden. MDS hingegen fügt keine neuen Variablen hinzu und platziert die Datenpunkte auf einer bestimmten Ebene entsprechend den Entfernungen zwischen ihnen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multidimensional scaling is a perfect tool for visualizing complex data for a comprehensible analysis. It provides insights into hidden relationships and patterns in various disciplines. This article will help you to get the most out of this powerful tool. The article first introduces you to the topic by explaining its definition, when to use it, and its types. Then, the article ends with two different examples of usage and listing its advantages.
Atakan is a content writer at forms.app. He likes to research various fields like history, sociology, and psychology. He knows English and Korean. His expertise lies in data analysis, data types, and methods.



 4 min lesen
4 min lesen

